Answers
Answer:
ummm hehe this is my time to shine
Explanation:
MERICIA!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
America
Related Questions
1. v=v0+at
2.d = vot+at²
3.v²=v² + 2ad
4.d = 0-20 t
Use the Equation 1 to solve the problem that follows. Use the GUESS method to help you
arrange your work.
Starting from rest, a pony increases its speed at a rate of 2 m/s² for 3.3 seconds. how fast is
the pony moving at the end of 3.3 seconds in m/s?
Answers
With 6.6 m/s velocity, the pony moving at the end of 3.3 seconds in m/s.
v0=0
v=?
a=2 m/s²
t=3.3 sc
v=v0+at
v=0+2×3.3
v=6.6 m/s
"The rate at which an item changes its location" is described by a vector number called velocity. Imagine someone walking swiftly, one step forward, one step back, and starting each step from the same location. Velocity is a vector quantity. Therefore, velocity is cognizant of direction. The direction must be taken into account when determining an object's velocity. A velocity of 55 miles per hour is not adequate information. It is necessary to account for the direction in order to accurately describe the object's velocity. Simply put, the direction of the velocity vector represents the motion of the object.
To know more about velocity visit : brainly.com/question/16379705
#SPJ9
Part G
List several examples of applied force, normal force, and friction?
Answers
Examples of following forces mentioned -
Normal Force :- Book kept on the table , Girl standing on floor, ...infact every object experience a normal force in the universe.Applied Force :- this term literally means force responsible for the movements in the object or changes in the object , like throwing stones , playing ball , pushing an object , moving a pen from desk to chair..etc...Friction force :-Force responsible for the resistance in the flow of system's work , For example air resistance a type of obstruction experienced in air when a Paper ball is thrown from terrace of a society , Viscosity of honey is also an example of liquid friction / viscous drag...Sometimes friction is useful for the stability of universe. But some times its necessary. It is due to this force we walk without collapsing into the core of earth as earth is a market of gravitational field. To substantiate the field effect , friction is necessary to necessitate the life in planet. Rubbing of hands in winter season is also another example.To Know more about different forces -
https://brainly.com/question/17035940
#SPJ1
20 POINTS
In order to maximize the acceleration of an object, one should
maximize the mass
maximize the force
minimize the velocity
maximize the inertia
Answers
What kind of reasoning is most often used to form hypotheses?
inductive
deductive
detective
invective
Answers
The drawing shows four sheets of polarizing material, each with its transmission axis oriented differently. Light that is polarized in the vertical direction is incident from the left and has an average intensity of 20 W/m2. Determine the average intensity of the light that emerges on the right in the drawing (a) when sheet A alone is removed, (b) when sheet B alone is removed, (c) when sheet C alone is removed, and (d) when sheet D alone is removed.
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
At the point when light is vertically polarized is incident on the polarizer whose axes are situated at angle points \(\theta _1 , \theta _2 , \theta _3\) the intensity power in the wake of going through all the polarisers is given by the Malus law, applied threefold for every one of the three axes.
\(I = I_o \ cos \theta _1 \ cos \theta _2 \ cos \theta _ 3\)
The heading of the direction of the polarization is equivalent to the pivoted axes of the polarizer provided that light is an electromagnetic wave, its course of polarization is therefore controlled by the electric field part.
∴
a)
When sheet A is removed, the transmitted light goes through B, at 30°.
\(I = I_o \ cos ^2 \theta _1 \ cos ^2 \theta _2 \ cos^2 \theta _3\)
\(I = 20 \ cos ^2 30 \ cos ^2 60 \ cos ^2 30\)
\(I = 2.81 \ W/m^2\)
b)
When B is removed, No light passes since the axis of A and the axis of C are perpendicular to each other.
c)
When C is removed, the intensity is indeed zero since the axes are aligned and adjusted at 90° to one another.
\(\mathbf{d) \ I - I_o cos^2 (0) cos^2 (30) \ cos^2 (60)}\)
\(\mathbf{d = 3.75 \ W/m^2}\)
A force of 600N is applied to an object that accelerates at a rate of 15m/s/s. What is the mass of the object?
Answers
Answer:
The answer will be it has a mass of 40 kg.
Explanation:
Because Force = mass x acceleration or F = m a, we can say Force divided by mass or F/a = m or mass so 600 divided by 15 equals 40 kg.
2. The second year of Peixotto Media's incorporation, the board of directors
announce that they will issue cash dividends to their shareholders. At this point,
shareholders own 70,000 shares of stock in the corporation. The dividends will be 10
cents per share.
a. How should Savannah journalize the declaration and payment of this dividend? (4
points)
b. Now, imagine that Peixotto Media had chosen to pay its shareholders a stock
Qividend instead of cash dividend. At the time, their stock is valued at $7.25 per
share. They choose to pay a 5 percent dividend. How would Savannah journalize the
declaration and payment of this dividend? (4 points)
c. Elena and Josh both own common stock in Peixotto Media. Elena owns 300
shares and Josh owns 75 shares. Compute the dividends payable to both
shareholders. Show your work. (2 points)

Answers
a. Savannah would debit retained earnings and credit dividends payable for the declaration of a cash dividend, and debit dividends payable and credit cash for the payment, b. To declare and pay a stock dividend, Savannah would debit retained earnings and credit common stock dividend distributable for declaration, then debit common stock dividend distributable and credit common stock for payment, and c. Dividends payable to shareholders like Elena and Josh can be computed by multiplying the number of shares owned by the dividend per share.
Dividends Payable is a liability account used to record the amount of dividends that a company owes to its shareholders but has not yet paid out. It represents the obligation of the company to pay out the declared dividend amount to its shareholders, and the balance is typically cleared out when the dividend payment is made. Companies usually set a record date and payment date to declare and pay dividends respectively.
a. To journalize the declaration and payment of the cash dividend, Savannah would make the following entries:
Declaration:
Debit: Retained Earnings
Credit: Dividends Payable
Payment:
Debit: Dividends Payable
Credit: Cash
b. To journalize the declaration and payment of the stock dividend, Savannah would make the following entries:
Declaration:
Debit: Retained Earnings
Credit: Common Stock Dividend Distributable (70,000 x 5% = 3,500 shares)
Payment:
Debit: Common Stock Dividend Distributable
Credit: Common Stock ($7.25 x 3,500 shares)
c. To compute the dividends payable to Elena and Josh, we would use the following formula:
Dividends Payable = Number of Shares x Dividend per Share
For Elena:
Dividends Payable = 300 shares x $0.10 per share = $30.00
For Josh:
Dividends Payable = 75 shares x $0.10 per share = $7.50
Therefore, To declare and pay a cash dividend, Savannah would debit retained earnings and credit dividends payable for declaration, and debit dividends payable and credit cash for payment. To declare and pay a stock dividend, Savannah would debit retained earnings and credit common stock dividend distributable for declaration, then debit common stock dividend distributable and credit common stock for payment. Dividends payable to shareholders like Elena and Josh can be computed by multiplying the number of shares owned by the dividend per share.
To learn more about Cash Dividends click:
https://brainly.com/question/31237280
#SPJ1
27 1 point
A student has tested several types of wood for density. The best way of presenting this information graphically would be to use which item?
Scatterplot
Pie Chart
Line Graph
Bar Graph
Previous
Search
Answers
The best way of presenting the information on density graphically would be to use a D, bar graph.
What is a bar graph?A bar graph is a type of chart that uses rectangular bars to represent data. The bars are typically arranged in columns, with the independent variable (in this case, the type of wood) on the x-axis and the dependent variable (in this case, the density) on the y-axis.
A bar graph is the best choice for this data because it allows for easy comparison of density of different types of wood. We can see at a glance which type of wood is the densest and which type of wood is the least dense.
Find out more on Bar Graph here: https://brainly.com/question/25196929
#SPJ1
Bone has a Young’s modulus of about
1.8 × 1010 Pa . Under compression, it can
withstand a stress of about 1.59 × 108 Pa before breaking.
Assume that a femur (thigh bone) is 0.49 m
long, and calculate the amount of compression
this bone can withstand before breaking.
Answer in units of mm.
Answers
The Young's modulus is of a material is the ratio of its stress to strain. Here, the original length of femur bone is 0.49 m. Then, change in length ΔL by the stress of 1.59 × 10⁸ Pa is 0.0043 m or 4 mm.
What is Young's modulus?The young's modulus is the measure of stress by strain. Stress is the force per unit area and strain be the ratio of change in length by compression or elongation to the original length.
Strain = ΔL/L
Young's modulus = stress/strain
Y= F/a / ΔL/L
Given that, Y = 1.8 × 10¹⁰ Pa
stress = 1.59 × 10⁸ Pa
then 1.59 × 10⁸ Pa /1.8 × 10¹⁰ Pa = ΔL/L
L = 0.49 m
ΔL = 1.59 × 10⁸ Pa × 0.49 m/1.8 × 10¹⁰ Pa
= 0.0043 m = 4 mm.
Therefore, the amount of compression that the bone can withstand before breaking is up to 4 mm.
Find more on Young's modulus:
https://brainly.com/question/13385352
#SPJ1
If an object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 16 cm then calculate the image distance from the lens?
Answers
Answer:
-48cm
Explanation:
For a convex lens f is +ve and V is +ve
Using the formula 1/f=1/v+1/u
u=12cm and f=16cm
1/16-1/12=1/v
1/v=-1/48
v=-48cm
The total initial energy of a closed system is 1020 J. During an experiment, 500 J of this energy is converted into kinetic energy. What is the total final energy of this closed system?
A. 1520 J
B. 520 J
C. 500 J
D. 1020 J
Answers
Answer:
D. 1020 J
Explanation:
In a closed system the law of conservation of energy is prevalent.
According to the law of conservation of energy "energy is neither created nor destroyed but transformed from one form to another".
The starting and ending amount of energy must be the same. If the system starts with 1020J, then it must end with 1020J All the energy transformations will add up to 1020J for the final state.A 1,250 kg car is moving due to 6,500 N engine force. If the kinetic friction coefficient between the car and the road is 0.32, what is the car's acceleration?
A) 32m/s²
B) 200m/s²
C) 50m/s²
D) 2m/s²
Answer and I will give you brainiliest
Answers
Answer:
b i hope this is correct answee
please help quick, i’m timed!
Question 2 (5 points)
What is the speed of sound in water if the wavelength is 2.5 m and the frequency
592 Hz?
What would happen to the frequency if the wavelength increased to 5 m?
Answers
Explanation:
v=592×2.5
v=1480m/s
ii) v=1480m/s, wavelength= 5m, f=?
f=1480/5
f=296Hz
Trace the decay of U-238 to Ra-226 as shown in Figure 39.15 in the textFigure out what particles must be emitted in each step, and write the reaction for that step in terms of symbols
Answers
The reaction equations for the steps involved in the decay of U-238 to Ra-226 are;
\(^{238}_{92}U\ \rightarrow \ ^{234}_{90}Th \ + \ ^{4}_{2}He\)
\(^{234}_{90}Th \ \rightarrow \ ^{230}_{88}Ra \ + \ ^{4}_{2}He\)
\(^{230}_{88}Ra \ \rightarrow \ ^{226}_{86}Ra \ + \ ^{4}_{2}He\)
What is the radioactive equation for the decay of U-238?The radioactive equation for the decay of U-238 to Ra-226 is calculated as follows;
First the uranium atom (U-238) will decay thorium by emitting alpha particle as shown in the equation below;
\(^{238}_{92}U\ \rightarrow \ ^{234}_{90}Th \ + \ ^{4}_{2}He\)
The second stage is, the thorium will decay to radium by emitting alpha particles again as shown below;
\(^{234}_{90}Th \ \rightarrow \ ^{230}_{88}Ra \ + \ ^{4}_{2}He\)
The third, and final stage, the radium will decay to an isotope of radium again, by emitting alpha particle as shown below;
\(^{230}_{88}Ra \ \rightarrow \ ^{226}_{86}Ra \ + \ ^{4}_{2}He\)
Thus, the reaction equations for the steps involved in the decay of U-238 to Ra-226 are;
\(^{238}_{92}U\ \rightarrow \ ^{234}_{90}Th \ + \ ^{4}_{2}He\)
\(^{234}_{90}Th \ \rightarrow \ ^{230}_{88}Ra \ + \ ^{4}_{2}He\)
\(^{230}_{88}Ra \ \rightarrow \ ^{226}_{86}Ra \ + \ ^{4}_{2}He\)
Learn more about alpha decay here: https://brainly.com/question/28261016
#SPJ1

Microwaves have a frequency of 10 000 million Hz. Their wavelength is 0.03 m.
Calculate the speed of microwaves.
Show clearly how you work out your answer.
Answers
The speed of the microwaves is 3 × 10^10 meters per second. This result indicates that microwaves, like all electromagnetic waves, travel at the speed of light in a vacuum.
The speed of a wave can be calculated using the formula: speed = frequency × wavelength. In this case, the frequency of the microwaves is given as 10,000 million Hz, which is equivalent to 10,000 × 10^6 Hz or 10^10 Hz. The wavelength is given as 0.03 m.
Plugging these values into the formula, we have:
Speed = (10^10 Hz) × (0.03 m)
Simplifying the calculation, we find:
Speed = 3 × 10^10 m/s
Therefore, the speed of the microwaves is 3 × 10^10 meters per second. This result indicates that microwaves, like all electromagnetic waves, travel at the speed of light in a vacuum. The speed of light is approximately 3 × 10^8 meters per second, so microwaves have a slightly higher speed due to their longer wavelength. It's important to note that the speed of light is a fundamental constant of nature and does not depend on the properties of the specific electromagnetic wave being considered.
For more questions on microwaves, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/1304742
#SPJ8
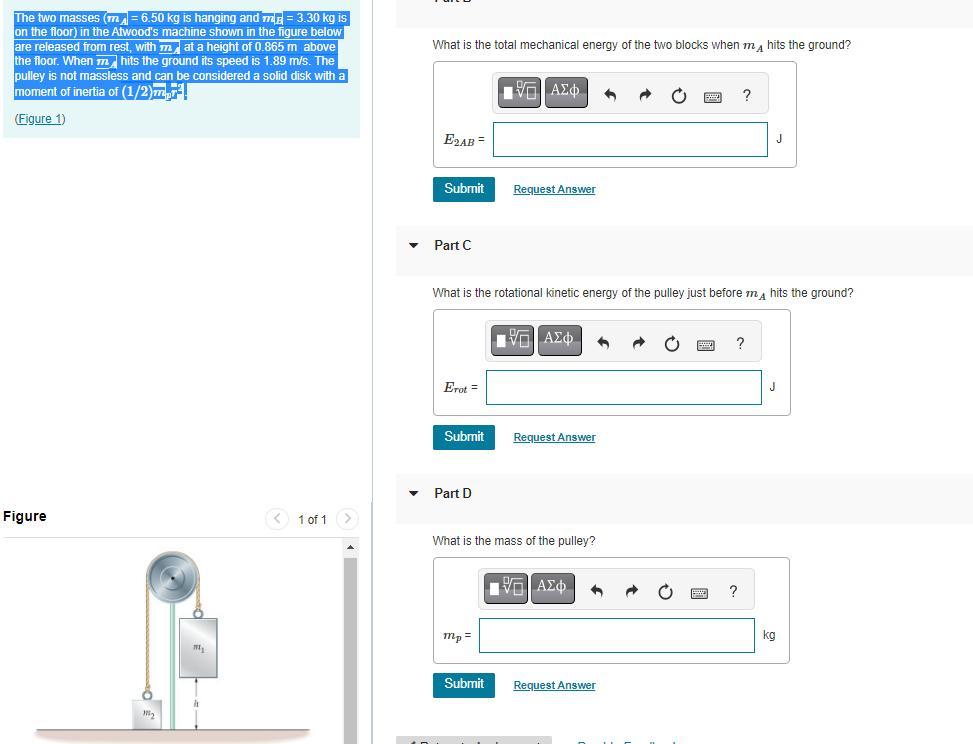
The two masses (mA
= 6.50 kg is hanging and mB
= 3.30 kg is on the floor) in the Atwood's machine shown in the figure below are released from rest, with mA
at a height of 0.865 m above the floor. When mA
hits the ground its speed is 1.89 m/s. The pulley is not massless and can be considered a solid disk with a moment of inertia of (1/2)mpr2
.
What is the total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest?
(Figure 1)
What is the total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA
hits the ground?
Part C
What is the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA
hits the ground?
Part D
What is the mass of the pulley?
Answers
A)The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest can be found by adding the gravitational potential energy of mA and the pulley to zero.
B).The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J,where mp is the mass of the pulley.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest is54.33 J + 0 J = 54.33 J
C) The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground is(0.178 mp) J.
D) The mass of the pulley ismp = (1/2)mpr²/R² =(1/2)(0.020 kg)(0.100 m)²/(0.200 m)² = 0.001 kg = 1 g.r = (1/2)R.
The Atwood's machine shown in Figure 1 consists of two masses mA = 6.50 kg and mB = 3.30 kg. The height of mA above the floor is 0.865 m. When mA hits the floor, its velocity is 1.89 m/s. The pulley has a moment of inertia (1/2)mpr². We have to find the total mechanical energy of the two blocks before they are released, the total mechanical energy when mA hits the ground, the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground, and the mass of the pulley. Let's solve these one by one. Part A The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest can be found by adding the gravitational potential energy of mA and the pulley to zero.
The equation for gravitational potential energy is mgh. The gravitational potential energy of mA and mB is mAg(h-hB)where h is the height of mA above the floor and hB is the height of mB above the floor. Since the pulley is at the same height as mB, its gravitational potential energy ismBg(h-hB).The gravitational potential energy of mA is6.50 kg × 9.81 m/s² × 0.865 m = 54.33 J.The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J,where mp is the mass of the pulley.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest is54.33 J + 0 J = 54.33 J.Part BThe total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA hits the ground can be found by adding the kinetic energy of mA, the kinetic energy of mB, and the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley to the gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley. The equation for kinetic energy is (1/2)mv². The kinetic energy of mA is(1/2) × 6.50 kg × (1.89 m/s)² = 11.54 J.The kinetic energy of mB is(1/2) × 3.30 kg × 0 m/s² = 0 J, since it is at rest.The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J.The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley is(1/2) × (1/2)mp × R² × ω²,where R is the radius of the pulley and ω is its angular velocity just before mA hits the ground. We can use the fact that the linear speed of the rope is the same on both sides of the pulley to find ω. The equation for linear speed is v = Rω. When mA hits the ground, its speed is 1.89 m/s. The speed of mB is zero. Since the rope is inextensible, the speed of the rope is also 1.89 m/s.
Therefore, the speed of the pulley is also 1.89 m/s. We can find the angular velocity of the pulley by dividing the linear velocity by the radius.ω = v/R = 1.89 m/s ÷ (0.200 m/2) = 18.9 rad/s.The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley is(1/2) × (1/2)mp × R² × ω² =(1/4)mpR²ω² =(1/4)mp(0.200 m)²(18.9 rad/s)² =(0.178 mp) J.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA hits the ground is11.54 J + 0 J + 0 J + (0.178 mp) J = 11.72 J + (0.178 mp) J.Part CThe rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground is(0.178 mp) J.Part DWe can find the mass of the pulley by using the moment of inertia of a disk and the mass of the pulley. The moment of inertia of a disk is (1/2)mr². Therefore,(1/2)mpR² = (1/2)mpr²,where R is the radius of the pulley and r is the radius of gyration of the pulley. The radius of gyration of a disk is (1/2)R.
for such more questions on mass
https://brainly.com/question/86444
#SPJ8
Select the best answer for the question.
7. What is the amount of MMF generated by a 50-turn electromagnetic coil supplied by 12 VDC at a current of 1 ampere?
O A. 50 ampere-turns
B. 38 ampere-turns
C. 12 ampere-turns
D. 600 ampere-turns
Answers
The correct answer is 600 ampere-turns
We shall first get the expression that provides the magnetomotive force. It is calculated by multiplying the number of spins on the wire by the current flowing through it. To get the solution, we shall alter and substitute the necessary values.
It is crucial to keep in mind that magnetomotive force (mmf), which is similar to electromotive force (emf), drives a current of electrical charge through magnetic circuits. The phrase "magnetomotive force" is deceptive, though, as it neither denotes a force nor something that moves.
M.M.F = NI
N= 50
I = 12 at a current of 1 ampere
M.M.F = NI
= 50 × 12
=600 ampere-turns
To learn more about magnetomotive force (mmf) refer the link:
https://brainly.com/question/11024291
#SPJ9
Elements known as noble gases do not have the ability or the room in their valence
electron shell to form bonds with other elements.
O True
O False
Answers
Answer:
true
Explanation:
noble gases are octet meaning they they have eight electrons in their outer shell so the are stable
objects want to ______ ___________ doing what they're __________ ____________ because they are "lazy." This is called __________.
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Objects want to continue doing what they're already doing because they are "lazy." This is called inertia.
Two vectors having magnitudes of 5.00 and 9.00 respectively. If the value of their dot product is 12.0, find the angle between the two vectors.
Answers
Answer:
C = 74.53°
Explanation:
Let the magnitudes of 5.00 and 9.00 be vectors A and B respectively, hence the dot product of this vector is defined as
A.B = |A||B|cosC; let C be the angle between the vectors
12 = 5×9 cos C
Hence cos C = 12/45
C = cos^-1(12/45)
C = 74.53°
10. When you push
a textbook,
what is the
agent and what
is the system?
gor
on the
Answers
Answer:
System - textbook ; Agent - Hand/fingers
Explanation:
Whatever applies the force on an object that it's in contact with is an agent. So in this case, your hand/fingers (or whatever means by which the textbook is pushed) is the agent.
The system is the object on which the force is applied which in this case is the textbook
Spring 1 and Spring 2 are the same type of spring. Both springs were pushed or compressed into different positions and clamped into place
L
Which spring has less potential energy?
Answers
Answer:
spring 1 has less potential energy
Explanation:
since spring 2 is clampped down further it will have a greater effect but since sping 1 is barely clamped down it wont show as much energy
Consider two positively charged particles, one of charge q0 (particle 0) fixed at the origin, and another of charge q1 (particle 1) fixed on the y-axis at (0,d1,0). What is the net force F⃗ on particle 0 due to particle 1? Express your answer (a vector) using any or all of k, q0, q1, d1, i^, j^, and k^.
Answers
Answer:
\(F_{10} = - \frac{k_{q1}* qo }{d_{1} ^{2} } j\)
Explanation:
The net force ( F ) on particle 0 due to particle 1 can be expressed as
\(F_{10} = \frac{K_{q1}*qo }{r_{10} ^{3} } r_{10}\)
k = coulomb constant
\(r_{10}\) = distance between charge o and charge 1
to get the vector form ( attached below ) we substitute \(d_{1}\) for \(r_{10}\) and \(- d_{1} j\) for \(r_{10}\)
The net force on \(q_{0}\) by \(q_{1}\) is , \(F=-K\frac{q_{0}*q_{1}}{r^{2} }j\)
The force between two charges is given by Coulomb force law.
\(F=K\frac{q_{0}*q_{1}}{r^{2} }\)
Where K is Coulomb constant, \(K=9*10^{9}Nm^{2}/C^{2}\)
and r is the distance between both charges.
Here given that, \(q_{0}\) is located as (0, 0, 0) and \(q_{1}\) is located at \((0,d_{1}, 0)\)
The force on \(q_{0}\) by \(q_{1}\) in the negative y - axis.
So that , Direction of force is, \(-j\)
Hence, the net force on \(q_{0}\) by \(q_{1}\) is , \(F=-K\frac{q_{0}*q_{1}}{r^{2} }j\)
Learn more:
https://brainly.com/question/14870624
An object of mass 2 kg moving with velocity of 12 m/s, collides head-on with a stationary object whose mass is 6 kg. Given that the collision is elastic, what are the final velocities of the two objects? Neglect friction.
Answers
Answer:
5. An object of mass m = 2 kg, moving with velocity Vi1 = 12 m/s, collides head-on with a stationary object whose mass is m2 = 6 kg. The velocities of the objects after the collision are vj1 -6 m/s and Vr2 = 6 m/s.
Explanation:
We can use the conservation of momentum and kinetic energy to solve for the final velocities of the two objects.
Conservation of momentum:
m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f
where m1 and v1 are the mass and velocity of object 1 before the collision, and m2 and v2 are the mass and velocity of object 2 before the collision.
Plugging in the values:
(2 kg)(12 m/s) + (6 kg)(0 m/s) = (2 kg)(v1f) + (6 kg)(v2f)
Simplifying:
24 kg m/s = 2 kg v1f + 6 kg v2f
Conservation of kinetic energy:
(1/2)m1v1i^2 + (1/2)m2v2i^2 = (1/2)m1v1f^2 + (1/2)m2v2f^2
Plugging in the values:
(1/2)(2 kg)(12 m/s)^2 + (1/2)(6 kg)(0 m/s)^2 = (1/2)(2 kg)(v1f)^2 + (1/2)(6 kg)(v2f)^2
Simplifying:
144 J = 1 kg v1f^2 + 3 kg v2f^2
Now we have two equations with two unknowns (v1f and v2f). Solving for v1f in terms of v2f in the first equation:
v1f = (24 kg m/s - 6 kg v2f)/2 kg = 12 m/s - 3v2f
Plugging this into the second equation:
144 J = 1 kg (12 m/s - 3v2f)^2 + 3 kg v2f^2
Simplifying and solving for v2f:
144 J = 1 kg (144 m^2/s^2 - 72 v2f + 9 v2f^2) + 3 kg v2f^2
144 J = 144 J - 72 kg m/s v2f + 9 kg m^2/s^2 v2f^2 + 3 kg v2f^2
6 kg v2f^2 - 72 kg m/s v2f + 144 J = 0
Dividing by 6 kg:
v2f^2 - 12 kg m/s v2f + 24 J/kg = 0
Using the quadratic formula:
v2f = [12 kg m/s ± sqrt((12 kg m/s)^2 - 4(1)(24 J/kg))]/(2)
v2f = [12 kg m/s ± sqrt(96) m/s]/2
v2f = 6 kg m/s ± 2sqrt(6) m/s
v2f ≈ 9.90 m/s or v2f ≈ 2.10 m/s
Plugging these values into the equation we found for v1f:
v1f = 12 m/s - 3v2f
v1f ≈ -16.70 m/s or v1f ≈ 38.70 m/s
Since the negative velocity doesn't make physical sense, the final velocities of the two objects are:
v1f ≈ 38.70 m/s and v2f ≈ 2.10 m/s
The unit for work is the
a. Calories
b. Celsius degrees
c. Kilogram
d. Joules
(3.1.4)

Answers
The work done is the amount of energy transferred by the force to move an object. Work done equals the product of force and displacement. It is the scalar quantity.
Work done, W = F.d, where F is the force and d is the displacement of the object. The unit of work done is N/m or joule. Hence, the unit of work done is the joule. Thus, the correct option is option D.
Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Energy is of two types and they are potential and kinetic energy. Potential energy is the energy possessed by the object when the object is at rest and the kinetic energy is the energy possessed by the object when it is in motion.
Thus, the kinetic energy is maximum at X and Z. Thus, the ideal solutions are options B and D. The potential energy is maximum at W. Hence, the correct option is A.
To learn more about potential and kinetic energy:
https://brainly.com/question/1413008
#SPJ1
let the samples of the noise voltage, v (nt) be jointly gaussian random variables. show that x(t) is a gaussian process.
Answers
Since x(t) is a linear function of v(nt) which is jointly Gaussian, and the mean of x(t) is a linear function of t, x(t) is also a Gaussian process.
What is Gaussian process?A Gaussian process is a stochastic process whose realizations are Gaussian random variables. To show that x(t) is a Gaussian process, we need to show that:The mean of x(t) is a linear function of t.The covariance function of x(t) is a valid covariance function.The mean of x(t) is defined as E[x(t)], where E[] denotes the expectation operator. Since the noise voltage v(nt) is jointly Gaussian, it follows that x(t) = v(nt) is also Gaussian, and thus its mean is a linear function of t.The covariance function of x(t) is defined as C(s,t) = E[(x(s) - E[x(s)]) (x(t) - E[x(t)])].Since v(nt) is jointly Gaussian, the covariance function of x(t) is also a valid covariance function.Therefore, x(t) is a Gaussian processx(t) = v(nt) is jointly GaussianSince x(t) is a linear function of v(nt) which is jointly Gaussian, and the mean of x(t) is a linear function of t, x(t) is also a Gaussian process.The covariance function of x(t) is a valid covariance function, as it is derived from jointly Gaussian variables.To learn more about Gaussian process refer:
brainly.com/question/13427232
#SPJ4
1.00 kg of ice at -24.0°C is placed
in contact with a 1.00 kg block of a
metal at 5.00°C. They come to
equilibrium at -8.88°C. What is
the specific heat of the metal?
Answers
1.00 kg of ice at -24.0°C is placed in contact with a 1.00 kg block of a metal at 5.00°C. They come to equilibrium at -8.88°C.
We can use the principle of conservation of heat to solve this problem. The heat lost by the metal must equal the heat gained by the ice.
The heat lost by the metal is given by
Q1 = m1c1ΔT1
Where m1 is the mass of the metal, c1 is its specific heat, and ΔT1 is the change in temperature.
The heat gained by the ice is given by
Q2 = m2c2ΔT2
Where m2 is the mass of the ice, c2 is its specific heat, and ΔT2 is the change in temperature.
Since the two objects come to thermal equilibrium, we can set Q1 equal to Q2
m1c1ΔT1 = m2c2ΔT2
Solving for c1, we get
c1 = m2c2ΔT2 / (m1ΔT1)
By putting these values we get
c1 = (1.00 kg)(2.06 kJ/kg·K)(-24.0°C - (-8.88°C)) / [(1.00 kg)(5.00°C - (-8.88°C))]
c1 = 0.902 kJ/kg·K
Hence, the specific heat of the metal is 0.902 kJ/kg·K.
To know more about equilibrium here
https://brainly.com/question/28844402
#SPJ1
The electric potential V in the space between two flat parallel plates 1 and 2 is given (in volts) by V=1500x 2
, where x (in meters) is the perpendicular distance from plate 1. At x=1.3 cm,
(a) what is the magnitude of the electric field and
(b) is the field directed toward or away from plate 1?
Answers
The magnitude of the electric field is 39 volts per meter and negative is the field directed toward plate 1.
The degree of labour required to transfer a unit of electric charge from a starting point to a particular spot in an electric field is known as the electric potential. Earth is typically chosen as the reference point, but any location outside the range of the electric field charge can be utilized.
The force per charge on the test charge is a straightforward method for determining the size of the electric field. As an electric field is defined as a force per charge, the power units are divided by charge units which will ultimately be the units of an electrical field.
To learn more about electric potential here
brainly.com/question/12645463
#SPJ4
Who has the best dog ever!?!?
Answers
Answer:
10x10=100
snoopy ofc :)
Answer:
Labrador Retriever.
hope it will help you
A frying pan is connected to a 1500 volt circuit. If the resistance of the frying pan is 25 ohms, how many amperes does the frying pan draw?
Answers
The current (in amperes) the frying pan draws from the 500 volt circuit, given that it has a resistance of 25 ohms is 60 amperes
How do i determine the current drawn by the frying pan?From the question given above, the following data were obtained:
Voltage of circuit (V) = 1500 V Resistance of frying pan (R) = 5 Ω Current (I) =?The current drawn by the frying pan can be obtained as follow:
Voltage (V) = Current (I) × resistance (R)
Inputting the given parameters, we have:
1500 = Current × 25
Divide both sides by 25
Current = 1500 / 25
Current = 60 amperes
Thus, from the above calculation we can conclude that the current drawn by the frying pan is 60 amperes
Learn more about current:
https://brainly.com/question/23754329
#SPJ1