Answers
Answer:
The frequency of the waves depends on the distance between wave fronts - considering a front as a maximum disturbance of the wave
(Consider the waves emitted by an organ pipe: condensation and rarefactions)
The waves themselves are a fixed distance apart -
as one moves towards the source the waves received will be closer together (higher frequency)
So if the frequency received increases, the distance between the source and the observer must be decreasing
Related Questions
A pendulum with a mass of 4.0 kg is released from a height of 2.9 cm above the height of its resting position. How fast will the pendulum be moving when it passes through the lowest point of its swing?
Answers
The pendulum will be moving at approximately 0.754 m/s when it passes through the lowest point of its swing.
To determine the speed of the pendulum when it passes through the lowest point of its swing, we can use the principle of conservation of mechanical energy.
At the highest point (2.9 cm above the resting position), the pendulum has gravitational potential energy. As it swings down, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, given by the equation:
Potential Energy (PE) = Kinetic Energy (KE)
The highest point's potential energy is given by:
PE = mgh
Where:
m = pendulum mass (4.0 kg).
g = acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s^2)
h = height above the resting position (2.9 cm = 0.029 m)
Substituting the values, we have:
PE = 4.0 kg * 9.8 m/s^2 * 0.029 m = 1.1356 J
Since energy is conserved, this potential energy will be completely converted into kinetic energy at the lowest point. Thus, the kinetic energy is also 1.1356 J:
KE = 1.1356 J
The following equation gives the kinetic energy:
KE = (1/2)mv^2
Where:
m = pendulum mass (4.0 kg).
v = velocity of the pendulum at the lowest point
Rearranging the equation to solve for v:
v^2 = (2KE) / m
v^2 = (2 * 1.1356 J) / 4.0 kg
v^2 = 0.5678 m^2/s^2
Taking the square root of both sides results in the following:
v ≈ 0.754 m/s
Therefore, the pendulum will be moving at approximately 0.754 m/s when it passes through the lowest point of its swing.
For more such questions on pendulum, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/26449711
#SPJ8
Frequency= Wavelength = 502 km Speed= 100 m/s
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Wavelength = 100m. Speed = V. 2.) Frequency = 20 Hz. Wavelength = 200 m. Speed = ... 2=1.7m. F=Y/2 f=2×10. 5.) Wavelength = 502 km. Speed= 100 m/s.
If a car has a suspension system with a force constant of 5.00x104 N/m, how much energy must the car's shocks remove to dampen an oscillation starting with a maximum displacement of 0.0750 m
Answers
Answer: 140.625
Explanation: Because energy gained due to damped motion and needs to be absorbed
Question 1
An 8 kg basketball is dropped from a height of 10 m. Calculate the Gravitational Potential Energy of the ball.
Question 1 options:
400 Joules
784 Joules
80 Joules
18 Joules
Question 2
A 50 kg dog runs with a speed of 20 m/s. Calculate the Kinetic Energy of the dog.
Question 2 options:
10,000 Joules
9,800 Joules
70 Joules
1000 Joules
Question 3
The Kinetic Energy of a skydiver is 100,000 Joules and the Gravitational Potential Energy of the same skydiver is 78,000 Joules. Calculate the Total Mechanical Energy of the Skydiver.
Question 3 options:
178,000 Joules
22,000 Joules
100,000 Joules
78,000 Joules
Answers
Answer:
For 1, it's 784
For 2, it's 10,000
For 3, it's 178,000
Explanation:
I have taken the K12 quiz :)
Happy Spooky Month Everyone!! Stay safe!
(1) The Gravitational Potential Energy of the ball is 784 J.
(2) The Kinetic Energy of the dog is 10,000 J.
(3) The total Mechanical Energy of the Skydiver is 78,000 J.
(1)
The Gravitational Potential Energy of the ball is the energy possessed by the ball due to its height above the ground.
P.E = mgh
P.E = 8 x 9.8 x 10
P.E = 784 J
(2)
The Kinetic Energy of the dog is possessed by the dog due to its motion.
K.E = ¹/₂mv²
K.E = 0.5 x 50 x 20²
K.E = 10,000 J
(3)
The total Mechanical Energy of the Skydiver is the sum of the potential energy and the kinetic energy.
M.A = P.E + K.E
M.A = 78,000 J + 100,000 J
M.A = 178,000 J
Learn more here:https://brainly.com/question/13818076
Bài 1. Một vật được đặt trên một mặt phẳng nghiêng hợp với mặt phẳng nằm ngang một góc = 300.
Answers
Answer:
3q
Explanation:
Two 10-cm-diameter charged rings face each other, 23.0 cm apart. Both rings are charged to 40.0 nC . What is the electric field strength You may want to review (Pages 641 - 643) . For general problem-solving tips and strategies for this topic, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Charge on a Van De Graaff.
Answers
The strength of the electric field is 1.10×10^4 N/C.
The data is sent to us.
r = d/2 = 0.1/2 = 0.05 m, d = 10 cm = 0.1 m, and z = 17 cm = 0.17 m
Q = 40 nC = 40×10^-9 C
A) in the middle of the two circles
Since the electric fields created by the two rings are directed in opposite directions, there is no electric strength.
B) midway down the left ring
Electric strength is equal to the sum of the electric fields created by the left and right rings.
Electric strength is equal to E leftring + E rightring, which equals 0 plus kQz/(r2 + z2).
Electric strength = k×Q×z/(r^2 + z^2)^
Electric strength = 9×10^9×40×10^-9×0.17/(0.05^2 + 0.17^2)
Electric strength= 1.10×10^4 N/C
To know more about Electric strength visit : https://brainly.com/question/26199225
#SPJ1
Two cars collide head-on and stick together.
Car A, with a mass of 2000 kg, was initially
moving at a velocity of 10 m/s to the east. Car
B, with an unknown mass, was initially at rest.
After the collision, both cars move together at
a velocity of 5 m/s to the west. What is the
mass of Car B?
OF
Answers
The mass of Car B is -6000 kg.
To solve this problem, we can apply the principle of conservation of momentum, which states that the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision.
Therefore, we can write the equation for the conservation of momentum as:
(mass of Car A * velocity of Car A) + (mass of Car B * velocity of Car B) = (mass of Car A + mass of Car B) * velocity after collision
Let's substitute the given values into the equation:
(2000 kg * 10 m/s) + (mass of Car B * 0 m/s) = (2000 kg + mass of Car B) * (-5 m/s)
Simplifying the equation:
20000 kg*m/s = -5 m/s * (2000 kg + mass of Car B)
Dividing both sides by -5 m/s:
-4000 kg = 2000 kg + mass of Car B
Subtracting 2000 kg from both sides:
mass of Car B = -4000 kg - 2000 kg
mass of Car B = -6000 kg
know more about momentum here:
https://brainly.com/question/30487676
#SPJ8
27 1 point
A student has tested several types of wood for density. The best way of presenting this information graphically would be to use which item?
Scatterplot
Pie Chart
Line Graph
Bar Graph
Previous
Search
Answers
The best way of presenting the information on density graphically would be to use a D, bar graph.
What is a bar graph?A bar graph is a type of chart that uses rectangular bars to represent data. The bars are typically arranged in columns, with the independent variable (in this case, the type of wood) on the x-axis and the dependent variable (in this case, the density) on the y-axis.
A bar graph is the best choice for this data because it allows for easy comparison of density of different types of wood. We can see at a glance which type of wood is the densest and which type of wood is the least dense.
Find out more on Bar Graph here: https://brainly.com/question/25196929
#SPJ1
Write two artificial and two natural source of light.
Answers
Two natural sources of light: the sun and the stars
Two artificial sources of light: light bulb and torches
Answer:
Natural lights: Sunlight, Moonlight, or Lightning
Artificial: Light bulb, Candles, or a lighter/matches
Explanation:
while spinning in a centrifuge a 70.0 kg astronaut experiences an acceleration of 5.00 g, or five times the acceleration due to gravity on the earth. what is the centripetal force acting on her
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
70.0(5.00)(9.81) = 3,433.5 = 3430 N
To solve this we must be knowing each and every concept related to centripetal force and its calculations. Therefore, the centripetal force acting on her is 3430 N.
What is centripetal force?The term centripetal relates to a propensity to gravitate toward the center. Centripetal refers to moving in the direction of the center. The force that maintains an item moving in a circular direction and helps it stay on the path is referred to as centripetal force.
Furthermore, centrifugal force is indeed the tendency of things to deviate from a circular route and fly in a straight line. People frequently confuse centripetal force with centrifugal force.
Mathematically,
F = m a
= 70 acceleration
= 70 × 5 × 9.81
= 3430 N
Therefore, the centripetal force acting on her is 3430 N.
To know more about centripetal force, here:
https://brainly.com/question/14249440
#SPJ5
A car traveling at 11.6 meters per second crashes into a barrier and stops in 0.287 meters. What force must be exerted on a child of mass 21.2 kilograms to stop him or her in the same time as the car? Answer must be in 3 significant digits.
Answers
The equation to obtain the final speed of car is,
\(v^2=u^2+2as\)Substitute the known values,
\(\begin{gathered} (0m/s)^2=(11.6m/s)^2+2a(0.287\text{ m)} \\ a=\frac{-134.56m^2s^{-2}}{2(0.287\text{ m)}} \\ \approx-234.4m/s^2 \end{gathered}\)The negative sign of acceleration indicates that the car is deaccelerating.
The force required to stop the car is,
\(F=ma\)Substitute the magnitude of known values,
\(\begin{gathered} F=(21.2kg)(234.4m/s^2)(\frac{1\text{ N}}{1kgm/s^2}) \\ =4969.28\text{ N} \\ \approx4970\text{ N} \end{gathered}\)Thus, the force required to stop the car is 4970 N.
The rainbow of visible colors in the electromagnetic spectrum varies continuously from the longest wavelengths (the reddest colors) to the shortest wavelengths (the deepest violet colors) our eyes can detect. Wavelengths near 655 nm are perceived as red. Those near 515 nm are green and those near 475 nm are blue. Calculate the frequency of light (in Hz) with a wavelength of 655 nm, 515 nm, and 475 nm.
HINT
(a)
655 nm
Hz
(b)
515 nm
Hz
(c)
475 nm
Hz

Answers
Answer:
The frequency of light can be calculated using the formula:
`c = λv`
Where `c` is the speed of light in a vacuum, `λ` is the wavelength of light, and `v` is the frequency of light.
The speed of light in a vacuum is `3.00 × 10^8 m/s`.
To convert the wavelength from nanometers to meters, we need to divide by `1 × 10^9`.
Thus, the frequency of light with a wavelength of 655 nm is:
`v = c/λ`
`v = (3.00 × 10^8 m/s)/(655 × 10^-9 m)`
`v = 4.58 × 10^14 Hz`
Therefore, the frequency of light with a wavelength of 655 nm is `4.58 × 10^14 Hz`.
Similarly, the frequency of light with a wavelength of 515 nm is:
`v = c/λ`
`v = (3.00 × 10^8 m/s)/(515 × 10^-9 m)`
`v = 5.83 × 10^14 Hz`
Therefore, the frequency of light with a wavelength of 515 nm is `5.83 × 10^14 Hz`.
Finally, the frequency of light with a wavelength of 475 nm is:
`v = c/λ`
`v = (3.00 × 10^8 m/s)/(475 × 10^-9 m)`
`v = 6.32 × 10^14 Hz`
Therefore, the frequency of light with a wavelength of 475 nm is `6.32 × 10^14 Hz`.
So, the frequency of light with a wavelength of 655 nm is `4.58 × 10^14 Hz`, the frequency of light with a wavelength of 515 nm is `5.83 × 10^14 Hz` and the frequency of light with a wavelength of 475 nm is `6.32 × 10^14 Hz`.
You have to lift a 15 kg object. What is your output force?
Using a lever, you push down 20 N to lift a 10 kg object.
A) Find the output force.
B) What is the input force?
C) How much does the ramp multiply your force?
You push with 10 N up a ramp to move a 40 N object to the top
of a table. By how much does the ramp multiply your force?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
A) The output force required to lift a 15 kg object would be equal to the weight of the object, which is given by:
Output force = Weight of object = m * g
where m is the mass of the object and g is the acceleration due to gravity. Assuming that g is equal to 9.81 m/s^2, we have:
Output force = 15 kg * 9.81 m/s^2 = 147.15 N
Therefore, the output force required to lift a 15 kg object would be 147.15 N.
B) In this case, the input force is the force that you are pushing down with the lever, which is given as 20 N.
C) The mechanical advantage of the ramp is given by the ratio of the output force to the input force. In this case, the output force is the weight of the object (40 N) and the input force is the force that you are pushing with (10 N). Therefore, the mechanical advantage of the ramp would be:
Mechanical advantage = Output force / Input force = 40 N / 10 N = 4
So, the ramp multiplies your force by a factor of 4.
Note that in all of these calculations, we have assumed that the system is ideal and that there are no losses due to friction or other factors. In practice, these losses will reduce the mechanical advantage of the system and make it more difficult to lift or move objects.
jpopwgtxfp give atleast 2 situations,in which you would store the data on cloud storage
Answers
Disaster recovery and cooperation are both benefited by cloud storage. It makes file sharing simple and guarantees that data is backed up and retrievable in the event of loss or damage.
What are the two benefits of keeping all of your data in the cloud?Your documents and data are kept in a safe data centre off-site by a cloud provider. You are no longer required to update software, maintain the servers, or make sure the hardware is working properly.
What kinds of information can be stored in the cloud?To store data, including files, business data, videos, or photographs, cloud storage uses remote servers. Users use an internet connection to upload data to servers, where it is stored on a virtual machine on a physical server.
To know more about retrievable visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/7185731
#SPJ9
A ball falls from height of 19.5 m, hits the floor, and rebounds vertically upward to height of 15.0 m. Assume that m ball = 0.215 kg.(a)What is the impulse (in kg · m/s) delivered to the ball by the floor?magnitude _____kg · m/sdirection _____(b)If the ball is in contact with the floor for 0.0300 seconds, what is the average force (in N) the floor exerts on the ball?magnitude _____Ndirection _____
Answers
The magnitude of the average force exerted by the floor on the ball during the collision is 215 N, and the direction is upward.
What is Potential Energy?
Potential energy is the energy that an object possesses due to its position or configuration relative to other objects, or due to the configuration of its internal components. It is a form of energy that is associated with the forces that act on an object, such as gravity, electric forces, and magnetic forces.
(a) To determine the impulse delivered to the ball by the floor, we can use the principle of conservation of energy to relate the ball's potential energy at the initial height to its potential energy at the rebound height, taking into account the loss of energy due to the collision with the floor. We can then use the impulse-momentum theorem to relate the impulse to the change in momentum of the ball during the collision.
The initial potential energy of the ball is given by:
PEi = mgh = (0.215 kg)(9.81 m/s^2)(19.5 m) = 41.6 J
At the rebound height, the potential energy is:
PEf = mgh = (0.215 kg)(9.81 m/s^2)(15.0 m) = 31.7 J
The loss of energy due to the collision is:
ΔPE = PEi - PEf = 9.9 J
This energy loss is due to both the work done by the force of gravity during the downward motion and the work done by the force of the floor during the upward motion. However, since the ball rebounds to a height that is less than its initial height, we know that the impulse delivered by the floor must be in the downward direction, opposite to the direction of the ball's motion during the collision.
Using the impulse-momentum theorem, we can write:
J = Δp = mΔv
where J is the impulse delivered by the floor, Δp is the change in momentum of the ball during the collision, and Δv is the change in velocity of the ball during the collision. Since the ball is moving downward before the collision and upward after the collision, we can write:
Δv = vf - vi = (15.0 m/s) - (-15.0 m/s) = 30.0 m/s
where vi is the initial velocity of the ball (before the collision) and vf is the final velocity of the ball (after the collision).
Thus, the impulse delivered to the ball by the floor is:
J = mΔv = (0.215 kg)(30.0 m/s) = 6.45 kg · m/s (downward)
So, the magnitude of the impulse delivered to the ball by the floor is 6.45 kg · m/s, and the direction is downward.
(b) To determine the average force exerted by the floor on the ball during the collision, we can use the definition of impulse as the product of force and time, and the fact that the ball is in contact with the floor for a known amount of time.
We know that the ball is in contact with the floor for 0.0300 seconds. Therefore, the average force exerted by the floor on the ball during the collision is:
Favg = J / Δt
where Δt is the time interval during which the impulse is delivered. In this case, Δt is equal to the contact time, which is 0.0300 seconds.
Thus, the average force exerted by the floor on the ball is:
Favg = J / Δt = (6.45 kg · m/s) / (0.0300 s) = 215 N (upward)
So, the magnitude of the average force exerted by the floor on the ball during the collision is 215 N, and the direction is upward.
Learn more about Potential Energy from given link
https://brainly.com/question/14427111
#SPJ1
what is the right optionA box is standing on a conveyor belt that is not in motion. At one point the belt starts moving with some acceleration. At that point the box starts moving too (without slipping). Which force is responsible for the acceleration of the box. a. The air resistance force. b. The force of the pull. c. The force of friction. d. The normal force.Answer only part B.

Answers
After reaching a certain velocity and the belt continues to move at the constant velocity(to the right).
Let's select the correct free body diagram for the box.
When the belt was at rest and the belt was placed, the horizontal velocity was zero.
When the belt started moving with some acceleration, the force of friction will try moving the box to the opposite direction.
But in this case, the belt has attained a certain velocity which makes it to start moving at a constant velocity. At constant velocity acceleration iz zero.
Since it is moving at a constant velocity, the net force is zero since there is no acceleration.
Therefore, there will be no acceleration, there is zero net force.
The free body diagram will be:
Therefore, the correct free body diagram is option b.
ANSWER:
B.

1.
Which of the following best explains the
relationship between molecules and atoms?
A
Atoms are molecules that have a charge.
B
Atoms have smaller parts, called
molecules.
С
Molecules are made up of two or more
atoms.
D
Molecules are atoms that have no mass.
Answers
Answer:
С . Molecules are made up of two or more atoms.
Explanation:
The relationship between molecules and atoms is that molecules are made up of two or more atoms.
Molecules are made up of atoms.
A molecule is the smallest particle of a substance element or compound capable of independent existence.
A molecule could be monoatomic, diatomic or polyatomic.
Monoatomic molecules are made up of one atom
Diatomic are made up of two different atoms
Polyatomic substances are made up of more than two kinds of atoms.
Two blocks are attached by a string as shown. The blocks are released from rest and
allowed to move freely. The sloped ramp angle is θ = 30⁰. Find the coefficient of friction
on the blocks (assume they have the same coefficient), assuming the blocks have the
same mass, and given that the blocks travel a distance of 0.50 m in a time of 0.935 s.
Answers
The coefficient of friction between the two blocks is 0.194.
The problem involves finding the coefficient of friction between two blocks of equal mass attached by a string that moves over a sloped ramp with an angle of 30 degrees. The blocks start from rest and are allowed to move freely. The distance traveled by the blocks is 0.50 m, and the time taken to travel this distance is 0.935 s. To solve the problem, we need to consider the forces acting on the system of blocks. The forces acting on the blocks are the gravitational force, the tension in the string, and the frictional force. As the blocks are moving up the ramp, the force of gravity is pulling them down. The tension in the string is pulling the blocks up the ramp. The frictional force is opposing the motion of the blocks and is acting in the opposite direction to the tension in the string.
To determine the coefficient of friction, we can use the equations of motion to find the acceleration of the blocks. Once we have the acceleration, we can use Newton's Second Law to find the net force acting on the blocks. We can then use the force of friction to find the coefficient of friction. Using the equations of motion, we can find the acceleration of the blocks:
a = 2d/t^2
where d is the distance traveled by the blocks and t is the time taken to travel the distance. Plugging in the given values, we get:
a = 2(0.50 m)/(0.935 s)^2 = 1.15 m/s^2
Next, we can use Newton's Second Law to find the net force acting on the blocks:
ΣF = ma
where ΣF is the sum of the forces acting on the blocks. Plugging in the known forces, we get:
T - mg sin θ - μmg cos θ = ma
where T is the tension in the string, m is the mass of the blocks, g is the acceleration due to gravity, θ is the angle of the ramp, and μ is the coefficient of friction.
We can simplify this equation by substituting mg sin θ for the component of the weight of the blocks that is acting down the ramp and mg cos θ for the component of the weight that is acting perpendicular to the ramp:
T - mg sin θ - μmg cos θ = ma
T - mg(1/2) - μmg(√3/2) = ma
We can also use the equation for the tension in the string:
T = 2mg sin θ
Substituting this into the equation for net force, we get:
2mg sin θ - mg(1/2) - μmg(√3/2) = ma
Simplifying and solving for μ, we get:
μ = (2gsinθ - a)/(2gcosθ)
Substituting the given values, we get:
μ = (2(9.81 m/s^2)sin 30° - 1.15 m/s^2)/(2(9.81 m/s^2)cos 30°) = 0.194
Therefore, the coefficient of friction between the two blocks is 0.194.
For such more questions on friction
https://brainly.com/question/14111192
#SPJ11
How much power does it take to lift a box with 350 newtons of force, 25 meters high, in 5 seconds? 70 watts 43,750 watts 2.8 watts 0 Points / 100
Answers
Answer:70 watts
Explanation: I took the test and got it correct
Which land feature is marked on the map by the $X$ ?
A. valley
B. plain
C. hill
D. mountain

Answers
Mountain is the land feature is marked on the map as x.
What features are shown on a topographic map?Simply described, a topographic map is a two-dimensional depiction of a piece of the earth's three-dimensional surface. Topographic maps are used to depict the land surface since topography is the form of the land surface. Since topographic maps depict how the earth's surface is shaped, they are useful tools in geologic investigations. By utilizing contour lines, cartographers are able to depict the three-dimensional land surface on a flat sheet of paper, making it possible to estimate both horizontal distances and vertical heights from a topographic map.A topographic map is easily recognized by the contour lines that depict the form of the Earth's surface.To unite locations of equal height on the land surface above or below a reference surface, such as mean sea level, contours are imaginary lines.Learn more about Topographic map refer to :
https://brainly.com/question/1026002
#SPJ1
An inclined plane of length 10m has a height of 6m. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the plane is 0.4.
Answers
Answer:
sorry but I don't know what exactly I'm supposed to calculate.you never actually stated it
In this experiment, you will use a track and a toy car to explore the concept of movement. You will measure the time it takes the car to travel certain distances, and then complete some calculations. In the space below, write a scientific question that you will answer by doing this experiment.
Answers
Answer: if weight affects how fast they go?
Explanation:
Answer:
How can we change the speed of a toy car on a racetrack to describe the car’s motion?
Explanation:
thats the sample respond
chandani was intrested in researching the plant by mixing things in soil she decided to test the effect of lime eurea table salt and compost on the soil the she put that soil then she bought a bucket of good soil from the garden and mixed it well she put that soil in 12 equal size vases she put two spoons urea each time two spoond of compost of table salt each in another three vases and two spoons of compost each each in three vases after that she planted the seed in all the vases everyday and measure the height of each plant daily and keep record then identify dependent ,indrpendent and controlled variable
Answers
The dependent, independent, and controlled variables are as follows:
1. Dependent - The effect of lime urea table salt and compost on the soil
2. Independent - The soil on which the elements are incorporated.
3. Controlled variable - The height of the plants.
What is the dependent, independent, and controlled variable?The dependent variable is that which is tested in the experiment and in this experiment, Chandani is testing the effect of lime, urea, table salt, and compost on the soil.
The independent variable is the altered element in the experiment and for this experiment, this is the soil that receives different additives. Finally, the controlled variable is that which remains constant and that is the height of each plant that the researcher checks.
Learn more about independent variables here:
https://brainly.com/question/82796
#SPJ1
1. A 75.0-kg box is falling with a constant velocity of -25.0 m/s. What
is the force of air resistance?
Answers
Treating the box as a particle, there are two forces acting on it in opposite directions: the box's weight mg pulling it downward and the resistive force of the air pointing upward.
The box is falling at a constant speed, so by Newton's second law we have
mg - r = 0
where mg = (75.0 kg) (9.80 m/s²) = 735 N is the weight of the box and r is the magnitude of air resistance. So we have
r = mg = 735 N
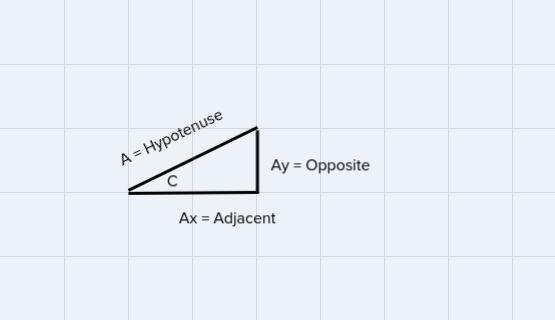
Vector A has a magnitude of 16.5 units and it points in a direction 340 counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. What are the x- and y- components of A?
Answers
We can find the components as:
\(\begin{gathered} A_x_{}=16.5\cos (340) \\ A_x=15.5 \\ ------------ \\ A_y=16.5\sin (340) \\ A_y=-5.64 \end{gathered}\)\(\begin{gathered} \sin (C)=\frac{opposite}{_{\text{ }}hypotenuse}=\frac{Ay}{A} \\ so\colon \\ _{\text{ }}if_{\text{ }}we_{\text{ }}solve_{\text{ }}for_{\text{ }}Ay \\ Ay=A\sin (C) \end{gathered}\)\(\begin{gathered} \cos (C)=\frac{adjacent}{_{\text{ }}hypotenuse}=\frac{Ax}{A} \\ so\colon \\ _{\text{ }}if_{\text{ }}we_{\text{ }}solve_{\text{ }}for_{\text{ }}Ax \\ Ax=A\cos (C) \end{gathered}\)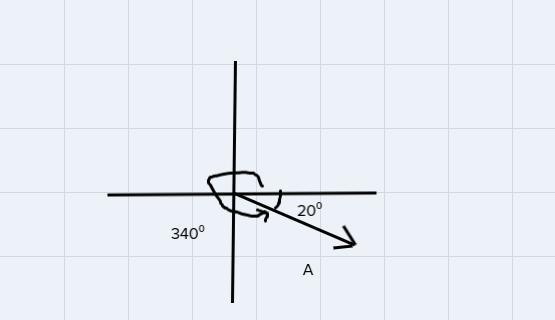
Forgetting takes place only in short-term memory. Please select the best answer from the choices provided T F
Answers
Answer:
false
Explanation:
Answer:
false
Explanation:
edge
6. A student travels 4.0 m east, 8.0 m south, 4.0 m west, and finally 8.0 m north. What is her
displacement?
What distance did she travel?
Answers
The student's path traces out a rectangle and she ends up at the same spot, so her displacement is 0 m.
On the other hand, she travels a total distance equal to the perimeter of that rectangle,
4.0 m + 8.0 m + 4.0 m + 8.0 m = 24 m
A motorcycle, travelling cast, starts from rest, moves in a straight line with a constant acceleration and covers a distance of 64 m in 4 s.Calculate a) Its acceleration b) Its final velocity c) At what time the motorcycle had covered half the total distance d) What distance the motorcycle had covered in half the total time.
Answers
The motorcycle had covered a distance of 16 meters in half the total time.
a) To calculate the acceleration, we can use the formula:
a = (v - u) / t
where a is the acceleration, v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity (which is 0 since the motorcycle starts from rest), and t is the time.
Given:
u = 0 m/s (initial velocity)
v = ? (final velocity)
t = 4 s (time)
s = 64 m (distance)
Using the equation of motion:
s = ut + 1/2at^2
We can rearrange the equation to solve for acceleration:
a = 2s / t^2
a = 2(64) / (4)^2
a = 128 / 16
a = 8 m/s^2
Therefore, the acceleration of the motorcycle is 8 m/s^2.
b) To find the final velocity, we can use the formula:
v = u + at
v = 0 + (8)(4)
v = 32 m/s
Therefore, the final velocity of the motorcycle is 32 m/s.
c) To determine the time at which the motorcycle had covered half the total distance, we divide the total distance by 2 and use the formula:
s = ut + 1/2at^2
32 = 0 + 1/2(8)t^2
16 = 4t^2
t^2 = 4
t = 2 s
Therefore, the motorcycle had covered half the total distance at 2 seconds.
d) To calculate the distance covered in half the total time, we use the formula:
s = ut + 1/2at^2
s = 0 + 1/2(8)(2)^2
s = 0 + 1/2(8)(4)
s = 0 + 16
s = 16 m
for such more questions distance
https://brainly.com/question/26550516
#SPJ11
Where does a body have more weight the poor at the eqator of the earth.
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Your body weighs more at the pole for two important reasons. Both have to do to the spin of the earth on its axis.
Because of its spin the earth is thicker around the equator than it is through the poles. This means that when you stand on the equator, you are farther away from the center of earth than you would be at the poles. As gravity decreases with the inverse of the square of distance, gravity will be weaker at the equator.
As you are also spinning with the earth, you will have a required centripetal acceleration and force to keep you attached to the ground, This force decreases the effect of gravity so again, you would weigh less at the equator.
Being a micro-manager is an example of using effective team building techniques
T or F
Answers
Answer:
TRUE
Explanation:
Answer:
True
Explanation: