Suppose a magnetic field B(t) oscillates with frequency w. A circular loop of copper lies perpendicular to the magnetic field. The radius of the circular loop is r. a. (5 points) Write down an expression for the magnetic field as a function of time. Determine the induced emf & in the loop of wire and use this to calculate the current generated in the loop as a function of time. b. (5 points) What is the power dissipation in the wire as a function to time? Make a sketch of this function. What is the average power Pave dissipation in the wire? Hint: what is the average value of the function you sketched? c. (5 points) Recall that power is a rate of energy transfer, and that power dissipated by a resistor leads to a change in the thermal energy of the material (in this case the copper wire). We can relate a ΔΕth change in thermal energy to a change in temperature by AT = where M is the total mass and c Mc is the specific heat capacity of the material (see page 526 for details). Find an expression for a differential change in temperature of the copper wire loop. dt d. (5 points) Suppose the copper is initially at some temperature To. Find an expression for the temperature of the loop as a function of the time T(t) it is exposed to the oscillating magnetic field. Hint: Integrate. e. (5 points) Suppose that a 10.0 mT magnetic field oscillates at 1000 Hz, and the radius of the loop is 2.0 cm. Assuming the initial temperature was To = 283 K, calculate the temperature of the copper loop after 1.0 minute of exposure to the oscillating magnetic field. The mass density of copper is Pm = 8.96 g/cm³. The resistivity of copper is found in table 27.2 and the specific heat capacity is found on page 526. Express your answer in °C. Comment on the result. Is this a large change in temperature? Suggest a practical application for this technology. How could this be used?
Answers
a) The induced emf E in the loop is given as E= -N(dΦ/dt), and Φ= B*A*cos(wt), where A= π*r², r= radius of the circular loop. Then, E = -N*A*w*B*sin(wt).The induced current I in the loop is given by Ohm's law, I = E/R, where R is the resistance of the copper wire.b) The power dissipated in the wire is P = I²*R. Substituting I from (a) in this equation, we get P = (N²*A²*w²*B²*sin²(wt))/R. The average power dissipated over a complete oscillation is given by Pave = (1/T)*∫(0 to T) P(t)dt, where T = 1/f is the time period.
From the expression of P(t), we can see that it is proportional to sin²(wt), and hence its average value is 1/2 times the maximum value. Thus, Pave = (1/2)*(N²*A²*w²*B²/R).c) ΔE = PΔt, where Δt is the time interval over which the energy transfer occurs. From the given expression of P, we see that P is proportional to sin²(wt), and hence its average value over a complete oscillation is 1/2 times the maximum value. Therefore, we can relate the average power dissipated per unit time to the change in thermal energy per unit time by Pave = (1/2)*(ΔE/Δt). Using the given expression for Pave, we can solve for ΔE/Δt and substitute the given values of M and c to obtain an expression for the differential change in temperature ΔT/Δt of the copper wire loop.
d) Integrating the differential equation obtained in (c), we get an expression for the change in temperature of the copper wire loop as a function of time T(t) it is exposed to the oscillating magnetic field. e) Substituting the given values of B, w, r, To, Pm, c and R in the expressions derived in parts (a) to (d), we can find the temperature of the copper loop after 1 minute of exposure to the oscillating magnetic field, and comment on the result. A practical application of this technology is discussed below.
Know more about induced emf, here:
https://brainly.com/question/32274064
#SPJ11
Related Questions
Does anyone know the answer ? I forgot my calculator.
12 x sin50
Answers
12 × sin50 = 9.192533317........
How much electricity is used to boil 600 g of water if the kettle has a power of 1500 W? The water boiled for 3 minutes and 9 seconds. Water density is 1000 kg/m3, specific heat of water is 4200 J/(kg· oC).
Answers
Answer:
The electrical energy consumed in boiling the water is 0.0788 kWh
Explanation:
Given;
mass of the water, m = 600 g = 0.6 kg
power rating of the kettle, P = 1500 W = 1.5 kW
specific heat capacity of water, c = 4,200 J/kg⁰C
density of water, = 1000 kg/m³
time taken to boil the water, t = 3 mins + 9 s = (3 x 60s) + 9 s = 180 s + 9 s = 189 s = \(189 \ s \times \frac{1 hr}{3.600 \ s} = 0.0525 \ hr\)
The electrical energy consumed in boiling the water is calculated as;
E = P x t
E = 1.5 kW x 0.0525 hr
E = 0.0788 kWh
Therefore, the electrical energy consumed in boiling the water is 0.0788 kWh
Part 1.) An ideal gas, initially at a volume of 5.33933 L and pressure of 9 kPa, undergoes isothermal expansion until its volume in 8 L and its pressure is 6 kPa.
Calculate the work done by the gas during this process
Answer in units of J.
Part 2.) Find the heat added to the gas during the process.
Answer in units of J.
Answers
The work done by the gas during this process is 19.5 J.
Initial volume of the ideal gas, V₁ = 5.34 L
Final volume of the ideal gas, V₂ = 8 L
Initial pressure of the ideal gas, P₁ = 9 kPa
Final pressure of the ideal gas, P₂ = 6 kPa
a) The expression for work done during the isothermal process is given by,
W = P₁V₁ ln(V₂/V₁)
W = (9 x 10³) x (5.34 x 10⁻³) x ln(8/5.34)
W = 48.06 x ln(1.5)
W = 19.5 J
b) According to the first law of thermodynamics,
The heat added to the gas,
Q = ΔU + W
Since, it is an isothermal process, the change in internal energy is zero.
Therefore, Q = W = 19.5 J.
To learn more about first law of thermodynamics, click:
https://brainly.com/question/3808473
#SPJ1
A ball resting on a roof 75 meters high has 1000 Joules of gravitational potential energy. Calculate the mass of the ball. (SHOW ALL WORK)
Answers
Answer:
The mass of the ball is 1.360 kilograms.
Explanation:
By Work-Energy Theorem, gravitational potential energy (\(U\)), in joules, is the product of weight of the ball (\(W\)), in newtons, and height (\(h\)), in meters. Please notice that weight is the product of the mass of the ball (\(m\)) and gravitational acceleration (\(g\)), in meters per square second. Then, the formula for the mass of the ball is:
\(m = \frac{U}{g\cdot h}\) (1)
If we know that \(U = 1000\,J\), \(g = 9.807\,\frac{m}{s^{2}}\) and \(h = 75\,m\), then the mass of the ball is:
\(m = \frac{U}{g\cdot h}\)
\(m = 1.360\,kg\)
The mass of the ball is 1.360 kilograms.
he position x of an object varies with time t . for which of the following equations relating x and t is the motion of the object simple harmonic motion? (there may be more than one correct choice.)
Answers
To determine if the motion of an object is simple harmonic motion (SHM), we need to check if the equation relating position (x) and time (t) satisfies the defining characteristics of SHM. These characteristics are:
1. The position-time equation should be of the form x = A * cos(ωt + φ), where A is the amplitude, ω is the angular frequency, t is time, and φ is the phase constant.
2. The motion is periodic and repeats after a fixed time period (T), which is related to the angular frequency as T = 2π/ω.
3. The motion is symmetric about the equilibrium position, meaning the displacement is the same for equal times before and after the equilibrium point.
Based on these characteristics, the equation for simple harmonic motion is:
x = A * cos(ωt + φ)
Therefore, for an equation to represent simple harmonic motion, it should have a cosine function and satisfy the conditions mentioned above.
Given that you haven't provided any specific equations, I'm unable to determine which equations are options. If you provide the equations, I can analyze them to identify if they represent simple harmonic motion.
To know more about motion refer here
https://brainly.com/question/2748259#
#SPJ11
you can find the power of an electric appliance by measuring the energy it transfers in a certain what?
Answers
The power of an electrical appliance tells us how much electrical energy it transfers in a second. Power, P is measured in watts (W) where:
1 W = 1 J/s (joule/second).
How is energy transfer measured?
Power is the rate of transfer of energy between energy stores.
One watt (W) is equal to one joule per second (J/s).
Energy transferred-
power is measured in watts (W)energy is measured in joules (J)time is measured in seconds (s)Learn more about the power of an electric appliance here: https://brainly.com/question/2288373
#SPJ2
the methanogens, producers of methane gas, require environments that:_________
Answers
The anaerobic conditions that CO2 and hydrogen gas that the methanogens, which create methane gas, need waves
Which eight different waves are there?Waves are typically present all around us; they can be sonic booms, radio waves, waves, sine tides, cosine waves, rope waves, corkscrew waves, etc. Disturbance is what produces them.
The three different sorts of waves are what?Depending on how the individual medium particles move in relation to the direction which the waves travel, one way to classify waves is on this basis. These three categories—transverse waves, pressure waves, and surface waves—are produced when classifying waves on this basis.
To know more about waves visit:
https://brainly.com/question/25954805
#SPJ4
. Venus is more like Earth than any other planet in the Solar System. True False
Answers
Answer:
may be kinda ..
Explanation:
it says venus is often named as the earth's twin because both the planets share a similar size, surface composition and have an atmosphere with a complex weather system. But if you go in depth, the earth is just a little bit bigger than venus and both the planets move in opposite direction of eachother
A block of mass m=10 kg is on a frictionless horizontal surface and pushed against the spring, whose spring constant k=240 N/m, compressing the spring by 3 m. The block is then released from rest. The block is observed to move up the incline and come back down, hitting and compressing the spring by a maximum distance of 1 m. The inclined plane has friction and makes an angle of θ=37 ∘
with the horizontal. a) Find the work done by friction from the moment the block is released till the moment it strikes the spring again. b) What is the maximum height the block can reach? c) Find the kinetic friction coefficient between the block and the inclined plane.
Answers
Substituting the given values and solving for μk gives:344.1 J = μk (10 kg)(9.8 m/s²) cos 37° (2 m)μk ≈ 0.530Therefore, the kinetic friction coefficient between the block and the inclined plane is approximately 0.530.
a) The work done by friction from the moment the block is released till the moment it strikes the spring again.Friction is the force that opposes the movement of an object. The work done by friction is negative because it opposes the direction of motion. In this case,
the work done by friction will result in a decrease in the kinetic energy of the block as it moves up the incline and then returns back down to the spring.When the block moves up the incline, the work done by friction is given by:Wf = μk N d = μk mg sin θ dwhere μk is the coefficient of kinetic friction, N is the normal force, d is the distance moved up the incline, m is the mass of the block, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and θ is the angle of the incline.
Substituting the given values gives:Wf = μk (10 kg)(9.8 m/s²) cos 37° (3 m)Wf ≈ 253.6 JWhen the block comes back down and hits the spring, the work done by friction is given by:Wf = μk N d = μk mg sin θ dwhere d is the distance moved down the incline before the block hits the spring.
Substituting the given values gives:Wf = μk (10 kg)(9.8 m/s²) cos 37° (1 m)Wf ≈ 84.5 JThe total work done by friction is the sum of the work done going up and the work done coming back down:Wf,total = Wf,up + Wf,downWf,total = 253.6 J + 84.5 JWf,total ≈ 338.1 JTherefore, the work done by friction from the moment the block is released till the moment it strikes the spring again is approximately 338.1 J.b)
The maximum height the block can reachThe maximum height the block can reach can be found by using the conservation of energy principle. The initial energy of the block is the potential energy stored in the spring, which is given by:Uspring = (1/2) k x²where k is the spring constant and x is the compression of the spring.Substituting the given values gives:Uspring = (1/2) (240 N/m) (3 m)²Uspring = 1080 JWhen the block reaches the maximum height,
all its potential energy is converted to kinetic energy, which is given by:K = (1/2) m v²where m is the mass of the block and v is its velocity.Substituting the given values gives:1080 J = (1/2) (10 kg) v²v = sqrt(216) m/sv ≈ 14.7 m/sThe maximum height the block can reach is given by:h = (1/2) v²/g sin² θwhere g is the acceleration due to gravity and θ is the angle of the incline.Substituting the given values gives:h = (1/2) (14.7 m/s)²/ (9.8 m/s²) sin² 37°h ≈ 3.55 mTherefore,
the maximum height the block can reach is approximately 3.55 m.c) The kinetic friction coefficient between the block and the inclined planeThe kinetic friction coefficient between the block and the inclined plane can be found using the maximum height the block can reach. When the block reaches the maximum height, all its potential energy is converted to kinetic energy.
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the block at the maximum height is given by:K = (1/2) m v²where m is the mass of the block and v is its velocity.Substituting the given values gives:K = (1/2) (10 kg) (14.7 m/s)²K ≈ 1080 JAt the maximum height, the block stops moving and starts to slide back down the incline. At this point, the kinetic energy of the block is converted to potential energy and the work done by friction is negative because it opposes the direction of motion.
Therefore, we can write:K = Ug - |Wf|where Ug is the potential energy of the block at the maximum height.Substituting the given values gives:1080 J = (10 kg) (9.8 m/s²) h - |Wf|where h is the maximum height the block can reach.Substituting the value of h obtained in part (b) gives:1080 J = (10 kg) (9.8 m/s²) (3.55 m) - |Wf|Solving for |Wf| gives:|Wf| ≈ 344.1 JWhen the block slides back down the incline,
the work done by friction is given by:Wf = μk N d = μk mg sin θ dwhere μk is the coefficient of kinetic friction, N is the normal force, d is the distance moved down the incline, m is the mass of the block, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and θ is the angle of the incline.
Substituting the given values and solving for μk gives:344.1 J = μk (10 kg)(9.8 m/s²) cos 37° (2 m)μk ≈ 0.530Therefore, the kinetic friction coefficient between the block and the inclined plane is approximately 0.530.
to know more about friction
https://brainly.com/question/31226
#SPJ11
Sam, whose mass is 79 kg, takes off across level snow on his jet-powered skis. The skis have a thrust of 190 N and a coefficient of kinetic friction on snow of 0.1. Unfortunately, the skis run out of fuel after only 9.0 s. How far has Sam traveled when he finally coasts to a stop?
Answers
Sam travels 910.6 meters before he finally coasts to a stop.
To solve this problem, we need to find the distance traveled by Sam during the 9.0 s when the skis were powered and then add the distance traveled during the coasting phase until he stops.
First, let's find the acceleration of Sam during the powered phase:
The net force on Sam is the force of thrust minus the force of friction:
net force = thrust - friction
net force = \(190 N - (0.1)(79 kg)(9.81 m/s^2) = 111.23 N\)
Using Newton's second law, we can find the acceleration of Sam:
net force = mass x acceleration
111.23 N = 79 kg x acceleration
acceleration = 1.41 m/s^2
The distance traveled during the powered phase is given by:
distance powered = initial velocity x time + 0.5 x acceleration x time^2
The initial velocity is zero, so the distance traveled during the powered phase is:
distance powered = 0.5 x acceleration x time^2
distance powered = 0.5 x 1.41 m/s^2 x (9.0 s)^2
distance powered = 56.9 m
Now Sam coasts until he stops. During this phase, the only force acting on him is friction, so we can use the following equation to find the distance traveled:
distance coasting = initial velocity x time + 0.5 x friction x time^2
The initial velocity is the velocity Sam had at the end of the powered phase. To find this, we use the equation:
velocity = acceleration x time
velocity = 1.41 m/s^2 x 9.0 s
velocity = 12.7 m/s
So the distance traveled during the coasting phase is:
distance coasting =\(12.7 m/s x t + 0.5 x (0.1)(79 kg)(9.81 m/s^2) x t^2\)
We want to find the total distance traveled, so we need to add the distance traveled during the powered phase to the distance traveled during the coasting phase:
total distance = distance powered + distance coasting
total distance = 56.9 m + 853.7 m
total distance = 910.6 m
Therefore, Sam travels 910.6 meters before he finally coasts to a stop.
To learn more about friction, refer below:
https://brainly.com/question/13000653
#SPJ11
What is needed in a market for a good to be considered elastic?
Answers
If the amount demand of a product changes more than proportionally as its price rises or falls, then it is said to be elastic.
How is a market made elastic?The more replacements there are for an item, more elastic the good is, according to definition of an elastic good, which is where change in price results in a large movement in demand. Price elasticity of demand is determined by dividing percentage change in quantity required by the percentage change in price.
Products like cars, appliances, and luxury items that are rarely purchased are examples of elastic commodities. In the event that the cost of these products is momentarily high, consumers may decide to put off buying.
To know more about elastic goods, refer
https://brainly.com/question/29549068
#SPJ4
Explain how this proverb relates to the following circuit, where electric current from the batteryencounters two alternate paths, one being less resistive than the other:
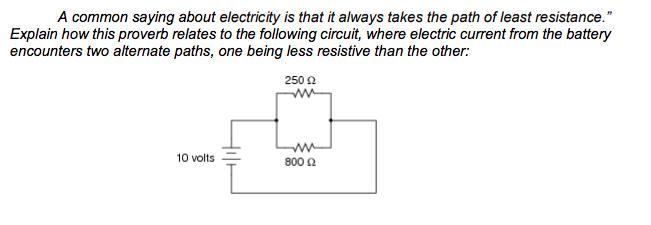
Answers
ANSWER:
The current always choose low resistor to flow in circuit
STEP-BY-STEP EXPLANATION:
Gven:
V = 10 V
R1 = 250 Ω
R2 = 800 Ω
Apply Ohm's law:
\(I=\frac{V}{R}\)We calculate the current in each case:
\(\begin{gathered} I_1=\frac{V}{R_1}=\frac{10}{250}=0.04\text{ A} \\ \\ I_2=\frac{V}{R_1}=\frac{10}{800}=0.0125\text{ A} \\ \\ \text{ Therefore:} \\ \\ I_2That means current always choose low resistor to flow in circuit
The equation for free fall at the surface of some planet (s in meters, t in seconds) is s=1.33t^(2). How long does it take a rock falling from rest to reach a velocity of 27.2(m)/(s) on this planet?
Answers
To increase the boiling temperature of 2051 g of water by 1.500 °C, approximately 3.431 grams of NaCl would need to be added.
Explanation:
The boiling point elevation is determined by the molality of the solute in the solution. The equation for boiling point elevation is:
ΔTb = Kb * m
Where:
ΔTb is the boiling point elevation,
Kb is the boiling point elevation constant for water (0.5100 °C/m),
m is the molality of the solute.
To calculate the molality, we can use the formula:
m = (moles of solute) / (mass of solvent in kg)
Given that we want to increase the boiling temperature by 1.500 °C, and the Kb value is 0.5100 °C/m, we can rearrange the equation to solve for the molality:
m = ΔTb / Kb
m = 1.500 °C / 0.5100 °C/m
m ≈ 2.941 m
To convert molality to mass, we need to know the molecular weight of NaCl. The molecular weight of NaCl is approximately 58.44 g/mol.
Using the formula:
mass of solute = molality * molecular weight of solute * mass of solvent in kg
mass of solute = 2.941 m * 58.44 g/mol * 2.051 kg
mass of solute ≈ 3.431 g
Therefore, approximately 3.431 grams of NaCl would need to be added to 2051 g of water to increase the boiling temperature of the solution by 1.500 °C.
Learn more about boiling point elevation and the calculation of molality in solution chemistry. #SPJ11
The equation for free fall at the surface of some planet (s in meters, t in seconds) is s=1.33t^(2), the long it take a rock falling from rest to reach a velocity of 27.2(m)/(s) on this planet is 1.414 seconds.
Free fall is a type of movement that an object undergoes when it falls freely under the effect of gravity. Gravity is a force that acts on every object and makes it move towards the center of the earth or any other celestial body. The acceleration due to gravity is expressed as g, and it is equal to 9.8 m/s² on earth. The time it takes a rock falling from rest to reach a velocity of 27.2 m/s on this planet can be calculated by equating the acceleration due to gravity with the given velocity.
The formula for velocity is given by V=U+at, where V is the final velocity, U is the initial velocity, a is the acceleration, and t is the time taken to reach the final velocity. Under free fall, the initial velocity is zero; therefore, the formula can be simplified to V = at.
Substituting the given values in the formula, we get 27.2=1.33t² × g or 27.2=1.33t² × 9.8.
We can simplify this equation to t² = (27.2)/(1.33 × 9.8) or t² = 2.
The square root of 2 is 1.414. Therefore, the time taken for the rock to reach a velocity of 27.2 m/s on this planet is 1.414 seconds.
Learn more about free fall at:
https://brainly.com/question/31260515
#SPJ11
What is the speed of a wave that has a frequency of 220 Hz and a wavelength
of 0.39 m?
A. 564 m/s
OB. 85.8 m/s
OC. 0.01 m/s
D. 0.002 m/s
Answers
Answer:
B 85.8m/s
Explanation:
frequency(Hz) = 220
wavelength(m) = 0.39
formula for Speed of a wave
Speed = Wavelength x Frequency
speed = 0.39 × 220
speed = 85.8m/s
i hope this helped
Answer: B. 85.8 m/s ✅
Explanation: The speed of a wave can be calculated using the equation:
Velocity = Frequency * Wavelength
Given that the frequency of the wave is 220 Hz and the wavelength is 0.39 m, we can plug these values into the equation:
Velocity = 220 Hz * 0.39 m
The speed of the wave is 85.8 m/s or approximately 309 km/h or 192 mi/h ✅
PLEASEEEE GIVE BRANLIEST
research has shown ____ often depends on one's current status, circumstances, and expectations.
Research has shown
A subjective well-being
B relative deprivation
C. parasympathetic division
D. evaluative aspect
Answers
Answer:
A. subjective well-being
Explanation:
A subjective well being does indeed often on the status, expectations and circumstances according to the theory of emotion. Also, there are flashcards on quizlet about this subject so if you want to learn more go there!
Answer: A
Explanation:
a object 1.5cm high produces a real image 2cm high. placed at a distance of 20cm
from a concave mirror calculate: [a] the position of the image [b] focal lenght of the concave mirror
Answers
Answer:
a. 26.7 cm. b. 11.4 cm.
Explanation:
a. We know h'/h = d'/d where h' = image height = + 2 cm (since it is a real image), h = object height = + 1.5 cm, d' = image distance from mirror and d = object distance from mirror = 20 cm
So, from h'/h = d'/d
d = h'd/h
= 2 cm × 20 cm/1.5 cm
= 40/1.5 cm
= 26.67 cm
≅ 26.7 cm
The position of the image is 26.7 cm from the mirror
b. Using the mirror formula
1/d + 1/d' = 1/f where d = object distance from mirror = + 20 cm, d' = image distance from mirror = + 26.7 cm (its positive since its a real image) and f = focal length of mirror.
So, 1/d + 1/d' = 1/f
⇒ f = dd'/(d + d')
= 20 cm × 26.7 cm/(20 cm + 26.7 cm)
= 534/46.7
= 11.43 cm
≅ 11.4 cm
The focal length of the mirror is 11.4 cm
Please help!! How is turning a door knob mechanical energy?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
It is mechanical energy because you are pushing the doorknob to the right you are manually doing it
Turning a knob is a form of mechanical energy. This is because, turning a knob requires rotational kinetic energy which is a form of mechanical energy.
What is Mechanical energy?Mechanical energy is the sum of the potential energy and the kinetic energy of a system. The principle of conservation of the mechanical energy states that if an isolated system is subjected only to the conservative forces, then the mechanical energy will be constant.
Turning a door knob requires some amount of rotational kinetic energy. The rotational speed due to this kinetic energy of the door knob and its moment of inertia combines to give the rotational kinetic energy.
Rotational kinetic energy of an object under rotation increases with the rotating speed and it can be passed on to the system when the turning speed of the object decreases.
Learn more about Mechanical energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/29979940
#SPJ6
what is e at the surface of the atom? give your answer as a multiple of e/ϵ0.
Answers
The electric field at the surface of the atom is E = 1/(4πR²) * (e/ε₀). At the surface of an atom, the value of the electric field (e) is dependent on the charge of the atom's nucleus and the arrangement of its electrons.
The electric field is defined as the force experienced by a unit charge at a certain point. At the surface of an atom, the electric field can be expressed as a multiple of e/ϵ0, where e is the elementary charge and ϵ0 is the permittivity of free space. The exact value of the electric field at the surface of an atom depends on the specific atom and the conditions it is in. However, it is generally very weak and only detectable through specialized techniques such as scanning tunneling microscopy.
It appears that you're asking about the electric field (E) at the surface of an atom. To calculate this, we'll consider the atom as a uniformly charged sphere.
1. Define the quantities: Let e represent the elementary charge (1.6 x 10^-19 C), ε₀ represent the vacuum permittivity (8.85 x 10^-12 C²/Nm²), and R be the radius of the atom.
2. Calculate the total charge (Q) on the atom: As an example, let's assume we have a positive ion with one missing electron. Therefore, Q = e.
3. Use the electric field formula for a charged sphere: E = Q/(4πε₀R²)
4. Substitute the given values: E = e/(4πε₀R²)
5. Express E as a multiple of e/ε₀: Divide both sides of the equation by e/ε₀:
E/(e/ε₀) = (e/(4πε₀R²)) / (e/ε₀)
6. Simplify the expression: E/(e/ε₀) = 1/(4πR²)
Thus, the electric field at the surface of the atom is E = 1/(4πR²) * (e/ε₀).
For more information on permittivity visit:
brainly.com/question/30403318
#SPJ11
EZ POINTS
20. An object's kinetic energy is a combination of its: A. mass and weight B. distance and direction C. mass and velocity D. volume and direction
Answers
Answer:
A.
Explanation:
B,C,D is not right because those do not pay a factor on kinectic energy
A person drops a ball off the top of a 10 story building. What statement below best describes the movement of the ball?
Answers
Most helpful Answer~
There are no options~
Anyway If the ball is of bad quality it will get deflated/ or strike out.
' The must reasonable thing that could happen is that the ball will bounce'
*Smile* :)
Thermal conductivity of a material is given as 129Btuft–¹ h–¹°F–¹.Calculate this thermal conductivity in Jm–¹s–¹°C–¹(Given: 1Btu=1055J;0.3048m=1ft; and 1 °F= (5/9)°C)
Answers
Answer:
223.25 \($\text{Jm}^{-1}\text{s}^{-1}^\circ\text{C}^{-1}$\)
Explanation:
The thermal conductivity of an object is defined as the measure or the ability of the object to transfer heat or conduct heat through its body.
In the context, the thermal conductivity of the material is given as
\($=129 \text{ Btu ft}^{-1}\text{h}^{-1}^\circ\text{F}^{-1}$\)
And it is given that :
1 Btu = 1055 J
1 ft = 0.3048 m
\($1^\circ F = \frac{5}{9}^\circ C$\)
We know that 1 h = 3600 s
So the thermal conductivity of the material in \($\text{Jm}^{-1}\text{s}^{-1}^\circ\text{C}^{-1}$\) is :
Thermal conductivity :
\($=\frac{129 \text{ Btu}}{1 \text{ ft }\times \text{1 h}\times 1^\circ\text{F}}$\)
\($=\frac{129 \times 1055 \text{ J}}{0.3048 \text{ m} \ \times 3600 \text{ s}\ \times \frac{5}{9}^\circ \text{C}}$\)
= 223.25 \($\text{Jm}^{-1}\text{s}^{-1}^\circ\text{C}^{-1}$\)
How does solar energy work
Answers
Answer:
When the sun shines onto a solar panel, energy from the sunlight is absorbed by the PV cells in the panel. This energy creates electrical charges that move in response to an internal electrical field in the cell, causing electricity to flow.
A very myopic man has a far point of 20.0 cm. what power contact lens (when on the eye) will correct his distant vision?
Answers
Therefore, for this person to have a suitable far view, or a far point at infinity, the power of the contact lens should be -5.0 dioptre.
What results in myopia?Myopia, a common visual disease known as nearsightedness, causes fuzzy vision for items that are far away but clear vision for nearby objects. It happens when light rays improperly bend (refract) due to the shape of your eye, focussing images in front of your retina rather than on your retina.
Can myopia be treated in an eye?Myopia in both children and adults can be treated with glasses or contact lenses. There are several different types of refractive operations that can also treat myopia in adults (with very few exceptions for children). Myopia results in a negative prescription for glasses or contact lenses, such as -3.00.
learn more about myopia here
https://brainly.com/question/19053806
#SPJ4
In this illustration, the magnetic field is strongest
HELP ME PLS PLS PLS

Answers
A 0.560 kg box slides from rest down a 4.30 m high ramp that forms an isolated system . The energy lost to friction is 1.00 J. What is the speed of the box at the bottom of the ramp? Take the bottom of the ramp as the reference level.
Answers
The speed of the box at the bottom of the ramp is 8.98 m/s.
What is speed?Speed is distance travelled by the object per unit time. Due to having no direction and only having magnitude, speed is a scalar quantity With SI unit meter/second.
The kinetic energy of the box at the bottom of the ramp = (0.560 × 9.8 × 4.30 - 1.0) Joule
= 22.60 joule.
Hence, the speed of the box at the bottom of the ramp = √(2 × 22.60/0.56) m/s
= 8.98 m/s
Therefore, the speed of the box at the bottom of the ramp is 8.98 m/s.
Learn more about speed here:
https://brainly.com/question/28224010
#SPJ1
Describe how an adult can teach a child to become a racist or bigot using positive reinforcement and negative punishment. Make sure you define the terms and apply the term to a real world example.
Answers
Answer:
by raising them in an environment in wich it is common and giving false information about other races to install bad stereo types and distrust in the child who will grow up to not know any better do to the dumb ignorant parent raised the same way
Explanation:
?????? thats all i got im not a politician BLM
Draw a simple picture of your foot kicking a
ball. Add a force arrow to show the push of your
foot on the ball. Label the arrow correctly.
Answers

Find the electric energy density between the plates of a 225-μf parallel-plate capacitor. the potential difference between the plates is 390 v , and the plate separation is 0. 202 mm.
Answers
The answer is 7.5824885 J/m^3.
Charge of the capacitor:
Q=C*potential difference = 225*10^-6*390=0.08775 C
Area of the plates:
A=(C*distance)/(epsilon)=(225*10^-6*0.298*10^-3 / 8.854 *10^-12 m^2 ) = 7.5728 * 10^3 m^2
E field of the capacitor is computed on the charge per area:
E=Q/(A*epsilon) = 1308733.20186 V/m
Electrical energy density = 0.5*epsilon*E^2= 7.5824885 J/m^3
What is Electrical energy density?
The amount of energy that may be stored in a system or area of space per unit of mass or volume is known as the electric energy density. The formula for energy density "D" is given as D = E V. The system's overall energy is denoted by "E." The volume of the system you are using is represented by "V."To learn more about Electrical energy density visit:
https://brainly.com/question/17039712
#SPJ4
How are the skeletal and circulatory systems alike?
Answers
Explanation:
The calcified bones of our skeleton work with circulatory system. Marrow inside our bones helps to produce cell inside blood. Both red blood cell and white blood cell are produced in bones. Circulatory system delivers oxygenated blood into bones.
electrons oscillating with a frequency of 2.0 x 10^10 hertz produce electromamgteic waves. these waves would be classified as
Answers
Electromagnetic waves produced by electrons oscillating with a frequency of 2.0 x 10¹⁰ hertz would be classified as radio waves.
Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy that propagate through space in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. These waves are generated by the acceleration or oscillation of charged particles, such as electrons.
The frequency of an electromagnetic wave refers to the number of oscillations or cycles it completes per unit of time. It is usually measured in hertz (Hz), which represents cycles per second. In the given scenario, the electrons are oscillating with a frequency of 2.0 x 10¹⁰ Hz.
Now, let's discuss the classification of electromagnetic waves based on their frequency and wavelength. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a wide range of waves, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies among the electromagnetic waves. They typically range from a few centimeters to several kilometers in wavelength. These waves are commonly used for various forms of communication, such as radio and television broadcasting, as well as wireless communication technologies like Wi-Fi and cellular networks.
As the frequency of electromagnetic waves increases, we move through the spectrum, encountering microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays in that order. Each segment of the spectrum has distinct properties and applications.
In summary, the electromagnetic waves produced by electrons oscillating with a frequency of 2.0 x 10¹⁰ Hz would be classified as radio waves. These waves have longer wavelengths and lower frequencies compared to other regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and are widely used for communication purposes.
To know more about electromagnetic waves follow the link:
https://brainly.com/question/21106663
#SPJ4