For several days, the weather where Cheyenne lives was cool. When the temperature did warm, Cheyenne noticed
that it was also very windy. How could winds influence the temperature?
A. Winds carry energy in the form of heat around Earth.
B. Winds are caused by the energy of the sun.
C. Winds move because of differential heating.
D. Winds transfer energy in the form of heat from the air to the ground
Answers
Related Questions
How do you rule a X-linked recessive pedigree?
Answers
Ruling a X-linked recessive pedigree involves analyzing the family history and pattern of inheritance of a trait or disorder to determine if it is likely to be inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern.
The disorder can be identified by:
Construct a pedigree by gathering information about the family history of the trait or disorder. Identify the pattern of inheritance by analyzing the transmission of the trait or disorder within the family. X-linked recessive disorders typically show a pattern of transmission in which affected males are only found in the direct line of descent from a female carrier. If the disorder is only found in males and not females, or if it is found mostly in males, it could be X-linked recessive.Exclude other possible modes of inheritance. Confirm the mode of inheritance by performing genetic testing. Genetic tests such as DNA sequencing or linkage analysis can be used to identify the specific genetic mutation causing the disorder in affected family members. Identify the specific gene mutation. With the help of genetic testing and linkage mapping it's possible to identify the specific gene and the mutation that causes the disorder.To know more about Pedigree analysis, click here,
brainly.com/question/14525981
#SPJ4
What are the 2 main ways to introduce variation into an organism that occur during the process of meiosis?
Answers
The 2 main ways through which variation can be introduced into an organism during the meiosis is: crossing over during Meiosis I and random orientation of sister chromatids during Meiosis II.
Meiosis is the process of cell division where a cell divides to form 4 daughter cells. This process is accomplishes in 2 stages: meiosis I and meiosis II. Each stage has 4 following phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Crossing over is the process that occurs in the Pachytene stage of the Prophase I of Meiosis. It is the exchange of genetic material between the non-sister chromatids of the 2 homologous chromosomes. This gives rise to recombinants.
To know more about crossing over, here
brainly.com/question/27256451
#SPJ4
What are the 4 types of basic tissue in humans?
Answers
Answer:
Tissue is classified into four types: connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscular tissue, and nerve tissue. Connective tissue supports and connects other tissues (bone, blood, and lymph tissues). Epithelial tissue serves as a protective layer (skin, the linings of the various passages inside the body).
Explanation:
I hope this helps! :) If it does could you please mark me brainliest?
Answer:
There are 4 basic types of tissue: connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Connective tissue supports other tissues and binds them together (bone, blood, and lymph tissues). Epithelial tissue provides a covering (skin, the linings of the various passages inside the body).
Explanation: Hope this helps. Mark me brainliest
Lesson 02. 01 Properties of Water
Identify that water is a compound common to living things
Recognize the importance of hydrogen bonding to the properties of water
Explain why many compounds dissolve in water
Lesson 02. 02 Microscopes
Explain how modern technology affects the study of biology
Compare the structure and function of various types of microscopes
Lesson 02. 03 Early Cells
Describe the developments that led to the cell theory
Differentiate between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
Describe the structure of the cell membrane
Distinguish between active and passive transport
Lesson 02. 03A Early Cells (Honors)
Describe the theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells (endosymbiosis)
Explain the evidence that supports the theory of endosymbiosis
Lesson 02. 04 Cell Structure and Function
Describe the internal structures of eukaryotic cells
Summarize the functions of the organelles found in plant and animal cells
Lesson 02. 05 Cellular Energy
Recognize the importance of ATP as an energy-carrying molecule
Identify energy sources used by organisms
Lesson 02. 06 Cellular Respiration
Describe the process of cellular respiration
Compare aerobic respiration to anaerobic respiration
Lesson 02. 07 Photosynthesis
Describe the process of photosynthesis
Compare cellular respiration to photosynthesis
Answers
Answer:
Lesson 02.01: Properties of Water
Water is a compound common to living things because it is essential for life. It is a major component of cells and plays a crucial role in many biological processes.
Hydrogen bonding is important to the properties of water. Water molecules are polar, meaning they have a slight positive charge on one end and a slight negative charge on the other. This polarity allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with each other. Hydrogen bonding gives water its high boiling point, high specific heat capacity, cohesion, and adhesion properties.
Many compounds dissolve in water due to its polarity. Water's polar nature allows it to form interactions with other polar molecules, such as salts and sugars, as well as with charged ions. The positive and negative ends of water molecules surround and separate the ions or polar molecules, effectively dissolving them in the water.
Lesson 02.02: Microscopes
Modern technology has greatly impacted the study of biology. Advanced microscopes, such as electron microscopes, have allowed scientists to observe structures at a much higher resolution and magnification than was previously possible. Techniques like fluorescence microscopy and confocal microscopy enable the visualization of specific molecules and cellular processes in living organisms.
There are various types of microscopes with different structures and functions:
Light microscopes: Use visible light to illuminate the specimen and produce an image. They are commonly used in educational and research settings and can magnify up to 1000x.
Electron microscopes: Use a beam of electrons instead of light to visualize specimens. They offer much higher magnification and resolution than light microscopes. There are two types: transmission electron microscopes (TEM) and scanning electron microscopes (SEM).
Scanning probe microscopes: Use a physical probe to scan the surface of a specimen. They can provide atomic-level resolution and are used in nanotechnology and materials science.
Lesson 02.03: Early Cells
The developments that led to the cell theory include:
Robert Hooke's discovery of cells in cork in 1665.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek's observations of microscopic organisms in pond water in the late 17th century.
Matthias Schleiden's and Theodor Schwann's formulation of the cell theory in the 19th century, stating that all living organisms are composed of cells, and cells are the basic units of life.
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells.
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a selectively permeable barrier that surrounds the cell. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The cell membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell and plays a vital role in maintaining cell homeostasis.
Active transport requires energy to move substances against their concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. Passive transport, on the other hand, does not require energy and involves the movement of substances along their concentration gradient, from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Lesson 02.03A: Early Cells (Honors)
The theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells is called endosymbiosis. It proposes that eukaryotic cells evolved from the symbiotic relationship between different types of prokaryotic cells.
The evidence supporting the theory of endosymbiosis includes:
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes, similar to prok
Send a message.
the survival of a species depends on
1. An environment that never changes
2. A continuously increasing life span
3. Reproduction within populations
4. A limit of no more than populations
Answers
When a patient undergoing a blood transfusion complains of flank pain and hematuria, which adverse reaction should be suspected?
Answers
When a patient undergoing a blood transfusion complains of flank pain and hematuria, the adverse reaction should be a suspected hemolytic transfusion reaction.
Hematuria is the presence of blood in someone's urine. Gross hematuria is when someone can see the blood in his or her urine, and microscopic hematuria is when someone cannot see the blood in his or her urine, but a fitness care professional can see it beneath a microscope.
Blood in the urine can have causes that aren't because of underlying disease. Examples include unexplained individual variations or workouts.
At the same time many times, the reason is innocent, blood inside the urine (hematuria) can suggest an extreme sickness. The blood that you may see is known as gross hematuria. Urinary blood is seen simplest under a microscope (microscopic hematuria) is observed while your doctor assesses your urine.
Learn more about hematuria here https://brainly.com/question/13253431
#SPJ4
As temperatures increase, gases such as CO2 diffuse faster. As a result, plant leaves will lose CO2 at a faster rate than normal. If the amount of light impacting on the leaf and the amount of water available is adequate, predict how this loss of gas will affect photosynthesis in the leaf.
Answers
Answer:
See the answer below
Explanation:
If the amount of light reaching a leaf and the water supply is adequate in the face of inadequate carbon dioxide, the latter becomes a limiting reagent in the process of photosynthesis.
The process of photosynthesis has two steps
1. The light reaction
2. The light-independent reaction/the Calvin cycle
Carbon dioxide is only required in the second step which is the Calvin cycle. This means that the light reaction proceeds at a normal rate but the Calvin cycle is slowed due to inadequate carbon dioxide. Overall, the rate of photosynthesis becomes limited to the amount of carbon dioxide that is available in the leaf.
streptomycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that binds to ribosomes. which bacterial process does streptomycin inhibit?
Answers
This substance thereby disrupts the formation of the initiation complex between mRNA and the bacterial ribosome, preventing the start of protein synthesis.
Which microorganisms is streptomycin effective against?A monosubstituted aminocyclitol with a disaccharide connected makes up the pseudotrisaccharide streptomycin. 9–11 Streptomycin, in contrast to penicillin, inhibited both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria as well as Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Who or what does streptomycin combat?The first aminoglycoside antibiotic, streptomycin, was first isolated from the bacteria Streptomyces griseus. It now primarily functions as a component of a multi-drug regimen used to treat pulmonary tuberculosis. Multiple aerobic gram-negative bacteria are also susceptible to its extra activity.
To know more about streptomycin visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/13252018
#SPJ4
Who is responsible for the gender of a new born baby a male or female
Answers
What are the three main ways that protists can move?
Answers
Answer:
cilia, flagella, or pseudo/axopodia
Explanation:
in the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis water is split, releasing high energy particles that pass down a gradient to produce energy in the form of atp. what are these particles called? group of answer choices photons protons electrons
Answers
Answer:
photons
Explanation:
protons and electrons are part of chemisty in elements
What is ittt please I need it rq
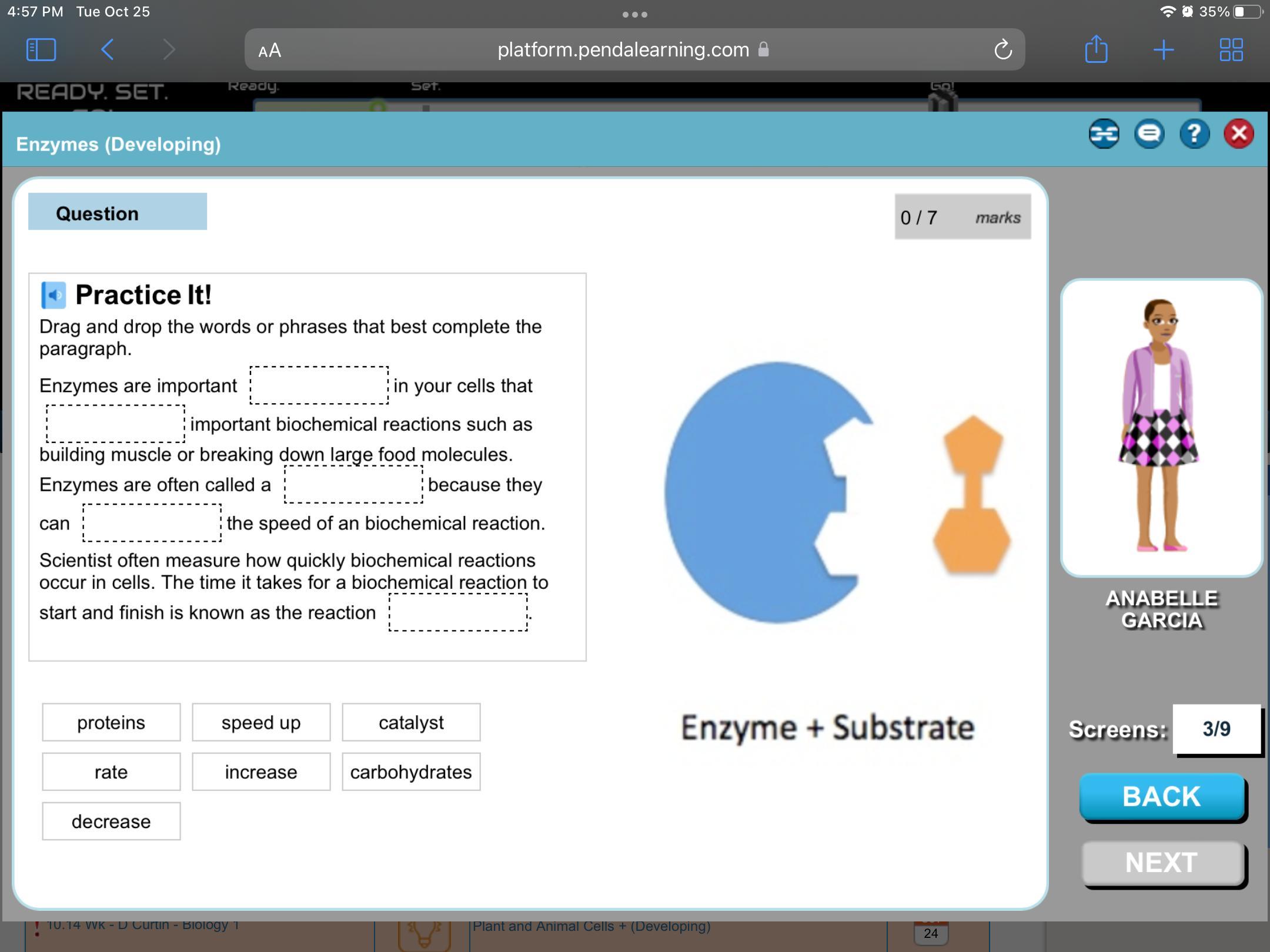
Answers
The correct words to fill in the gaps respectively are proteins, speed up, catalysts, increase, and rate.
What are enzymes?Enzymes are simply biological catalysts found in living cells. They are proteinous in nature and work by speeding up on increasing the rate of biological reactions.
The rate of any reaction is a measure of how much of the products of the reaction are being produced per unit of time.
Thus, the complete paragraph with the missing words would be:
Enzymes are important proteins in your cells that speed up important biological reactions such as building muscles or breaking down large food molecules.
Enzymes are often called a catalyst because they can increase the speed of any biochemical reaction.
Scientists often measure how quickly biochemical reactions occur in cells. The time it takes for biochemical reactions to start and finish is known as the reaction rate.
More on enzymes can be found here: https://brainly.com/question/14953274
#SPJ1
Why is Global warming occurring?
Answers
Answer:
Global warming occurs when carbon dioxide (CO2) and other air pollutants collect in the atmosphere and absorb sunlight and solar radiation.
Explanation: do you want one?
Investigating the Cell Cycle Results: Part I: The Yeast Cell Cycle: Determining the length of \( \mathrm{G} 1, \mathrm{~S}, \mathrm{G} 2 \& \mathrm{M} \) in the yeast cell cycle
Answers
The yeast cell cycle is a process by which a single yeast cell divides into two daughter cells. The cell cycle is divided into four main phases: G1, S, G2, and M. The length of the yeast cell cycle is about 10-15 hours, with the G1, S, G2, and M phases each lasting about 1-2 hours, 6-8 hours, 2-3 hours, and 1-2 hours, respectively.
Each phase is important for the proper division of the cell.
The G1 phase is the first phase of the cell cycle and is characterized by cell growth and preparation for DNA synthesis. The length of the G1 phase varies depending on the type of cell, but it typically lasts about 1-2 hours in yeast cells.
The S phase is the second phase of the cell cycle and is characterized by DNA synthesis. During this phase, the cell's DNA is replicated in preparation for cell division. The S phase typically lasts about 6-8 hours in yeast cells.
The G2 phase is the third phase of the cell cycle and is characterized by further cell growth and preparation for mitosis. The G2 phase typically lasts about 2-3 hours in yeast cells.
The M phase, also known as mitosis, is the final phase of the cell cycle and is characterized by the division of the cell into two daughter cells. The M phase typically lasts about 1-2 hours in yeast cells.
Overall, the length of the yeast cell cycle is about 10-15 hours, with the G1, S, G2, and M phases each lasting about 1-2 hours, 6-8 hours, 2-3 hours, and 1-2 hours, respectively.
For such more question on yeast:
https://brainly.com/question/25088514
#SPJ11
What allows carbon to bond with up to four other atoms at a time and form the macromolecules that are essential to life ?
Answers
Answer:
A covalent bond is formed when atoms share electrons in their valence shells. Carbon …
Explanation:
A covalent bond is formed when atoms share electrons in their valence shells. Carbon …
Which statement about sister chromatids is true? One sister chromatid is inherited from each parent. Sister chromatids are always in every cell. Sister chromatids are only present during cell reproduction. Each sister chromatid forms a lobe of a chromosome.
Answers
Answer:
One sister chromatid is inherited from each parent.
Explanation:
Answer:
its C
Explanation:
63. Considered the "Father of Taxonomy". His classification system was built on visible characteristics and is still used today. Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
a. Aristotle b. Linnaeus c. Woese
Answers
Drag each tile to the correct location.
Sort the statements based on whether they describe DNA replication in eukaryotes or prokaryotes.
Replication takes place in
the nucleus.
Replication happens at just
one point on the chromosome.
There is only one origin of
replication.
Replication takes place
in the cytoplasm.
Prokaryotes
G
There are multiple origins
of replication.
Replication occurs at multiple
points along the chromosome.
Eukaryotes
Answers
The nucleus is where replication occurs in eukaryotes. Replication has several different origins. Along the chromosome, replication takes place several times. Prokaryotes replicate within their cytoplasm. Only one location on a chromosome experiences replication. There is just one origin for replication.
The process of DNA replication, which is managed by the enzyme DNA polymerase, involves the genetic material of a cell—in this case, the DNA—making a perfect copy of itself. In comparison to bacteria, which replicate at a pace of about 500 nucleotides per second, mammals replicate at a rate of about 50 nucleotides per second.
Prokaryotic DNA replication happens through a single origin of replication, whereas eukaryotic DNA replication occurs through numerous replication origins. This is the primary distinction between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA replication.
Thus, we can conclude that the location, complexity, and size of the cell have a role in the differences between DNA replication in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
LEARN MORE ABOUT DNA REPLICATION HERE:
https://brainly.com/question/16464230
#SPJ1
The physical and biological components of an environment and the relationships between them make up a(n)
A) species.
B) biosphere.
C) atmosphere.
D) ecosystem.
Answers
The physical and biological components of an environment and the relationships between them make up an ecosystem.
An ecosystem refers to a community of living organisms (biological components) in conjunction with the non-living elements (physical components) of their environment. It encompasses both the living organisms (such as plants, animals, and microorganisms) and the abiotic factors (such as soil, water, air, temperature, and sunlight) within a specific area.
The interactions and relationships between these components are fundamental to the functioning of an ecosystem. Organisms within an ecosystem depend on each other and the physical environment for resources, energy flow, and various ecological processes. These interactions shape the structure, dynamics, and stability of the ecosystem.
Therefore, an ecosystem provides a holistic framework to understand the interconnections between the living and non-living components of an environment, emphasizing the intricate web of relationships that exist in natural systems.
Know more about ecosystem here:
https://brainly.com/question/31459119
#SPJ11
Which statement is an example of a scientific theory? A. The Earth is the third planet from the Sun and has one moon, which orbits the Earth. B. Hummingbirds do not like the color white because they visit other colored flowers more often. C. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells, which came from pre-existing cells. D. The amount that caffeine affects a person's heart rate differs based on the person's age.
Answers
Answer:
D: The amount that caffeine affects a person's heart rate differs based on the person's age.
Which term is used to describe the evidence of preexisting life found in layers of
sedimentary rock?
flora
invertebrates
fauna
fossilized
Answers
Answer: I think its fossils
Explanation:
Why porters place a round piece of clothes on their heads, when they have to carry loads?
Answers
Answer:
so they can grip the pot well
potters usually place a round cloth which is mainly rough to get a grip and so that the pot does not fall
Based on the graph, how would Cook County, Georgia, be affected in the future if the trend continues and aquifers are eventually depleted
Answers
We can see here that Cook County, Georgia, will be affected in the future if the trend continues and aquifers are eventually depleted in the following way: C. Farmers would have less or no water for irrigation
What is trend?A trend refers to a general direction or pattern of change in a particular field, domain, or society over a period of time. It represents the prevailing tendency or inclination towards a certain style, behavior, concept, or phenomenon that gains popularity or widespread acceptance.
Trends can emerge in various areas, including fashion, technology, culture, business, social media, entertainment, and more.
The graph shows that the water level in the aquifer is decreasing over time. This means that there will be less water available for irrigation in the future.
Learn more about trend on https://brainly.com/question/30772562
#SPJ1
The complete question is:
Based on the graph, how would Cook County, Georgia, affected in the future if the trend continues and aquifers are eventually depleted?
USGS well 18H016, Cook County, Georgia
160
165
170
175
180-
185
1967
1974
1981
Year
1988
1995
2002
A. Land may rise because the weight of the water no longer compacts it.
B. It would become easier to cultivate crops.
C. Farmers would have less or no water for irrigation
D. Vegetation fed by groundwater would flourish.
Is glucose more or less complex than the rest of the biomolecules? Explain.
Answers
Answer:
Less complex.
Explanation:
Glucose is both a monomer and simple sugar.
Glucose is a monosaccharide. It is a biomolecule. It is less complex than the rest of the biomolecules, such as proteins, lipids, and other complex carbohydrates like glycogen.
What is a biomolecule?
Biomolecules are present inside the cell. Carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids are some examples of biomolecules. Carbohydrates are divided into monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
A monosaccharide has a single unit. Examples are glucose, fructose, etc. A disaccharide consists of two units. An example is maltose. Maltose is made up of two units of glucose connected by a glycosidic bond. An example of a polysaccharide is glycogen. Multiple sugar units are connected by glycosidic bonds to form glycogen. It is a storage product.
Carbohydrates are present on our cell surface as peptidoglycan. Protein is a biomolecule that is made up of amino acid monomers. They make the different structures of a cell, such as actin fibers, etc. Lipid is made up of hydrogen and carbon. Examples are cholesterol, phospholipids, etc.
Hence, in comparison to all other biomolecules, glucose is the simplest.
To learn more about biomolecule, refer to the following link:
https://brainly.com/question/12299485
#SPJ2
Suppose that a plant disease kills all the fruit. The change could become a on the birds?
Answers
Some animal cells have ___, while others do not
Answers
Answer:
Centrosome or Lysosomes
Explanation:
Animal cells each have a centrosome and lysosomes, whereas plant cells do not. Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts and other specialized plastids, and a large central vacuole, whereas animal cells do not
Please give me brainliest
Explanation:
Neuromodulation is the release of chemicals (other than ____________ ) from cells that locally regulate or alter the response of neurons to neurotransmitters. The substances released are called ____________ . Neuromodulation generally results in either facilitation or inhibition. When there is greater response from a postsynaptic neuron because of the release of neuromodulators it is ____________ . This may result from either ____________ amount of neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft or ____________ number of receptors on postsynaptic neurons. When there is less response from a postsynaptic neuron because of the release of neuromodulators, it is called ____________ . This results from either ____________ amount of neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft or ____________ number of receptors on postsynaptic neurons.
Answers
Answer:
Neurotransmitters; neuromodulators; facilitation; an increased; an increased; inhibition; a decreased; a decreased.
Explanation:
In Biology, stimulus can be defined as an obvious change in either the chemical or physical structure of an organism' environment (either external or internal). Thus, all living organisms (both animals and plants) respond to changes in their environment and consequently, an appropriate response or reaction is made. Also, stimulus arising from within the organism is known as internal stimulus while those from its environment are known as the external stimulus.
In organisms, the specialized cells that detect stimulus are generally known as sensory receptors while a group of these receptors is referred to as sense organ.
Neuromodulation is the release of chemicals (other than neurotransmitters ) from cells that locally regulate or alter the response of neurons to neurotransmitters. The substances released are called neuromodulators. Neuromodulation generally results in either facilitation or inhibition. When there is greater response from a postsynaptic neuron because of the release of neuromodulators it is facilitation. This may result from either an increased amount of neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft or an increased number of receptors on postsynaptic neurons. When there is less response from a postsynaptic neuron because of the release of neuromodulators, it is called inhibition. This results from either a decreased amount of neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft or a decreased number of receptors on postsynaptic neurons.
bones that are small round and tend to develop in tendons are
Answers
The bones that are small, round, and tend to develop in tendons are called sesamoid bones.
Sesamoid bones are specialized bones that develop within certain tendons, typically in locations where the tendon passes over a joint. They are usually small and rounded in shape, resembling a sesame seed, which is how they acquired their name. Sesamoid bones can be found in various locations in the body, such as the patella (kneecap), which is the largest sesamoid bone, and the sesamoid bones found in the hands and feet.
These bones act as pulleys, helping to reduce friction and increase the mechanical advantage of muscles. The most well-known sesamoid bones are the patella (kneecap) and the two sesamoid bones located under the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot (the ball of the foot).
Know more about sesamoid bones here:
https://brainly.com/question/6848255
#SPJ11
Which of the following levels of gene expression control allows a cell to conserve the most resources?
post-translational control
pre-RNA splicing control
transcriptional control
translational control
Answers
The level of gene expression control that allows a cell to conserve the most resources is transcriptional control. Option C is correct.
Transcriptional control refers to the regulation of gene expression at the stage of transcription, where the DNA is transcribed into RNA. This level of control occurs before RNA processing, translation, and post-translational modifications take place. By regulating gene expression at the transcriptional level, the cell can prevent the unnecessary synthesis of RNA and subsequent translation of proteins that are not needed.
By conserving resources at the transcriptional level, the cell can avoid the expenditure of energy and resources required for RNA processing, splicing, translation, and post-translational modifications. It allows the cell to selectively transcribe and produce specific RNAs and proteins based on its current needs and environmental conditions.
In contrast, post-translational control, pre-RNA splicing control, and translational control occur at later stages of gene expression and may involve additional energy and resources for processing, modifying, and degrading RNA and proteins.
Hence, C. is the correct option.
To know more about gene expression here
https://brainly.com/question/30969903
#SPJ4
--The given question is incomplete, the complete question is
"Which of the following levels of gene expression control allows a cell to conserve the most resources? A) post-translational control B) pre-RNA splicing control C) transcriptional control D) translational control."--
Which of the following organisms in the arctic tundra ecosystem retains the least chemical energy fixed by photosynthesis?
a. arctic fox
b. caribou
c. snow goose
d. lichen
Answers
The lichen is the creature in the polar tundra ecosystem that fixes the least amount of chemical energy.
The symbiotic relationship between a fungus and an alga or cyanobacterium results in lichen. Lichen can endure harsh environments, but they grow slowly and are not very good at storing the energy produced by photosynthesis. In the polar tundra ecosystem, lichen makes up the base of the food chain and is a source of nutrition for herbivores like caribou and snow geese.
However, they have the lowest trophic level in the food chain since they retain the least energy. The arctic fox has a higher trophic level and maintains more chemical energy since it eats herbivores like caribou and snow geese.
To learn more about Lichen:
https://brainly.in/question/11755836