Answers
Answer:
mining
Explanation:
because they use the most heavy duty machines
Related Questions
Estimate the constant rate of withdrawal (in m3 /s) from a 1375 ha reservoir in a month of 30 days during which the reservoir level dropped by 0.75 m in spite of an average inflow into the reservoir of 0.5 Mm3 /day. During the month, the average seepage loss from the reservoir was 2.5 cm, total precipitation on the reservoir was 18.5 cm and the total evaporation was 9.5 cm
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
1 ha = 10⁴ m²
1375 ha = 1375 x 10⁴ m² = 13.75 x 10⁶ m²
In flow in a month = .5 x 10⁶ x 30 m³ = 15 x 10⁶ m³
Net inflow after all loss = 18.5 - 9.5 - 2.5 cm = 6.5 cm = .065 m
Net inflow in volume = 13.75 x 10⁶ x .065 m³= .89375 x 10⁶ m³
Let Q be the withdrawal in m³
Q - 15 x 10⁶ - .89375 x 10⁶ = 13.75 x 10⁶ x .75 = 10.3125 x 10⁶
Q = 26.20 x 10⁶ m³
rate of withdrawal per second
= 26.20 x 10⁶ / 30 x 24 x 60 x 60
= 26.20 x 10⁶ / 2.592 x 10⁶
= 10.11 m³ / s
The rate of withdrawal is 10.11 cubic meter per second
Given-
Total reservoir is 1375 hectare. which is equal to \(1375\times 10^4\) meter square.
The average seepage loss from the reservoir is 2.85 cm or 0.0285 m.
Total precipitation on the reservoir is 18.5 cm or 0.185 m.
Total evaporation is 9.5 cm or 0.085 m.
The average inflow into the reservoir is \(0.5\times10^6\) cubic meter per day.
The total inflow in a month can be calculate is
\(=0.5\times 30=1500\times10^4\)
Net inflow is equal to the total precipitation on the reservoir subtract by all the losses.It can be represent as,
\(Q_{net}=0.185 - 0.095 - 0.025\)
\(Q_{net}=0.065\)
Total volume inflow is equal to the product of net inflow and total reservoir,
\(V_{net} =1375\times 10^4\times Q_{net}\)
\(V_{net} =1375\times 10^4\times 0.065\)
\(V_{net} =89.375\)
The constant rate of withdrawal in cubic meter can be calculated by adding the net inflow in a month, total volume inflow and the reservoir.
\(Q=1375\times 10^4\times 0.75+89.375\times 10^4+1500\times10^4\)
\(Q=2620\times10^4\)
For per second withdrawal,
\(Q=\dfrac{2620\times10^4}{30\times24\times60\times60}\)
\(Q=10.11\)
Hence, the rate of withdrawal is 10.11 cubic meter per second.
For more about the flow, follow the link below,
https://brainly.com/question/1410288
Describe what will happen (if anything )to mass and weight when you go to the moon.
Answers
Answer:
your mass and weight will be spilt in half
Explanation:
due to the low gravittalional pull of the moon
A current of 4.00 mA flows through a copper wire. The wire has an initial diameter of 4.00 mm which gradually tapers to a diameter of 1.00 mm. The wire length is
2.00 m and copper has a number density of 8.50 × 1028 m–3.
Find the change in mean drift velocity for electrons as they pass from one end of the wire to the other and therefore calculate the average acceleration of the electrons.
Answers
The change in mean drift velocity for electrons as they pass from one end of the wire to the other is 3.506 x 10⁻⁷ m/s and average acceleration of the electrons is 4.38 x 10⁻¹⁵ m/s².
The given parameters;
Current flowing in the wire, I = 4.00 mAInitial diameter of the wire, d₁ = 4 mm = 0.004 mFinal diameter of the wire, d₂ = 1 mm = 0.001 mLength of wire, L = 2.00 mDensity of electron in the copper, n = 8.5 x 10²⁸ /m³The initial area of the copper wire;
\(A_1 = \frac{\pi d^2}{4} = \frac{\pi \times (0.004)^2}{4} =1.257\times 10^{-5} \ m^2\)
The final area of the copper wire;
\(A_2 = \frac{\pi d^2}{4} = \frac{\pi (0.001)^2}{4} = 7.86\times 10^{-7} \ m^2\)
The initial drift velocity of the electrons is calculated as;
\(v_d_1 = \frac{I}{nqA_1} \\\\v_d_1 = \frac{4\times 10^{-3} }{8.5\times 10^{28} \times 1.6\times 10^{-19} \times 1.257\times 10^{-5}} \\\\v_d_1 = 2.34 \times 10^{-8} \ m/s\)
The final drift velocity of the electrons is calculated as;
\(v_d_2 = \frac{I}{nqA_2} \\\\v_d_2 = \frac{4\times 10^{-3} }{8.5\times 10^{28} \times 1.6\times 10^{-19} \times 7.86\times 10^{-7}} \\\\v_d_2 = 3.74\times 10^{-7} \ m/s\)
The change in the mean drift velocity is calculated as;
\(\Delta v = v_d_2 -v_d_1\\\\\Delta v = 3.74\times 10^{-7} \ m/s \ -\ 2.34 \times 10^{-8} \ m/s = 3.506\times 10^{-7} \ m/s\)
The time of motion of electrons for the initial wire diameter is calculated as;
\(t_1 = \frac{L}{v_d_1} \\\\t_1 = \frac{2}{2.34\times 10^{-8}} \\\\t_1 = 8.547\times 10^{7} \ s\)
The time of motion of electrons for the final wire diameter is calculated as;
\(t_2 = \frac{L}{v_d_1} \\\\t_2= \frac{2}{3.74 \times 10^{-7}} \\\\t_2 = 5.348 \times 10^{6} \ s\)
The average acceleration of the electrons is calculated as;
\(a = \frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t} \\\\a = \frac{3.506 \times 10^{-7} }{(8.547\times 10^7)- (5.348\times 10^6)} \\\\a = 4.38\times 10^{-15} \ m/s^2\)
Thus, the change in mean drift velocity for electrons as they pass from one end of the wire to the other is 3.506 x 10⁻⁷ m/s and average acceleration of the electrons is 4.38 x 10⁻¹⁵ m/s².
Learn more here: https://brainly.com/question/22406248
Answer:
The change in mean drift velocity for electrons as they pass from one end of the wire to the other is 3.506 x 10⁻⁷ m/s and average acceleration of the electrons is 4.38 x 10⁻¹⁵ m/s².
The given parameters;
Current flowing in the wire, I = 4.00 mA
Initial diameter of the wire, d₁ = 4 mm = 0.004 m
Final diameter of the wire, d₂ = 1 mm = 0.001 m
Length of wire, L = 2.00 m
Density of electron in the copper, n = 8.5 x 10²⁸ /m³
The initial area of the copper wire;
The final area of the copper wire;
The initial drift velocity of the electrons is calculated as;
The final drift velocity of the electrons is calculated as;
The change in the mean drift velocity is calculated as;
The time of motion of electrons for the initial wire diameter is calculated as;
The time of motion of electrons for the final wire diameter is calculated as;
The average acceleration of the electrons is calculated as;
Thus, the change in mean drift velocity for electrons as they pass from one end of the wire to the other is 3.506 x 10⁻⁷ m/s and average acceleration of the electrons is 4.38 x 10⁻¹⁵ m/s².
Learn more here: brainly.com/question/22406248
Explanation:
If the fundamental frequency produced by a guitar string is 400 Hz, what is the frequency of the second overtone?
Answers
Given data:
* The fundamental frequency of the guitar string is f = 400 Hz.
Solution:
The frequency of the second overtone is,
\(\begin{gathered} f^{\prime}=3f \\ f^{\prime}=3\times400 \\ f^{\prime}=1200\text{ Hz} \end{gathered}\)Thus, the frequency of the second overtone is 1200 Hz.
What’s the speed of light in ethyl alcohol?
Answers
The speed of light in a medium such as ethyl alcohol is generally less than the speed of light in a vacuum.
The speed of light in a medium can be determined using the equation:
v = c/n,
where v is the speed of light in the medium, c is the speed of light in a vacuum (approximately 299,792 kilometers per second), and n is the refractive index of the medium.
The refractive index of ethyl alcohol varies with the wavelength of light, but we can approximate it to a value of around 1.36 for visible light. Using this value, we can calculate the speed of light in ethyl alcohol:
v = c/n = (299,792 km/s) / 1.36 ≈ 220,163 km/s.
Therefore, the speed of light in ethyl alcohol is approximately 220,163 kilometers per second. It is important to note that this value is approximate and may vary slightly depending on the specific conditions and the wavelength of the light being considered.
For more such questions on speed of light ,
https://brainly.com/question/104425
#SPJ11
Help pls it’s urgent
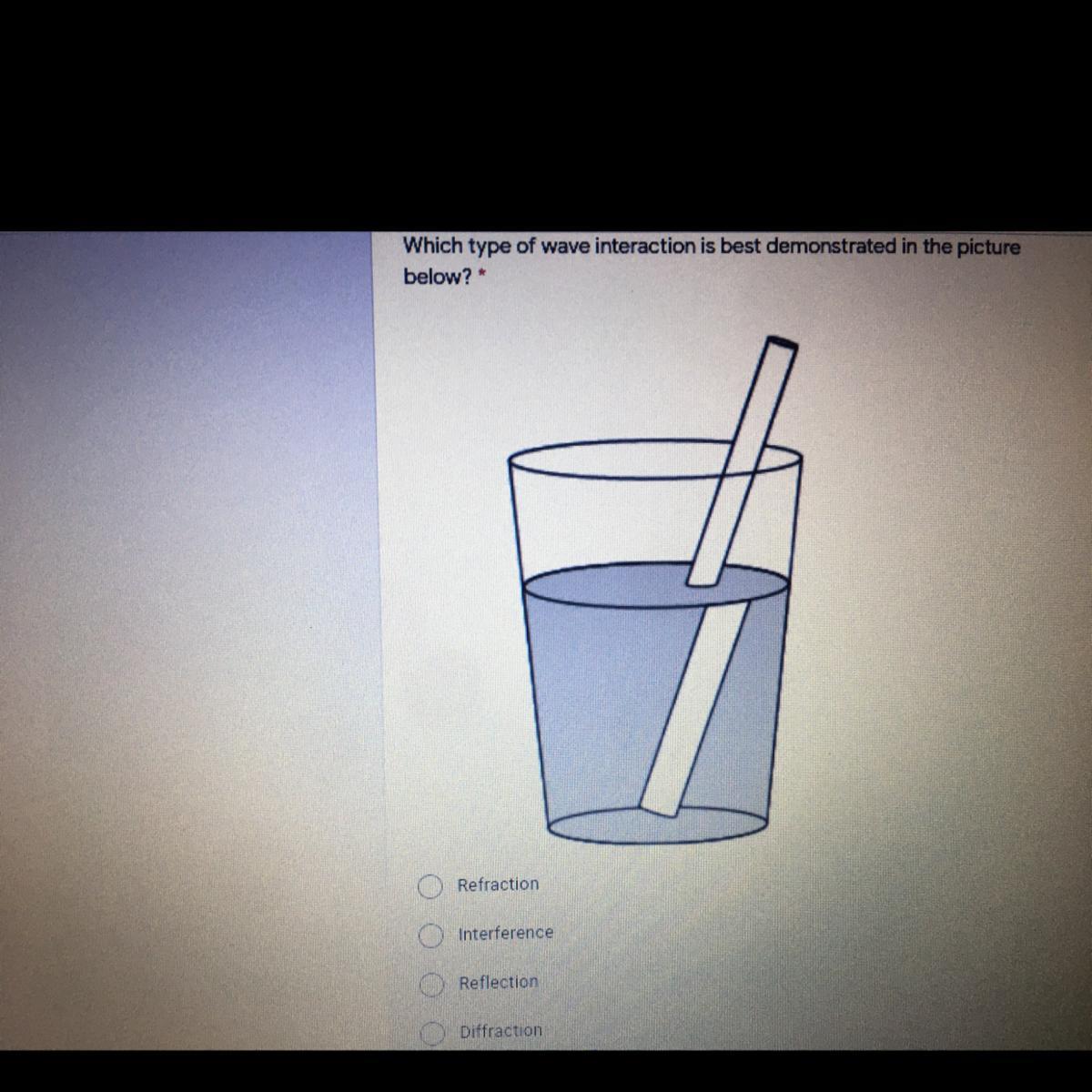
Answers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Refraction
explanation: refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium into another.
why does pure water increase in volume when heated
Answers
Answer:
Pure water increases in volume when heated due to the phenomenon of thermal expansion. When water is heated, the kinetic energy of its molecules increases, causing them to move faster and spread out. This increased molecular movement leads to an increase in the average distance between water molecules, resulting in an expansion of the water.
Explanation:
.......
A 10 kg piano is hoisted on a crane and delivered through the window of a six story apartment 20 m above the ground what is the potential energy of the piano?
Answers
Answer:
1962 J
Explanation:
potential energy= mgh
m=10 kg
h=20 m
g=9.81 (always unless otherwise stated)
PE= 10(20)(9.81)=1962 J
A car of mass 1200 kg travels at a steady dpeed of 22 m/s around a bend of radius 50 m. Find the centripetal force required?
Answers
Compute the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration a :
a = (22 m/s)² / (50 m) = 9.68 m/s²
Then the magnitude of the centripetal force is
F = (1200 kg) (9.68 m/s²) = 11,616 N ≈ 12,000 N
The truck needs 11,616 N of centripetal force to bend around a radius 50 m.
From the centripetal acceleration,
\(a = \dfrac{v^2}{r}\)
Where,
\(a\)- Centripetal acceleration
\(v\)- velocity = 22 m/s
\(r\)- radius = 50 m
Put the values,
\(a =\dfrac { (22 \rm \ m/s)^2}{(50\rm \ m)}\\\\a = 9.68\rm \ m/s^2\)
So, the centripetal force is
\(F = ma\)
Where, m is the mass = 1200 kg
So,
\(F= 1200\rm \ kg\times 9.68\rm \ m/s^2 \\\\F = 11,616\rm \ N\)
Therefore, the truck needs 11,616 N of centripetal force to bend around a radius 50 m.
To know more about centripetal force,
https://brainly.com/question/10596517
As seen in the figure, four points with a distance of 2d between two “neighboring” charges –Q, +Q, -Q and +Q charges “x”
are placed on the axis.

Answers
a) The net area revealed by the four charges at the point P on the y-axis will be directed outwards from the origin in a radial direction. This can be shown schematically by arrows pointing away from the origin.
What is radial direction?Radial direction is a direction that is perpendicular to the tangent of a circle at any given point. It is the same as the radius of a circle and is also known as the normal direction.
b) The contributions of the 1st and 2nd charges to the net area at point P can be expressed as:
Ē₁ =(Q/48πε₀)(1/y)î + (Q/48πε₀)(1/d+y)î
Ē₂ =(Q/48πε₀)(1/d+y)î - (Q/48πε₀)(1/y)î
where Q is the charge of each point, d is the distance between two neighboring charges, y is the distance of point P from the coordinate origin, k is the electrostatic constant and Ī is the unit vector in the x-direction.
c) The net area at point P can be obtained by subtracting the contributions of the 1st and 2nd charges, i.e.,
Enet = Ē₁ - Ē₂ = (Q/48πε₀)(2/d)î
d) Assuming that d = 2cm, Q = 5µC and y = 1m (y >> d), the acceleration of the charge q = - 0.2µC will be given by:
a = qEnet/m = - 0.2µC (Q/48πε₀)(2/d)î/0.5kg = - 0.8µC (Q/48πε₀)î/0.5kg
which is equal to - 6.4 x 10⁻⁶ m/s². The direction of the acceleration will be in the opposite direction of the net area, i.e., towards the origin.
e) The acceleration of charge q does not remain constant during motion because the electric field and thus the net area changes as the charge moves. As the charge moves closer to the origin, the magnitude of the electric field increases, resulting in an increase in the acceleration of the charge. Similarly, as the charge moves further away from the origin, the magnitude of the electric field decreases, resulting in a decrease in the acceleration of the charge.
To learn more about radial direction
https://brainly.com/question/29118725
#SPJ1
Consider a series of motion scenarios. Each scenario is accompanied by a short description and an arrow indicating the instantaneous velocity. Assume that air resistance is negligible in every scenario. The only forces present in each scenario are gravity, surface (or normal) forces, and friction if indicated. Place the appropriate arrow, or zero, next to each scenario to indicate the direction of the net force acting on the block.

Answers
The resultant force is obtained by taking into account the magnitude and direction of all the forces involved.
What is motion?Motion refers to change in position with respect to time. The instantaneous velocity is the velocity at a given time during motion.
Since force is a vector quantity, we must note that the net force will point in a given direction after taken all other forces into account. The net/resultant force is the force tat will have the same effect in magnitude and direction as all the forces taken together.
Learn more about resultant force: https://brainly.com/question/7041906
Part A- Variation in the speed of sound Sound is a longitudinal wave, and its speed depends on the medium through which it propagates. In air, sound travels at 343 m/s. In an experiment, you observo a sound with a frequency of 500 Hz and a wavelength of 6.4 m. What is the speed of sound in this differont medium? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HÅ ? Value Units Submit Request Answer Sounds vary in intensity and loudness across a very wide range, and we use the logarithmic decibel scale to quantify sound. Sort and match the following sounds with their decibel level. Place each sound in the appropriate in for its decibel level. Only one sound may be placed in each bin. Reset Help Operating a lawnmower Your clothing rusting Telephone hold music A whisper across a football field Abrary with people studying -20 dB 10 dB 30 dB 60 dB 90 dB Part D- Calculating the limits of hearing In a large perfectly quiet room, at what maximum distance could you hear a bee with a power output of 1W? Recall that the threshold of hearing is 10-12 W/m² Express your answer with the appropriate units. HA ? T Value Units Submit Request Answer
Answers
The Velocity is 4270 m/s it is equal to product of frequency and wavelength.
Given: -
Frequency(f) = 700 Hz
Wavelength(λ) = 6.1m
velocity = f x λ
velocity = 700 x 6.1
velocity = 4270 m/s
Wavelength is a fundamental concept in physics, particularly in the study of waves, which includes electromagnetic radiation, light, and sound waves. It is defined as the distance between two successive points of the same phase, such as the crest or trough of a wave. This distance is usually measured in units of meters, and it is inversely proportional to the frequency of the wave.
In electromagnetic radiation, the wavelength is an important property that determines the type of radiation, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each type of radiation has a unique range of wavelengths that can be measured using instruments like a spectroscope or a radio antenna.
To learn more about Wavelength visit here:
brainly.com/question/7143261
#SPJ4
2.
A ball player hits a home run, and the ball just clears the wall which is 22.0 m high.
The ball is hit at an angle of 37.0" with a velocity of 45.0 m/s. If the ball is hit from
a height of 0.750 m above the ground, (a) How long is the ball in the air until it
clears the wall while on its way down? (b) How far is the wall from home plate?
Answers
a.) the ball was going up at 0.95 seconds and coming down at 4.58 seconds
b.) the distance of the wall from the plate is 34 m
Given that a ball player hits a home run, and the ball just clears the wall which is 22.0 m high. The ball is hit at an angle of 37.0" with a velocity of 45.0 m/s.
Since the ball is hit at an angle of 37.0 degrees, We need to find the vertical and horizontal component of the velocity.
\(U_{y}\) = 45 Sin 37 = 27.08 m/s
\(U_{x}\) = 45 cos 37 = 35. 94 m/s
Let us first calculate the maximum height reached.
\(V^{2}\) = \(U_{y} ^{2}\) - 2gH
At maximum height, V = 0
0 = \(27.08^{2}\) - 2 x 9.8H
19.6H = 733.3
H = 733.33/19.6
H = 37.4 m
If the ball is hit from a height of 0.750 m above the ground,
(a) To calculate the time the ball stays in the air until it clears the wall while on its way down, we will use the formula below.
h = \(U_{y}\)t - 1/2g\(t^{2}\)
Substitute for all the parameters
22 - 0.75 = 27.08t - 0.5 x 9.8 x \(t^{2}\)
21.25 = 27.08t - 4.9\(t^{2}\)
4.9\(t^{2}\) - 27.08t + 21.25
We will use quadratic formula
a = 4.9
b = - 27.08
c = 21.25
t = \(\frac{-b+/- \sqrt{b^{2} - 4ac } }{2a}\)
t = \(\frac{27.08 +/- \sqrt{27.08^{2} - 4 * 4.9 * x^{2} 21.25 } }{2 * 4.9}\)
t = \(\frac{27.08 +/-\sqrt{733.3 - 416.5} }{9.8}\)
t = \(\frac{27.08 +/- 17.8}{9.8}\)
t = 44.88/9.8 or 9.28 / 9.8
t = 4.58 s or 0.95 s
This means that the ball was going up at 0.95 seconds and coming down at 4.58 seconds
(b) The distance of the wall from home plate will be the range which is
R = \(U_{x}\)t
R = 35.94 x 0.95
R = 34.143 m
Therefore, the distance of the wall from the plate is 34 m approximately
Learn more about projectile here: https://brainly.com/question/4441382
The half-life of iodine-131 is 8.07 days. If 1.3 g are left after 93.2 days, how many grams werein the original sample?
Answers
The formula that describes radioactive decay over time, is the following:
\(A=A^{}_0\cdot2^{-t/t_0}\)Where A is the amount of a radioactive element after a time t, if t_0 is the half-life of the given element, for an initial sample A_0.
Solve for A_0, and substitute A=1.3g, t=93.2 and t_0=8.07 to find the initial amount of iodine-131 in the original sample:
\(undefined\)write state of matter with 5 example of each
Answers
There are broadly 3 states of matter (there are 5, but they don't teach 2 of them at school).
1. Solid
Examples: Iron, wood, steel, ice, paper
2. Liquid
Examples: Water, mercury, milk, soup, juice
3. Gas
Examples: Oxygen, Chlorine, Carbon dioxide, Sulphur dioxide, Nitrogen
According to the law of conservation of energy, which changes would INCREASE the total energy of a system?
A. An addition of 400 J of thermal energy and a loss of 550 J of kinetic energy
B. An addition of 200 J of thermal energy and a loss of 550 J of thermal energy
C. An addition of 300 J of GPE and a loss of 450 J of thermal energy
D. An addition of 500 J of kinetic energy and a loss of 450 J of thermal energy
Answers
The changes that would increase the total energy of a system is an addition of 500 J of kinetic energy and a loss of 450 J of thermal energy.
What is conservation of energy?The term conservation of energy means that energy can not be created nor destroyed.
In this case, the changes that would increase the total energy of a system is an addition of 500 J of kinetic energy and a loss of 450 J of thermal energy.
Learn more about conservation of energy:https://brainly.com/question/2137260
#SPJ1
A grinding wheel with radius of 20 cm is speed of 200 rpm when its power is cut off. It slows to a stop in 90s What was is the angular displacement of a point located at Yr? b) That is the angular displacement of a point located at r? Through what linear distance will the point at h travel? d) Through what linear distance will the point at travel? Before it was cut off, what was the period of one rotation?
Answers
The angular displacement of a point located at r is 7200π radians.
The angular displacement of a point located at Yr can be calculated using the formula: θ = ωₒt + (1/2)αt^2, where ωₒ is the initial angular velocity (in radians per second), t is the time it takes to come to rest, and α is the angular acceleration (in radians per second squared).
The initial angular velocity of the wheel can be calculated as ωₒ = 2πnₒ, where nₒ is the initial speed in revolutions per minute (RPM). We have nₒ = 200 RPM, so ωₒ = 2π * 200 / 60 = 40π radians per second.
The angular acceleration can be calculated as α = - ωₒ / t = - 40π / 90 = - 2π / 4.5 radians per second squared.
Plugging in the values, we get θ = 40π * 90 + (1/2)(-2π / 4.5) * 90²2 = 3600π radians.
The angular displacement of a point located at r can be calculated as θ = 2θ, since the distance traveled is twice as long. So, the angular displacement of a point located at r = 2θ = 2 * 3600π = 7200π radians.
The linear distance traveled by the point at h can be calculated as d = θ * Yr, where Yr is the radius of the wheel. Plugging in the values, we get d = 7200π * 20 cm = 144000π cm.
The period of one rotation before it was cut off can be calculated as T = 60 / nₒ = 60 / 200 = 0.3 seconds.
For more questions like Angular displacement visit the link below:
https://brainly.com/question/29258974
#SPJ4
100 POINTS AND BRAINLIEST! What were the Magdeburg Hemispheres?
Answers
Answer:
Magdeburg hemispheres are two half-spheres of equal size. Placing them together traps air between them. This air is merely trapped, and not compressed, so the pressure inside is the same as the pressure of the atmosphere outside the spheres. The spheres thus pull apart with nearly no resistance.
The Magdeburg hemispheres are a pair of large copper hemispheres, with mating rims. They were used to demonstrate the power of atmospheric pressure. When the rims were sealed with grease and the air was pumped out, the sphere contained a vacuum and could not be pulled apart by teams of horses.
If a pair of shoes weighs 0.3 N on Pluto what is the strength of gravity on Pluto
Answers
Answer:
0.6 m/s 2
Explanation:
2. For electric circuit shown in Figure find currents in each resistor.

Answers
The current flowing in the 2Ω and 1Ω is 1.14 A and the current flowing in the 3Ω and 4Ω is 0.286 A.
What is the current flowing in each resistor?The value of the current in each resistor is calculated by applying Kirchoff voltage law as follows;
The total voltage in loop 1 is calculated as;
2 + 4 - I₁R₁ - (I₁ - I₂)R₂ - I₁R₃ = 0
6 - 2I₁ - 3(I₁ - I₂) - 1₁ = 0
The current flowing in loop 2 is calculated as;
I = V/R
I₂ = ( 6 V - 4 V ) / (3 + 4)
I₂ = 0.286 A
The value of the current flowing in loop 1 is calculated as;
6 - 2I₁ - 3(I₁ - I₂) - 1₁ = 0
6 - 2I₁ - 3(I₁ - 0.286) - 1₁ = 0
6 - 3I₁ - 3₁ + 0.858 = 0
-6I₁ = -6.858
I₁ = 6.858 / 6
I₁ = 1.14 A
Learn more about current in circuit here: https://brainly.com/question/19255262
#SPJ1
why do astronauts weigh less on the moon than on earth
Answers
Answer:
Explanation: The moon of the Earth is much lighter in mass than the planet itself. In addition to being smaller than Earth, the Moon is also only approximately 60% as dense. A human weighs less on the Moon because there is less gravitational attraction there than there is on Earth.
Moon has lesser mass as conpared to earth, therefore gravitational force exerted by moon on any object is lesser than that of gravitational force exerted by earth on the same object, hence we can say that astronauts weight less on moon, i.e approximately 1/6 th of their weight on earth.
calculate the potential energy of a stone of mass 0.5g thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 10m/s. calculate:
1. The potential energy at the greatest height and value of h
2. The kinetic energy on reaching the ground again
Answers
A body is moving along a circular path with variable speed, it has both radial and tangential acceleration.
Select one:
True
False
Answers
Answer:
True; ar = v^2 / R Radial acceleration because it moves in a circular path
at = α R = tangential acceleration because its speed changes
a = at + ar total acceleration equals sum of radial and tangential
What happens to the mechanical advantage of a machine if the output force is less than the input force? What must happen to output distance? Give an example of a machine that does this?
Answers
A rightward force is applied to a 10-kg object to move it across a rough surface at constant velocity.
The coefficient of friction between the object and the surface is 0.2. Use the diagram to determine the
gravitational force, normal force, applied force, frictional force, and net force. (Neglect air resistance.)
Fnorm"
Feriet"
P=0.2
Fgrav".
m - 10 kg
a=0 m/s/s
Fnet
Fapp
Answers
***These questions were answered assuming that down and to the left are negative
Constant velocity means that the net force is 0 (you can prove using derivatives).
Fnet = 0 N
The force of gravity can be calculated using the equation Fg = mg.
Fg = mg = 10 (-9.8) = -98 N
Since the force of gravity and the normal force are the only forces in the vertical direction and the net force is 0, they must obey -Fn = Fg (if they don't follow this, the net force will not be 0).
Fn = -Fg = -(-98) = 98 N
The frictional force can calculated using the equation Ff = μFn, where μ is the coefficient of friction.
Ff = μFn = -0.2 (98) = -19.6 N
The force applied can also be calculated using the fact that the net force is 0. For the net force to be 0, the forces in the x direction must cancel (add up to 0), meaning they must be equal magnitude in opposite directions. Therefore Fa = -Ff.
Fa = -Ff = -(-19.6) = 19.6 N
Organisms in the same family are less closely related than organisms in the same order.
True
O
False
Answers
Answer:
False
Explanation:
HELP I NEED IT NOW PLEASE

Answers
Please make me as brainliest.
proof that the kinetic energy of a moving body is half mv square
Answers
Answer:
1
Explanation:
Forensic Entomology
Forensic Entomology
The study of the life cycle of insects that feed on the flesh to the dead, to establish time of death and occasionally identify chemicals present in a person's body at the time of death.
Time since death
Arrive a few hours after a death and are active through decomposition process. They feed on larvae and other insects rather than the corpse itself.
Larvae that feed on human excrement and remains, and are found late in the decomposition process.
Answers
Forensic Entomology is the study of life cycles of insects that feed on the flesh of dead, to establish time of death and occasionally identify chemicals present in a person's body at time of death
What is meant by Forensic Entomology?The scientific study of the colonization of dead body by arthropods is called forensic entomology .
Larvae and adults feed on dry skin and hairs of corpse and arrive later in decomposition process : Carpet Beetles
Time since death : postmortem Interval.
Rove Beetles : Arrive a few hours after death and are active throughout decomposition process. They feed on larvae and other insects rather than the corpse itself.
To know more about forensic entomology, refer
https://brainly.com/question/8060082
#SPJ1
The motion of a particle
executing S.H.M is given by x
= 0.01 sin 100 ti (t+0.5)
where x is in meter and 't' in
second. The time period is
Answers
Answer:0.02 seconds
Explanation: