Drag the tiles to the correct boxes to complete the pairs.
Match the correct economic terms to their descriptions.
Federal government's way to influence the economy through taxes
Federal reserve's tool to influence the money supply in the economy
A market where firms buy services related to production
A market where finished goods and services are traged

Answers
Product market: A market where finished goods and services are traded.
Monetary Policy: Federal governments way to influence the economy through taxes.
The last one which I can’t see: Federal reserves tool to influence the money supply in the economy.
:D
Related Questions
Which of the following supports a business strategy that incorporates the key
operational capability of flexibility?
O Utilizing specialized, automated equipment for consistent product buildup
O Using electronic tools to improve customer communications
Having high quality standards for suppliers
O Reducing labor and shelving costs
O Maintaining excess production capability
Answers
Business strategy that incorporates the key operational capability of flexibility is utilizing specialized, automated equipment for consistent product buildup.
Thus, the correct option is A.
What is Business strategy?
A business strategy explains the precise methods through which a company intends to position itself, accomplish its short- and long-term objectives, and expand over time.
A plan outlining how a corporation will accomplish its objectives is known as a business strategy. Although there are many distinct business strategies, cost leadership, differentiation, and focus are a few typical examples.
Cost, quality, distribution, technology, and intellectual property are the only five corporate tactics (IP). These five concepts, or a mixture of them, form the basis of all corporate strategy. Focusing your business on just one thing is generally the simplest to implement.
A strategy is essentially just a hypothesis. For a strategy to be effective, the issue that needs to be resolved must be accurately diagnosed, a guiding policy must be established to handle the issue, and a set of cogent actions must be proposed to carry out the policy.
Learn more about Business strategy, here
https://brainly.com/question/28561700
#SPJ1
Question Content Area
Journalize the entries to record the following selected transactions:
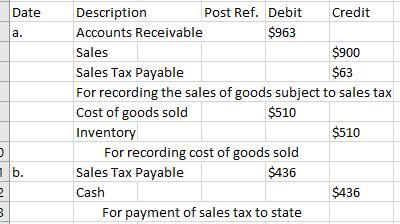
a. Sold $900 of merchandise on account, subject to 7% sales tax. The cost of the goods sold was $510.
b. Paid $436 to the state sales tax department for taxes collected.
If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.
a.
- Select -
- Select -
blank
- Select -
- Select -
- Select -
- Select -
b.
Answers
When the final sale in the supply chain is made, the retailer is responsible for collecting sales tax. The required journalized entries for the selected transactions involving sales tax are attached below.
The state levies a consumption tax, the so-called sales tax, on the purchase of goods and services. A standard sales tax is collected at the point of sale, collected at the store and remitted to the government.
Depending on the regulations in that country, a business may be responsible for sales taxes in that jurisdiction if it has a presence there, which can be a physical site, an employee, or an associate. The calculation of sales tax for (a) is:
Sales Tax Payable = Amount of sales× Sales Tax
= $900 × 7%
= $63
Therefore, all the selected transactions are explained with the help of the journal entries.
To learn more on sales tax, here:
https://brainly.com/question/29442509
#SPJ3
Your question is incomplete, but most probably the full question was,
Question Content Area
Journalize the entries to record the following selected transactions:
a. Sold $900 of merchandise on account, subject to 7% sales tax. The cost of the goods sold was $510.
b. Paid $436 to the state sales tax department for taxes collected.
If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.
a.
- Select -
- Select -
blank
- Select -
- Select -
- Select -
- Select -
b.
- Select -
- Select -
blank
I need the answer please help

Answers
As given that the taxable state income for the year is $70,000, the applicable tax rate is 5.5%, thus, the tax payable is $3,850.
What does a progressive tax means?A progressive tax is one in which the tax rate rises in proportion to the taxable amount. The term progressive refers to the manner in which the tax rate rises from low to high, resulting in a taxpayer's average tax rate being less than the person's marginal tax rate. The term can refer to either individual taxes or an entire tax system.
We are given that the taxable state income for the year is $70,000. Note that for this salary range, the tax rate of 5.5% is applicable.
Tax payable is computed as:
= $70,000 * 5.5%
= $3,850
Read more about progressive tax
brainly.com/question/4343640
#SPJ1
The production possibilities curves suggest that rev: 09_17_2020_QC_CS-228777 Multiple Choice West Mudville should specialize in, and export, both baseballs and baseball bats. workers will try to immigrate from West Mudville to East Mudville. West Mudville should specialize in, and export, baseball bats. East Mudville should specialize in, and export, baseball bats.
Answers
Answer: West Mudville should specialize in, and export, baseball bats.
Explanation:
Each country should specialize in the good that it has a lower opportunity cost in producing.
West Mudville
Opportunity cost of producing baseball bats = 9/9 = 1 baseball
Opportunity cost of producing baseball = 9/9 = 1 baseball bat
East Mudville
Opportunity cost of producing baseball bats = 8/4 = 2 baseballs
Opportunity cost of producing baseball = 4/8 = 0.5 baseball bats
From the above, West Mudville has a lower opportunity cost than East Mudville in the production of baseball bats and so it should specialize in and export that.

Have you ever had your dream crushed before
Answers
Answer:
yes but dont let it slip away
Explanation:
student self assessment essay
Answers
Answer:
I will write it
Explanation:
Please send the question
Rand Company had May operations as follows. Units actually produced 76,000 Actual direct labor hours worked 160,000 Actual variable overhead incurred $500,000 Actual fixed overhead incurred 384,000
Based on monthly normal volume of 100,000 units (200,000 direct labor hours), Rand's standard cost system contains the following overhead costs:
Variable $6 per unit
Fixed 4 per unit
The unfavorable variable overhead spending variance was:_________
A. 12,000
B. 20,000
C. 24,000
D. 44,000
Answers
Answer:
B. 20,000
Explanation:
Standard Variable overhead rate = $6 per units / 2 direct labour hour
Standard Variable overhead rate = $3 per hour
Variable Overhead Spending Variance = Actual hours worked * (Actual overhead rate - Standard overhead rate)
Variable overhead spending variance = 160,000 * (3.125 -3)
Variable overhead spending variance = 160000*0.875
Variable overhead spending variance = 20,000
Why are credit card debuts so expensive?
Answers
Bell Hill Mfg. is considering a rights offer. The company has determined that the ex-rights price would be $78. The current price is $100 per share, and there are 25 million shares outstanding. The rights offer would raise a total of $50 million. What is the subscription price?
Answers
Answer:
6.5
Explanation:
We can calculate Ex-Rights using following formula:
Ex-Rights = (Current Shares * Shares outstanding + Amount Raised) / (Current Shares + Amount Raised / Subscription Price)
Here
Market Value is $100
Shares Outstanding are 25 million
Amount Raised is $50 million
Ex-Rights price is $78
By putting values, we have:
$78 = (($100 * 25m) + $50m) / (25m + (50m/Subscription price))
$78 = ($2550) / (25m + ($50m/Subscription Price))
$78 / ($2550m) = 1 / (25m + ($50m/Subscription Price))
0.0000030588 = 1 / (25m + ($50m/Subscription Price))
Taking reciprocal, we have:
1 / 0.0000030588 = (25m + ($50m/Subscription Price))
$32.6923m = $25m + $50m / Subscription Price
$32.6923m - $25m = $50m / Subscription Price
$7.6923m = $50m / Subscription Price
$7.6923m / $50m = 1 / Subscription Price
0.153846 = 1 / Subscription Price
Taking Reciprocal, we have:
Subscription Price = 6.5
makes sure an agenda is sent out before the meeting
Answers
Answer:
Facilitator
Explanation:
Facilitators manage the meeting process.
Hope that helps!
The following trial balance relate to Lubuto company at 31 March 2022
K’000 K’000
Plant and Equipment at cost (iii) 155,500
Accumulated amortisation/ depreciation at 1 April 2021
Right of use asset 25,000
Plant and Equipment 43,500
Right of use – leased property at cost 100,000
Bank interest 900
Administration expenses 36,800
Distribution costs 33,500
Cost of sales 290,600
Loan note interest and dividends paid (notes(iv) and(v) 13,380
Revenue 490,000
Inventories at 31st March 2022 61,000
Trade received 63,000
Trade payables 32,200
Bank 5,500
Equity shares of 25ngwee each (notes ii) 56,000
Share premium 25,000
Retained earnings at 1 April 2021 26,080
5% convertible loan note (note iv) 50,000
Current tax note (vi) 3,200
Deferred tax (note (vi) 4,600
757,880 757,880
The following notes are relevant:
(i) Revenue includes and amount of K20 million for cash sales made through Lubuto
co’s retail outlets during the year on behalf of francis. lubuto Co, acting as agent, is
entitled to a commission of 10% of the selling price of these goods. By 31st March
2022, Lubuto Co had remitted to Francis K15million ( of the K20 million sales) and
recorded this amount in cost of sales
(ii) On 1st August 2021, Lubuto Co made a fully subscribed rights issue of equity share
capital based on two new shares at 60 ngwee each for every five shares held. The
issue has been fully recorded in the trial balance figures.
(iii) Plant and equipment is depreciated at 12.5% per annum on the reducing balance
basis. Leased property was purchased 20yrs ago and depreciation is charged on
straight line. All amortisation and depreciation of non-current assets is charged to cost
of sales.
(iv) On 1 April 2021, Lubuto co issued a 5% K50 million convertible loan note at par.
Interest is payable annually in arears on 31 March each year. The loan note is
redeemable at par or convertible into equity shares at the option of the loan note
holders on 31 March 2024. The interest on an equivalent loan note without the
conversion rights would be 8% per annum. The present values of K1 received at the
end of each year, based on discount rates of 5% and 8% are:
5% 8%
End of year 1 0.95 0.93
2 0.91 0.86
3 0.86 0.79
(v) An equity dividend of 4ngwee per share was paid on 30 May 2021 and, after the
rights issue, a further dividend of 2 ngwee per share was paid on30th November 2021.
(vi) The balance on current tax represent represents the under/over provision of the tax
liability for the year ended 31st March 2021. A provision of K28 million is required
for current tax for the year ended 31st March 2022 and at this date the deferred tax
liability was assessed at K8.3 million.
Required
(a) Prepare the statement of profit or loss for Lubuto for the year ended 31st March 2022.
(12marks)
(b) Prepare the statement of financial position for; Lubuto for the year ended 31 March 2022,
Answers
Statement of profit or loss for Lubuto for the year ended 31st March 2022:
Revenue K490,000
Less: Commission to Francis (1.5M) [Note (i)]
Net revenue 488,500
Cost of sales 306,100
Opening inventory 75,000
Add: Purchases 290,600
Less: Closing inventory (61,000)
Gross profit 182,400
:
Administration expenses (36,800)
Distribution costs (33,500)
Depreciation - Plant and Equipment (21,719) [Note (iii)]
Depreciation - Right of use asset (5,000)
Amortisation - Right of use - leased property (14,500)
Bank interest (900)
Loan note interest and dividends paid (13,380) [Note (iv)]
Profit before tax 57,601
How to explain the statement of financial positionStatement of financial position for Lubuto for the year ended 31st March 2022:
Explanation:
Non-current assets:
Plant and equipment at cost 155,500
Less: Accumulated depreciation (43,500)
Net plant and equipment 112,000
Right of use asset 20,000 [Note (iii)]
Right of use - leased property at cost 100,000
Less: Accumulated amortisation (14,500)
Net right of use - leased property 85,500
5% convertible loan note 50,000 [Note (iv)]
Total non-current assets 267,000
Current assets:
Inventories 61,000
Trade receivables 63,000
Bank 5,500
Total current assets 129,500
Total assets 396,500
Learn more about profit and loss on;
https://brainly.com/question/26483369
#SPJ1
Select the correct answer.
Which of the following careers is NOT part of the career areas discussed in this unit?
A. Preschool teacher
B. Special education teacher working with two year olds
C. Elementary school teacher
D. School social worker
Answers
Calculating Cost of Debt For the firm in the previous problem, suppose the book value of the debt issue is $35 million. In addition, the company has a second debt issue on the market, a zero coupon bond with 12 years left to maturity; the book value of this issue is $80 million and the bonds sell for 61 percent of par. What is the company’s total book value of debt? The total market value? What is your best estimate of the aftertax cost of debt now?
Answers
The best estimate of the aftertax cost of debt for the firm is 3.47% in the given case.
To calculate the total book value of debt, we sum the book values of both debt issues:
Total book value of debt = Book value of debt issue 1 + Book value of debt issue 2
Total book value of debt = $35 million + $80 million
Total book value of debt = $115 million
To calculate the market value of the zero coupon bond, we need to find 61% of the face value:
Market value of zero coupon bond = 0.61 x Face value of zero coupon bond
Market value of zero coupon bond = 0.61 x $80 million
Market value of zero coupon bond = $48.8 million
The total market value of debt is the sum of the market values of both debt issues:
Total market value of debt = Market value of debt issue 1 + Market value of debt issue 2
Total market value of debt = $35 million + $48.8 million
Total market value of debt = $83.8 million
To find the aftertax cost of debt, we need to first calculate the yield to maturity on the zero coupon bond. We know that the bond has 12 years left to maturity and sells for 61% of par, so we can use the following formula to find the yield to maturity:
61% of face value = $48.8 million
Par value = $100 million
Years to maturity = 12
Yield to maturity = ?
Solving for the yield to maturity using a financial calculator or spreadsheet, we get:
Yield to maturity = 4.83%
Next, we need to find the aftertax cost of debt for both debt issues separately and then weight them by their respective market values. We are given that the company's tax rate is 40%.
For the first debt issue, we are given that the coupon rate is 8% and that the bonds are currently selling at par, so the beforetax cost of debt is 8%. The aftertax cost of debt is:
Aftertax cost of debt issue 1 = Beforetax cost of debt issue 1 x (1 - Tax rate)
Aftertax cost of debt issue 1 = 8% x (1 - 40%)
Aftertax cost of debt issue 1 = 4.8%
For the zero coupon bond, we already calculated the yield to maturity, which is the beforetax cost of debt. The aftertax cost of debt is:
Aftertax cost of debt issue 2 = Beforetax cost of debt issue 2 x (1 - Tax rate)
Aftertax cost of debt issue 2 = 4.83% x (1 - 40%)
Aftertax cost of debt issue 2 = 2.90%
Finally, we can weight the aftertax costs of debt by their respective market values to get the overall aftertax cost of debt:
Overall aftertax cost of debt = (Market value of debt issue 1 / Total market value of debt) x Aftertax cost of debt issue 1 + (Market value of debt issue 2 / Total market value of debt) x Aftertax cost of debt issue 2
Plugging in the numbers, we get:
Overall aftertax cost of debt = ($35 million / $83.8 million) x 4.8% + ($48.8 million / $83.8 million) x 2.90%
Overall aftertax cost of debt = 3.47%
To know more about debt here
https://brainly.com/question/1957305
#SPJ1
Which of the following is NOT a feature in the Formulas menu of the Macabacus Excel add-in? Review Later Summary Statistics Error Wrap Quick CAGR Formula Flow
Answers
The following that is NOT a feature in the Formulas menu of the Macabacus Excel add-in is Formula Flow. This is further explained below.
What is Formula Flow?Generally, The formula for the volumetric flow rate is as follows: Vf = A*v, where A is the cross-sectional area and v is the flow velocity.
In conclusion, Macabacus is an Excel add-in that has many useful features, but Formula Flow is not one of them.
Read more about Formula Flow
https://brainly.com/question/11814436
#SPJ1
The graphs illustrate an initial equilibrium for the economy. Suppose that the stock market broadly increases.
Use the graphs to show the new positions of aggregate demand (AD), short-run aggregate supply (SRAS), and long-run
aggregate supply (LRAS) in both the short run and the long run, as well as the short-run and long-run equilibriums resulting
from this change. Then, indicate what happens to the price level and real GDP (or aggregate output) in the short run and in the
long run.
Answers
Since the stock market increases broadly, this has the effect of expanding the aggregate demand thus, shifting it rightwards. This consequently leads to an increase in price level and real GDP. See the Short Run Effect Graph.
In the Long Run, given that demand shifted to the right, this created an imbalance between demand and expected price levels.
All things being, equal the laws of demand and supply as it affects price trigger an upward adjustment in price hence creating a new equilibrium point. See the Long Run Effect Graph.
What is aggregate demand?Aggregate demand, also known as domestic final demand in macroeconomics, is the entire demand for final products and services in an economy at any particular time.
It is frequently referred to as effective demand, albeit this phrase is differentiated at times. This is a country's demand for its gross domestic output.
Aggregate demand is estimated by combining consumer expenditure, government and business investment spending, and net imports and exports. AD = C + I + G + Nx is the equation that represents it.
Learn more about Short Run and Long Run in Economics:
https://brainly.com/question/13029724
#SPJ1


A security is currently selling for $8,000 and promises to pay $1,000 annually for the next 9 years, and $1,500 annually in the 3 years thereafter with all payments occurring at the end of each year. If your required rate of return is 7% p.a., should you buy this security and why?
Answers
Answer:
Yes, because the return is greater than 7%
Explanation:
You will get NPV = 656.41. Because the NPV > 0, the cash inflows are greater than the cost (i.e., thecash outflows). So, again, this is a good investment.
A security providing such returns shall not be bought if the required rate of return is 7%.
What is required rate of return?The expected percentage of returns over an investment at the time of making such investment is known as the required rate of return. In the given case, the required rate of return is 7%.
The actual returns earned over making such purchase of the security for $8000 and getting returns of $4500 is calculated around a return of 4.5%.
Hence, the security should not be bought is the rate of return required is 7% over the investments made.
Learn more about required rate of return here:
https://brainly.com/question/13987385
#SPJ2
Which two statements about financial service companies are true?
Answers
Answer:
b. and d.
Explanation:
On January 1, 2021, the Shagri Company began construction on a new manufacturing facility for its own use. The building was completed in 2022. The only interest-bearing debt the company had outstanding during 2021 was long-term bonds with a book value of $11,000,000 and an effective interest rate of 8%. Construction expenditures incurred during 2021 were as follows:
January 1 $600,000
March 1 660,000
July 31 540,000
September 30 700,000
December 31 400,000
Required:
Calculate the amount of interest capitalized for 2021.
Answers
Answer:
The amount of interest capitalized for 2021 is $124,000
Explanation:
First, we need to calculate the weighted expenditure by the time period it spent in the period.
The weighted expenditure calculation is made in the PDF file attached with this answer please find it.
Weights are calculated as follow
January 1 = 12/12 = 1
March 1 = 10/12 = 0.83
July 31 = 5/12 = 0.42
September 30 = 3/12 = 0.25
December 31 = 0/12 = 0
The amount of Interest capitalized is calculated as follow
Amount of Interest capitalized = Weighted average expenditure x Interest rate = $1,550,000 x 8% = $124,000
The process of allocating funds to projects and investments includes the following:
A. Analysis
B. Selection
C. Monitoring
D. Evaluating performance
Analyze or explain any three of the above.
Answers
The process of allocating funds to projects and investments involves several important steps, including analysis, selection, and monitoring. By following these steps, organizations can make informed decisions about where to invest their resources and ensure that their investments are delivering the expected returns.
The process of allocating funds to projects and investments involves several important steps, including analysis, selection, monitoring, and evaluating performance. Here are explanations of three of these steps:
Analysis: This step involves gathering and analyzing information about potential projects and investments to determine whether they are financially viable and aligned with the organization's goals and objectives. This includes conducting market research, analyzing financial statements and projections, assessing risks, and identifying potential barriers to success. The analysis phase helps decision-makers to make informed choices about which projects and investments to pursue.
Selection: Once potential projects and investments have been analyzed, the next step is to select the most promising ones. This involves using the information gathered during the analysis phase to compare options and choose the projects and investments that are most likely to provide the greatest returns on investment. The selection process may involve developing criteria for evaluating potential options, ranking them based on their financial potential, and weighing the costs and benefits of each option.
Monitoring: Once projects and investments have been selected and funded, it is important to monitor their progress and performance over time. This involves regularly reviewing financial and operational data to identify any potential issues or risks, and taking action to address them. Monitoring can help decision-makers to stay informed about the status of their investments, identify opportunities for improvement, and make adjustments to their funding strategies as needed.
for more question on investment visit:
https://brainly.com/question/29547577
#SPJ11
A country is angry at a neighboring country for creating too much water and
air pollution. It passes a law that forbids its citizens from doing any business
with the other country until that country cleans up the pollution. If the
pollution continues, there will be no trade between the countries.
This is an example of which type of trade barrier?
A. Tariffs
B. Embargoes
C. Subsidies
D. Quotas
Answers
The trade barrier which is displayed is called as Embargoes. Hence, Option B is the correct statement.
What do you mean by Embargoes?An embargo is a central authority order that restricts trade or alternates with a precise country, commonly due to political or financial problems.
An embargo is commonly created due to damaging political or financial occasions among nations. It is designed to isolate a rustic and create problems for its governing body, forcing it to behave on the difficulty that brought about the embargo.
Hence, Option B is the correct statement.
learn more about embargo here:
https://brainly.com/question/873934
#SPJ2
Equity capital is....
a. paid back within one year.
b. not a loan but a form of stock.
c. a loan from family.
d. paid back after five years.
Answers
Answer:
b. not a loan but a form of stock.
Explanation:
Capital can either be equity or debt capital. Debt capital refers to borrowed funds either from the banks or other lenders.
Equity capital is the owner's contribution to the business. It is what the shareholders of the business have given to the business as capital. Equity is not a loan, nor is it meant to be refunded. It represents the owner's investment in the business.
As an investor, what is the risk involved when investing in companies on the stock
exchange?
a. Investors can lose their existing shares if the value of the stock does not
increase within 90 days of purchase
b. Once they purchase a share, investors cannot sell them at a higher price
The price of stocks can decrease; for example, when the company
receives bad press
d. Investors are only at risk if the purchase a share when the stock price has
fallen
C.
Answers
Answer:d
Explanation:
The investor are only at risk if the purchase of a share when the stoc price has fallen
Use the adjusted trial balance for Stockton Company to answer the question that follows. Stockton Company Adjusted Trial Balance December 31 Cash 6,794 Accounts Receivable 2,730 Prepaid Expenses 792 Equipment 13,043 Accumulated Depreciation 1,480 Accounts Payable 1,629 Notes Payable 4,364 Common Stock 1,000 Retained Earnings 11,996 Dividends 641 Fees Earned 7,100 Wages Expense 2,175 Rent Expense 702 Utilities Expense 363 Depreciation Expense 236 Miscellaneous Expense 93 27,569 27,569 Determine the net income (loss) for the period.
Answers
The Stockton Company's net income (loss) for the period is $3,531.
Net income = Total revenue - Total Expenses= $3,531 ($7,100 - $3,569)
Data and Calculations:
Fees Earned $7,100
Total Expenses:
Wages Expense $2,175
Rent Expense 702
Utilities Expense 363
Depreciation Expense 236
Miscellaneous Expense 93
Total Expenses = $3,569
Thus, the Stockton Company's net income for the period is $3,531.
Related link: brainly.com/question/14550470
Calculate the NPV and IRR for this project and decide if it should be undertaken.
A U.S. based company wants to establish a subsidiary in Japan, use the following information.
-The initial investment is 100 million YEN
-The project is expected to last 5 years with a salvage value of 30 million YEN
-The prices, demand, and variable costs are as follows:
Year Price in YEN Demand (units) VC/unit in YEN
1 200 600,000 180
2 210 700,000 190
3 220 800,000 200
4 220 800,000 210
5 200 500,000 210
-Fixed costs in YEN are expected to be 10 million / year
-The Spot exchange rate for Yen is (direct quote = 1 USD = 136.33 JYP and indirect quote = 1 JPY = 0.0073 USD
-The YEN is expected to behave as follows:
Year 1: Loss of 3%
Year 2: Additional loss of 3%
Year 3: Same as year 2
Year 4: Gain of 3%
Year 5: Same as year 4
-The company expects the NWC requirements as follows:
Initial NWC Investment of 30 million YEN
Annual NWC Requirements = 0 million YEN
Japan will impose a 25% tax on income and a 10% tax on remitted funds
There are no U.S. taxes
All Cash flows will be sent to the U.SA parent company at the end of the year
Depreciation expense is 10 years using the straight-line method
-The Required Rate of return on the project is 15%
SHOW ALL CALCULATIONS/FORMULAS and using Excel is preferred :)
Answers
Answer:
To calculate the NPV and IRR for this project, we need to first calculate the cash flows for each year using the given information.
Year 1:
Sales revenue = 200 x 600,000 = 120,000,000 YEN
Variable costs = 180 x 600,000 = 108,000,000 YEN
Fixed costs = 10,000,000 YEN
Depreciation = (100,000,000 - 30,000,000) / 10 = 7,000,000 YEN
Taxable income = 120,000,000 - 108,000,000 - 10,000,000 - 7,000,000 = -5,000,000 YEN
Tax expense = 0.25 x (-5,000,000) = -1,250,000 YEN
Net income after tax = -5,000,000 - 1,250,000 = -6,250,000 YEN
Operating cash flow = -6,250,000 + 7,000,000 = 750,000 YEN
Net cash flow = 750,000 / 136.33 = $5,504.26
Year 2:
Sales revenue = 210 x 700,000 = 147,000,000 YEN
Variable costs = 190 x 700,000 = 133,000,000 YEN
Fixed costs = 10,000,000 YEN
Depreciation = 7,000,000 YEN
Taxable income = 147,000,000 - 133,000,000 - 10,000,000 - 7,000,000 = -3,000,000 YEN
Tax expense = 0.25 x (-3,000,000) = -750,000 YEN
Net income after tax = -3,000,000 - 750,000 = -3,750,000 YEN
Operating cash flow = -3,750,000 + 7,000,000 = 3,250,000 YEN
Net cash flow = 3,250,000 / (136.33 x 1.03) = $23,977.35
Year 3:
Sales revenue = 220 x 800,000 = 176,000,000 YEN
Variable costs = 200 x 800,000 = 160,000,000 YEN
Fixed costs = 10,000,000 YEN
Depreciation = 7,000,000 YEN
Taxable income = 176,000,000 - 160,000,000 - 10,000,000 - 7,000,000 = -1,000,000 YEN
Tax expense = 0.25 x (-1,000,000) = -250,000 YEN
Net income after tax = -1,000,000 - 250,000 = -1,250,000 YEN
Operating cash flow = -1,250,000 + 7,000,000 = 5,750,000 YEN
Net cash flow = 5,750,000 / (136.33 x 1.03 x 1.03) = $42,373.99
Year 4:
Sales revenue = 220 x 800,000 = 176,000,000 YEN
Variable costs = 210 x 800,000 = 168,000,000 YEN
Fixed costs = 10,000,000 YEN
Depreciation = 7,000,000 YEN
Taxable income = 176,000
Explanation:
Gti two employees are paid weekly. As of the end if the year, two days salaries have accrued at the rate of 180 per day per per employee
Answers
The adjusting journal entry for GTI is as follows:
Adjusting Journal Entry:Date Account Titles Debit Credit
Dec. 31 Wages Expenses $720
Wages Payable $720
To accrue the two days' wages owed to two employees.What is an adjusting journal entry?An adjusting journal entry is a period-end journal entry to accrue expenses that have been incurred but not paid in cash.
Adjusting journal entries can also be used to record Depreciation Expenses, Earned and Unearned Revenues, Prepayments, and correction of accounting errors.
Transaction Analysis:Wages Expenses $720 Wages Payable $720
Two Employees' wages for two days = $720 (180 x 2 x 2)
Thus, the Wages Expenses account will be debited, while the Wages Payable account will be credited to show that GTI is owing two employee wages for 2 days.
Learn more about adjusting journal entries at https://brainly.com/question/13035559
#SPJ1
Question Completion:Prepare the adjusting journal entry to record the accrual.
Year
2016
2017
2018
2019
Cow
P
$300
$350
$370
$380
Q
1000
1050
1100
1200
Bicycle
P
$120
$130
$140
$150
Q
1200
1300
1500
1600
1. Calculate nominal GDP for each year
2. Calculate real GDP for each year
3. Calculate GDP deflator and inflation rate
Answers
Consumer sentiment suddenly crashes below early-pandemic levels in the US #accelerationism
A rational decision maker
Answers
Answer:yes
Explanation:because yes
Sergei asks his career counselor why the average salary for a human resources manager is so much higher than the average salaries for other careers. What is the BEST possible response?
A.
The job of human resources manager requires advanced math skills.
B.
This job usually requires people to make split-second decisions.
C.
This job usually requires a college degree plus years of experience.
D.
The job of human resources manager is an entry-level position.
Answers
The correct answer is The BEST possible response to Sergei's question about the higher average salary for a human resources manager is option C, which is that this job usually requires a college degree plus years of experience.
Human resources managers are responsible for overseeing personnel operations, including recruitment, hiring, training, and compensation. This is a specialized and important role that requires a combination of business acumen, communication skills, and knowledge of employment laws and regulations.Typically, human resources managers are required to have a college degree in a relevant field such as human resources, business, or psychology, and several years of experience in the field. This level of education and experience is necessary to develop the skills and knowledge required to excel in this role.
To learn more about manager click the link below:
brainly.com/question/29023210
#SPJ1
The amount you pay each time you visit a health care provider or have a prescription filled is called a
Answers
The amount that a person pays when they visit health care providers or have their prescription filled is a Copayment.
What is a copayment?A copayment refers to the amount that people pay to their healthcare providers out of their pocket when they go to get services such as having their prescriptions filled.
Copayments are usually fixed amounts that depend on the kind of care you receive from your healthcare provider.
In conclusion, that amount that is paid by a person when they visit a health care provider or go to fill up their prescription is a Copayment.
Find out more on copayments at https://brainly.com/question/17373826
#SPJ1
The information of manufacturing cost of product A and products B in
THANH company in 200N as follows:
Production cost per unit (S)
Product A
Materials 200
Wages 100
Fixed overhead 350
Variable overhead 150
Profit 200
Selling price 1000
Output per week 200
Product B
Materials 150
Wages 200
Fixed overhead 100
Variable overhead 200
Profit 350
Selling price 1000
Output per week 100
Required:
Comments on the relative profitability of product A and products B in THANH company in 200N
Answers
Manufacturing cost of both product A and product B have a profit margin of $0 per unit.
To assess the relative profitability of product A and product B in the THANH company in 200N, we need to compare their profit margins. Profit margin is calculated by subtracting the production cost per unit from the selling price per unit.
Let's calculate the profit margins for both products:
Product A:
Selling price per unit: $1000
Production cost per unit: $200 (Materials) + $100 (Wages) + $350 (Fixed overhead) + $150 (Variable overhead) + $200 (Profit) = $1000
Profit margin per unit = Selling price per unit - Production cost per unit = $1000 - $1000 = $0
Product B:
Selling price per unit: $1000
Production cost per unit: $150 (Materials) + $200 (Wages) + $100 (Fixed overhead) + $200 (Variable overhead) + $350 (Profit) = $1000
Profit margin per unit = Selling price per unit - Production cost per unit = $1000 - $1000 = $0
From the calculations, both product A and product B have a profit margin of $0 per unit.
Based solely on the profit margins, it appears that neither product A nor product B is profitable for the THANH company in 200N. However, it's important to note that this analysis only considers the production cost per unit and does not take into account other factors such as demand, market conditions, or overall company profitability.
for similar questions on manufacturing cost.
https://brainly.com/question/13767214
#SPJ8