Answers
Answer:
B. Boats need to float.
Related Questions
What is SeaWorld?
What is this
What is that
Answers
SeaWorld is a chain of theme parks and oceanariums that showcase marine life through educational exhibits, live shows, and thrilling rides. While it has faced criticism for its treatment of animals, SeaWorld has made changes to prioritize conservation and phased out its orca breeding program.
SeaWorld is a chain of theme parks and oceanariums that primarily focuses on marine life and entertainment. The company operates various parks across the United States, including SeaWorld parks in Orlando, San Diego, and San Antonio, as well as Busch Gardens parks in Tampa and Williamsburg. SeaWorld offers a combination of educational exhibits, live shows, and thrilling rides, with a special emphasis on marine animals such as dolphins, whales, sea lions, penguins, and sharks.
SeaWorld parks provide visitors with opportunities to observe and interact with marine creatures up close, while also offering educational programs that aim to raise awareness about marine conservation and preservation. The parks feature captivating shows featuring trained animals, where they perform impressive behaviors and stunts, showcasing their intelligence and natural abilities.
Over the years, SeaWorld has faced criticism from animal rights activists and environmentalists, who argue that the captivity and use of marine animals for entertainment purposes is unethical and harmful to the animals' well-being. These concerns have led to significant changes in the company's practices, including the phasing out of its orca breeding program and the introduction of more educational and conservation-focused initiatives.
To learn more about SeaWorld
https://brainly.com/question/13298282
#SPJ8
map.
Which best describes the motion of the object
between 1 and 4 seconds?
کے م
The object has decreasing acceleration and
increasing velocity.
The object has positive acceleration and eventually
stops.
The object has decreasing acceleration and
decreasing velocity.
The object has negative acceleration and eventually
stops.
Answers
Answer:
The object has decreasing acceleration and decreasing velocity.
A 50N force is applied to the free end of a spiral spring of force constant 100N/m. Calculate the work done by the force to stretch the spiral spring.
Answers
Explanation:
I solved it in the picture but I'm not a hundred percent sure

Block A, mass 250 g , sits on top of block B, mass 2.0 kg . The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between blocks A and B are 0.34 and 0.23, respectively. Block B sits on a frictionless surface. What is the maximum horizontal force that can be applied to block B, without block A slipping
Answers
Answer:
F = 69.3 N
Explanation:
For this exercise we use Newton's second law, remembering that the static friction force increases up to a maximum value given by
fr = μ N
We define a reference system parallel to the floor
block B ( lower)
Y axis
N - W₁-W₂ = 0
N = W₂ + W₂
N = (M + m) g
X axis
F -fr = M a
for block A (upper)
X axis
fr = m a (2)
so that the blocks do not slide, the acceleration in both must be the same.
Let's solve the system by adding the two equations
F = (M + m) a (3)
a =\(\frac{F}{ M+m}\)
the friction force has the formula
fr = μ N
fr = μ (M + m) g
let's calculate
fr = 0.34 (2.0 + 0.250) 9.8
fr = 7.7 N
we substitute in equation 2
fr = m a
a = fr / m
a = 7.7 / 0.250
a = 30.8 m / s²
we substitute in equation 3
F = (2.0 + 0.250) 30.8
F = 69.3 N
Do this for alot of points

Answers
1. A complete fitness and exercise program should incorporate three basic components: Endurance (Aerobic), Flexibility, and Strength. Each of these components has specific guidelines, which govern their effectiveness
-- Jax
How would the field lines change if one charges was tripled in magnitude?
Answers
The number of field lines entering a negative charge or exiting a positive charge is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charge. That is, the greater the magnitude of the charge denser would be the field lines around the charge.
Thus, when one of the charges is tripled, the field lines around that charge would increase.
a) Write the names of the materials used in the ohm law according to the Figure 1?
b) If the voltage of a circuit is 12 V and the resistance is 40 , What is the generated power?

Answers
Answer:
a. i. conducting wire
ii high-pass and low-pass filters
iii. Cobra-4 Xpert-link
iii. voltage source
b. Power generated is 3.6 W.
Explanation:
Ohm's law state that the current passing through a metallic conductor, e.g wire is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends, provided temperature is constant.
i.e V = IR
i. conducting wire
ii high-pass and low-pass filters
iii. Cobra-4 Xpert-link
iii. voltage source
b. Given that; V = 12 V and R = 40 Ohm's.
P = IV
From Ohm's law, I = \(\frac{V}{R}\)
So that;
P = \(\frac{V^{2} }{R}\)
= \(\frac{12^{2} }{40}\)
= \(\frac{144}{40}\)
= 3.6 W
The power is 3.6 W.
An 8000 kg car moving at a constant speed of 14m/s strikes a barrier. The two stick together and move for a while at a speed of 5m/s. What is the mass of the barrier?Show Your Solution using latex
Answers
ANSWER:
14400 kg
STEP-BY-STEP EXPLANATION:
Given:
Mass car (m1) = 8000 kg
The initial speed of the car (u1) = 14 m/s
The initial speed of the barrier (u2) = 0 m/s
The final speed of the car and barrier (v) = 5 m/s
We do the momentum balance to be able to determine the mass of the barrier just like this
\(\begin{gathered} m_1u_1+m_2u_2=(m_1+m_2)v \\ \\ \text{ We replacing} \\ \\ 8000\cdot14+m_2\cdot0=(8000+m_2)\cdot5 \\ \\ 112000=40000+5m_2 \\ \\ 5m_2=112000-40000 \\ \\ m_2=\frac{72000}{5} \\ \\ m_2=14400\text{ kg} \end{gathered}\)Therefore, the mass of the barrier is equal to 14400 kg
A car travels at an average speed of 60 km / h for 15 minutes. How far does the car travel in 15 minutes?
Answers
Answer:
15km
Explanation:
Given parameters:
Average speed = 60km/hr
Time taken = 15min
Unknown:
Distance = ?
Solution:
The distance traveled can de derived using the expression below;
Distance = Average speed x time taken
Now let us convert the time to hr;
60min = 1hr
15min = \(\frac{15}{60}\) = 0.25hr
Distance = 60km/hr x 0.25hr = 15km
Assume: The bullet penetrates into the block and stops due to its friction with the block. The compound system of the block plus the bullet rises to a height of 10 cm along a circular arc with a 18 cm radius.
Assume: The entire track is frictionless. A bullet with a m1 = 30 g mass is fired horizontally into a block of wood with m2 =
4.8 kg mass.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s^2.
Calculate the total energy of the composite system at any time after the collision. Answer in units of J.
Taking the same parameter values as those in Part 1, determine the initial velocity of the bullet. Answer in units of m/s.
Answers
Answer:
1)4.7334J
2)225.4m/s
Explanation:
v= the Velocity of both the bullet and the block after collision=?
H= Height of the bullet along circular arc= 10cm=0.1m
g= acceleration due to gravity= 9.81m/s^2
R= Radius of the circular arc= 18cm= 0.18m
m= Mass of the bullet= 30g= 0.03kg
M= Mass of the block = 4.8 kg
Using the law of conservation of energy
Potential energy of the system= Kinectic energy of the system
1/2 mv^2= mgh..............eqn(1)
But we have two mass m and M
We can write eqn(1) as
0.5(m+M)v^2= (m+M)gh ...........eqn(2)
If we make "v" subject of the formula we have
v = √2gh
Then substitute the values we have
= √2 x 9.81 x 0.1 = 1.40m/s
1) We can now calculate the total energy of the system after collision as
KE = 1/2(m+M)v^2
= 1/2 x (0.03+4.8) x (1.40)^2
KE = 4.7334J
Hence, the total energy of the composite system at any time after the collision is 4.7334J
2)to determine the initial velocity of the bullet.
From law of momentum conservation, which can be expressed as
m1u1+m2u2=(m1+m2)v
Where the initial Velocity of the bullet u1= ?
Final velocity of the bullet = 0
the Velocity of both the bullet and the block after collision=v= 1.40m/s
(0.03×u1) +(u×0)= (4.8+0.03)1.4
0.03u1=6.762
U1=225.4m/s
Hence, the initial velocity of the bullet is 225.4m/s
The total energy of the composite system at any time after the collision is 4.7334 J and initial velocity of the bullet is 225.4 m/s.1`
What is conservation of momentum?
Momentum of a object is the force of speed of it in motion. Momentum of a moving body is the product of mass times velocity.
When the two objects collides, then the initial collision of the two body is equal to the final collision of two bodies by the law of conservation of momentum.
Total energy of the composite system at any time after the collision-
The mass of the bullet is 30g and the mass of the wood block is 4.8 kg. Thus the total mass of these two is,
\(m=0.03+4.8\\m=4.83 \rm kg\)
As the compound system of the block plus the bullet rises to a height of 10 cm. Thus, the speed of it is,
\(v=\sqrt{2gh}\\v=\sqrt{2\times9.81\times0.1}\\v=1.4\rm m/s\)
Now, the total energy of the composite system at any time after the collision is equal to the kinetic energy. Therefore,
\(E=\dfrac{1}{2}mv^2\\E=\dfrac{1}{2}4.83(1.4)^2\\E=4.7334\rm J\)
Total energy of the composite system at any time after the collision is 4.7334 J.
The initial velocity of the bullet-The block was at rest initial, thus it has initial velocity of it is zero. Thus, the initial momentum of the bullet is equal to the final momentum of bullet and block. Therefore,
\(0.03\times u_o=4.83\times1.4\\u_o=225.4\rm m/s\)
Thus, the total energy of the composite system at any time after the collision is 4.7334 J and initial velocity of the bullet is 225.4 m/s.1`
Learn more about the conservation of momentum here;
https://brainly.com/question/7538238
E._____________________
Answers
15-letter words that start with e
electromagnetic
experimentation
electrophoresis
excommunication
extracurricular
ethnomusicology
epichlorohydrin
exemplification
electrodynamics
experimentalism
extralinguistic
electromyograph
electronegative
electrodialysis
ecclesiasticism
encephalography
electrokinetics
electropositive
electroanalysis
enterobacterium
eclaircissement
econometricians
econometrically
ecocatastrophes
ecclesiological
ecclesiologists
echinodermatous
echocardiograms
ecophysiologies
easygoingnesses
egocentricities
eggheadednesses
egregiousnesses
efficaciousness
effortfulnesses
effectualnesses
effectivenesses
egalitarianisms
educationalists
enterobacterial
enterocolitises
enterogastrones
enjoyablenesses
entomologically
entrepreneurial
envenomizations
environmentally
enumerabilities
encephalographs
encephalitogens
encephalopathic
enantiomorphism
enantiomorphous
emulsifications
endoparasitisms
endonucleolytic
endocrinologies
endocrinologist
enfranchisement
electroacoustic
electrification
electrochemical
electroanalyses
electrophoretic
electrophoresed
electrophoreses
electromyograms
electrodialytic
electrodeposits
electrodialyses
electrofishings
elaboratenesses
electrosurgical
electrowinnings
emancipationist
embryologically
employabilities
emotionlessness
extrajudicially
extraordinarily
externalization
extinguishments
extracellularly
exteriorization
externalisation
extensivenesses
extensibilities
extemporisation
extemporization
extendabilities
exquisitenesses
exsanguinations
experimentalist
expensivenesses
expeditiousness
expendabilities
expansivenesses
expressionistic
exponentiations
water pressurized to 450000 pa is flowing at 5.0m/s in a horizontal pipe which contracts to 1/3 its former area. what are the pressure and velocity of the water after the contraction?
Answers
the pressure of the water after the contraction is -50000 Pa (or 50 kPa below atmospheric pressure), and the velocity of the water after the contraction is 15.0 m/s.
The continuity equation states that the product of the cross-sectional area and the velocity of an incompressible fluid is constant along a pipe, so we can use it to relate the pressure and velocity before and after the contraction:
A₁v₁ = A₂v₂
where A₁ and v₁ are the area and velocity of the pipe before the contraction, and A₂ and v₂ are the area and velocity of the pipe after the contraction.
We can also use the Bernoulli equation, which relates the pressure and velocity of a fluid along a streamline:
P₁ + 1/2 ρv₁² = P₂ + 1/2 ρv₂²
where P₁ and v₁ are the pressure and velocity of the fluid before the contraction, and P₂ and v₂ are the pressure and velocity of the fluid after the contraction, and ρ is the density of the fluid, which we assume to be constant.
Solving for the pressure and velocity after the contraction, we can use the continuity equation to express v₁ in terms of v₂ and substitute it into the Bernoulli equation:
A₁v₁ = A₂v₂
v₁ = (A₂/A₁) v₂
P₁ + 1/2 ρ((A₂/A₁) v₂)² = P₂ + 1/2 ρv₂²
Simplifying and solving for P₂, we get:
P₂ = P₁ + 1/2 ρ(v₁² - v₂²)
Substituting the given values, we get:
A₂ = (1/3) A₁
v₁ = 5.0 m/s
P₁ = 450000 Pa
ρ = 1000 kg/m³
Using the continuity equation, we can find the value of v₂:
A₁v₁ = A₂v₂
v₂ = (A₁/A₂) v₁
v₂ = 3 × 5.0 m/s
v₂ = 15.0 m/s
Substituting this value into the Bernoulli equation, we can find the pressure P₂:
P₂ = P₁ + 1/2 ρ(v₁² - v₂²)
P₂ = 450000 Pa + 1/2 × 1000 kg/m³ × (5.0 m/s)² - (15.0 m/s)²
P₂ = 450000 Pa - 500000 Pa
P₂ = -50000 Pa
Learn more about velocity here:
https://brainly.com/question/17127206
#SPJ1
During the Egg Drop lab sim you manipulated several variables like height, egg mass and impact surface. Which varible combination would produce the biggest force of impact on the egg?
Large time of impact and small speed at impact
Small time of impact and small speed at impact
Large time of impact and large speed at impact
Small time of impact and large speed at impact
Answers
Varible combination that would produce the biggest force of impact on the egg (E). Small time of impact and large speed at impact.
IntroductionHi ! This problem is the application of the impulse to the change in momentum. Impulse is the total force applied in a certain time interval. Impulses can cause a change of momentum, because momentum itself is a mass that is affected by the velocity of an object. We know that velocity is a vector quantity easy to change its direction. The relationship between impulse and change in momentum is formulated by :
\( \sf{I = \Delta p} \)
\( \sf{F \cdot \Delta t = (m \cdot v') - (m \cdot v)} \)
\( \boxed{\sf{\bold{F \cdot \Delta t = m (v' -v)}}} \)
With the following condition :
I = impulse that given (N.s)\( \sf{\Delta p} \) = change of momentum (kg.m/s)F = force that given (N)m = mass of the object (kg)v = initial velocity (m/s)v' = final velocity (m/s)\( \sf{\Delta t} \) = interval of the time (s)ExplanationIn this case, to produce a great force, then here, we refine the formula again to:
\( \sf{F \cdot \Delta t = m (v' -v)} \)
\( \boxed{\sf{F = \frac{m (v' -v)}{\Delta t}}} \)
Remember, when the result is a comparison, then the numerator part will be proportional to the force. The number that is the denominator will have an inversely proportional value. For this reason, if you want a great force, then:
Increase the mass of the egg or choose a heavier egg, this is because the mass will be proportional to the force.Increase the change of velocity, this occurs because the change in velocity of the egg is also proportional to the force.Reduce the time interval (you can throw it at close range), this happens because the value of time is inversely proportional to the value of the force.ConclusionVarible combination that would produce the biggest force of impact on the egg (E). Small time of impact and large speed at impact.
honey solidifies from the bottom whereas water from the top. Why?
Answers
Answer:
it is due to anamolous expansion of water as water cools from 4dg.c to 0dg.c. it expand making ice lighter than water to float
A motorcycle stoop is at a traffic light, when the light turns green, the motorcycle accelerates to a speed of 78 km/h over a distance of 50 m. What is the average acceleration of the motorcycle over this distance?
Answers
The average acceleration of the motorcycle over the given distance is approximately 9.39 m/s².
To calculate the average acceleration of the motorcycle, we can use the formula:
Average acceleration = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time
First, let's convert the final velocity from km/h to m/s since the distance is given in meters. We know that 1 km/h is equal to 0.2778 m/s.
Converting the final velocity:
Final velocity = 78 km/h * 0.2778 m/s = 21.67 m/s
Since the motorcycle starts from rest (initial velocity is zero), the formula becomes:
Average acceleration = (21.67 m/s - 0 m/s) / time
To find the time taken to reach this velocity, we need to use the formula for average speed:
Average speed = total distance/time
Rearranging the formula:
time = total distance / average speed
Plugging in the values:
time = 50 m / 21.67 m/s ≈ 2.31 seconds
Now we can calculate the average acceleration:
Average acceleration = (21.67 m/s - 0 m/s) / 2.31 s ≈ 9.39 m/s²
To learn more about acceleration
https://brainly.com/question/2303856
#SPJ8
4.
What is the role of a compressor in an air conditioner?
O It exchanges warm air for cold air and blows it into the room.
O It increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant.
O It absorbs heat from the room and blows it outside.
Answers
Answer:
b
Explanation:
it compresses hot air turning into cool air almost like a reverse tornado
Answer:
It increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant.
Explanation:
The purpose of the compressor is to circulate the refrigerant in the system under pressure, this concentrates the heat it contains. At the compressor, the low pressure gas is changed to high pressure gas.
what is fish farming? what are the disease found in its.
Answers
Define power and describe how to determine power.
Answers
Answer:Power is a measure of the amount of work that can be done in a given amount of time. Power equals work (J) divided by time (s). The SI unit for power is the watt (W), which equals 1 joule of work per second (J/s). Power may be measured in a unit called the horsepower
Explanation:
Answer:
Explanation:Power equals work (J) divided by time (s).
Two sound waves W1 and W2, of the same wavelength interfere destructively at point P. The waves originate from two in phase speakers. W1 travels 36m and W2 travels 24m before reaching point P. Which of the following values could be the wave length of the sound waves?
a. 24m
b. 12m
c. 6m
d. 4m
Answers
Answer:
a. 24 m
Explanation:
Destructive interference occurs when two waves arrive at a point, out of phase. In a completely destructive interference, the two waves cancel out, but in a partially destructive interference, they produce a wave with a time varying amplitude, but maintain a wavelength the wavelength of one of the original waves. Since the two waves does not undergo complete destructive interference, then the possible value of the new wave formed can only be 24 m, from the options given.
i
e. network executives make hasty
When winding an old clock, it is important not to overwind it. Over-
winding occurs when the mainspring is almost fully wound, but the
operator continues to turn the winding key. This causes the main
spring to coil too tight, and might even break it.
110. This paragraph best supports the statement that
a. clocks have changed over the years.
b. old-fashioned clocks become fragile with age.
c. old-fashioned clocks were operated by an internal spring.
d. overwinding clocks used to be a common mistake.
e. time flies when you're having fun.
Answers
The paragraph primarily discusses the concept of overwinding old clocks and its consequences, indicating that overwinding clocks used to be a common mistake. Here option D is the correct answer.
The paragraph explains that overwinding occurs when the mainspring is almost fully wound, but the operator continues to turn the winding key, resulting in the spring coiling too tightly or even breaking.
This suggests that overwinding was a mistake commonly made in the past when operating old-fashioned clocks. The other options, such as clocks changing over the years or clocks becoming fragile with age, are not directly addressed in the paragraph and are therefore less supported.
The option e. "time flies when you're having fun" is unrelated to the paragraph and can be disregarded as an irrelevant answer choice. Hence option D is the correct answer.
To learn more about overwinding
https://brainly.com/question/20709424
#SPJ8
What best describes the speed of light waves in solids, liquids, and gases?
The speed is fastest in solids.
The speed is fastest in liquids.
The speed is fastest in gases.
The speed is the same in all matter.
Answers
Answer: It’s fastest in gases. Letter C !
Explanation:
Answer:
its c
Explanation:
The girl in the diagram is accelerating down the hill. What is the girl's acceleration?
m = 50kg
f net = 150 N right
(Hint: Use the formula a=\frac{F}{m}a= m F.)
A. a = 3 m/s2 A. is correct.
B. a = 5 m/s2
C. a = 150 m/s2
D. a = 6 m/s2
Answers
Answer:
150÷50=3 and the answer is letter A76. Two electric charges -6μC and
+6μC are placed respectively in two
points A and B distant of 1m apart. The
electric field is null at the point C:
A.Located in the middle of the
segment AB
B.Located outside segment AB at
1m from A.
C.Located outside segment AB at
1m from B
D.Outside the line AB
E.No answer is right.
Answers
A. The electric field is null at the point C; located in the middle of the
segment AB.
What is electric field?Electric field is the region of space where the influence of electric force is felt.
Electric field at the middle of ABE = kq/r²
where;
r is the middle of AB = 0.5 mE(+6μC) = (9 x 10⁹ x 6 x 10⁻⁶) / (0.5²)
E(+6μC) = +216,000
E(-6μC) = (9 x 10⁹ x 6 x 10⁻⁶) / (0.5²)
E(-6μC) = -216,000
Sum of the electric field at the middle of ABE(net) = E(+6μC) + E(-6μC)
E(net) = 216,000 - 216,000 = 0
Thus, the electric field is null at the point C; located in the middle of the
segment AB.
Learn more about electric field here: https://brainly.com/question/26199225
#SPJ1
Two small objects A and B are fixed in place and separated by a distance of 3.00 cm in a vacuum. Object A has a
charge of +2.00 С and object B has a charge of -2.00 C. How many electrons must be removed from object A and
placed on object B to make the electrostatic force into an attractive force with a magnitude of 68.0 N.
Answers
The number of electrons that must be removed from object A and placed on object B is 1.24 * \(10^{19}\)
We know that,
E = k \(q_{1}\) \(q_{2}\) / r²
where,
E = Electrostatic force
k = Coulomb's constant
\(q_{1}\), \(q_{2}\) = Point charges
r = Distance between two charges
Given that,
\(q_{1}\) = 2 + ne C
\(q_{2}\) = - 2 - ne C
r = 3 cm
k = 9 * \(10^{9}\) N m² / C²
E = - 68 N ( Since it is attractive )
- 68 = 9 * \(10^{9}\) ( 2 - ne ) ( - 2 + ne ) / ( 3 * \(10^{-2}\) )²
68 * \(10^{-4}\) / 3 * \(10^{9}\) = ( 2 - ne )²
2.27 * \(10^{-12}\) = ( 2 - ne )²
1.5 * \(10^{-6}\) = 2 - ne
ne = 1.98
n = 1.98 / 1.6 * \(10^{-19}\) = 1.24 * \(10^{19}\)
The given problem is an electrostatic attractive force because the two point charges are unlike charges. If the charges are like, then the electrostatic force will be repulsive.
Therefore, the number of electrons that must be removed from object A and placed on object B is 1.24 * \(10^{19}\)
To know more about electrostatic forces
https://brainly.com/question/9774180
#SPJ1
7 2. Name the independent variable: 3. Name the dependent variable:
Answers
Answer:
independent variable is found on the x axis while dependent variable is found on the y axis
A rock, a book and a can of soda all have the same mass. Which of the following best describes their relationship?
A. They are all the same size
B. They each contain the same amount of matter.
C. They are each made of the same element.
D. They each occupy the same amount of space.
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
d
A rock, a book and a can of soda all have the same mass. They each contain the same amount of matter.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Since the rock, book, and can of soda all have the same mass, it means that they contain the same amount of matter, regardless of their size or the material they are made of.
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, so if their masses are equal, it implies that the quantity of matter is the same in each of them.
The size, shape, and material composition can be different for each object, but their masses remain the same in this scenario.
Hence, A rock, a book and a can of soda all have the same mass. They each contain the same amount of matter.
Hence, the correct option is D.
To know more about matter here
https://brainly.com/question/32009895
#SPJ2
what evidence supports the information consolidation theory?
PLEASE HELP ME ITS DUE NEXT PERIOD
Answers
Explanation:
Memory loss in retrograde amnesia has long been held to be larger for recent periods than for remote periods, a pattern usually referred to as the Ribot gradient. One explanation for this gradient is consolidation of long-term memories. Several computational models of such a process have shown how consolidation can explain characteristics of amnesia, but they have not elucidated how consolidation must be envisaged. Here findings are reviewed that shed light on how consolidation may be implemented in the brain. Moreover, consolidation is contrasted with alternative theories of the Ribot gradient. Consolidation theory, multiple trace theory, and semantization can all handle some findings well but not others.
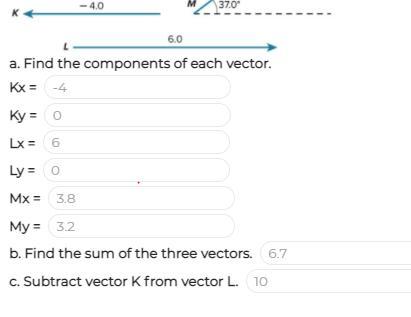
 1–Find the components of each vector
Kx=
Ky=
Lx=
Ly=
Mx=
My=
2–find the sum of the three vectors
3–subtract vector K from vector L
Please write correct answers❤️i will give you 20 points and brainiest answer

Answers
Answer:
ANSWERS ARE 100 % correct
Explanation:
trust me
5. Hilda is trying to move a 40 kg couch across a level floor and pushes with a horizontal force of
150 N, but the couch does not move. What is the minimum coefficient of static friction with the
floor? Assume the acceleration due to gravity is g = 9.8 m/s2
Answers
The minimum coefficient of static friction with the floor is 0.3846.
To find the minimum coefficient of static friction with the floor, we need to consider the forces acting on the couch. In this case, the force of gravity is pulling the couch downward with a magnitude of mg, where m is the mass of the couch (40 kg) and g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s²).
Since the couch does not move, the force of static friction between the couch and the floor must be equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the horizontal pushing force of 150 N.
Therefore, we have the equation F_friction = F_push, where F_friction is the force of static friction.
The force of static friction can be calculated using the formula F_friction = μ_s * N, where μ_s is the coefficient of static friction and N is the normal force.
Since the couch is on a level floor and is not accelerating vertically, the normal force N is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force of gravity, which is mg.
Substituting the values into the equation, we have μs * mg = 150 N.
Solving for μs, we get μs = 150 N / (mg).
Substituting the given values, we have μ_s = 150 N / (40 kg * 9.8 m/s²).
Simplifying, we find that μs = 0.3846.
For more such questions on friction visit:
https://brainly.com/question/24386803
#SPJ8
A closed vessel can sink to a depth of 41.0 m in the water before the external pressure crushes it. To what depth could this same contained be immersed in a deep vat of mercury (density = 13.6 x 10^3 kg/m^3) without it being crushed?
Answers
The vessel can be immersed to a depth of 0.3006 m in the deep vat of mercury without being crushed.
The question requires us to determine the depth to which a closed vessel that can sink to a depth of 41.0 m in water before the external pressure crushes it could be immersed in a deep vat of mercury without being crushed. We can determine this using the concept of pressure.Pressure is defined as the amount of force acting per unit area. Pressure is given by the formula:
P = F/A,
where P is pressure, F is force, and A is area. Since the area remains constant, we can say that pressure is directly proportional to force. Thus, the greater the force acting on an object, the greater the pressure exerted on the object. The pressure exerted by a liquid depends on the density of the liquid, the depth of the liquid, and the acceleration due to gravity. This can be expressed using the formula:
P = ρgh,
where P is pressure, ρ is density, g is acceleration due to gravity, and h is depth. Let us first calculate the pressure exerted by the water at a depth of
41.0 m:ρ of water = 1000 kg/m³g = 9.81 m/s²h = 41.0 m
Substituting these values in the formula, we get:
P = ρgh= (1000 kg/m³)(9.81 m/s²)(41.0 m)= 405570 Pa
Now, we need to determine the depth to which the vessel can be immersed in mercury without being crushed. Let us call this depth "d". The pressure exerted by the mercury at this depth is equal to the pressure exerted by the water at a depth of 41.0 m. Thus, we can equate the two pressure values:
ρ of mercury = 13600 kg/m³g = 9.81 m/s²P = 405570 Pa
Substituting these values in the formula, we get:ρgh = P(13600 kg/m³)(9.81 m/s²)(d) = 405570 PaSolving for d, we get:d = 0.3006 m.
For more question vat
https://brainly.com/question/14480417
#SPJ8
