Answers
Answer:
0.117m/s
Explanation:
Speed = distance/time
Given
Distance (radius of string) = 15.3cm
Convert to metres
15.3cm = 15.3/100
15.3cm = 0.153m
Period (time) = 1.31s
Substitute into the formula
Speed of the rubber = 0.153/1.31
Speed of the rubber = 0.117m/s
Hence the speed of the rubber block in m/s is 0.117m/s
Related Questions
Which property of metals allows aluminum to be flattened into thin sheets of aluminum foil? shininess malleability brittleness hardness
Answers
Malleability
Knowledge Enhancer★ Malleability: The property which allows the metal to be hammered into thin sheets is called malleability.
★ Brittleness: The property due to which non-metals break down on hammering is called brittleness .
★ Ductility: The property which allows the metal to be drawn into wires is called dutility.
Answer:
The answer to this question is malleability.
Plz help w answer 1:/ confused ash

Answers
Answer:
I would say d I had the same question yesterday and I got it correct so hope that helps

A rocket has been fired upward to launch a stellite in its orbit name two forces acting on the rocket immediately after leaving the launching pad
Answers
Two forces acting on the rocket immediately after leaving the launching pad are the gravitational force and the thrust force.
1. Gravitational Force: The gravitational force is the force exerted by the Earth on the rocket due to their mutual gravitational attraction. It acts downward and is responsible for the rocket's weight.
This force can be represented by the equation Fg = mg, where Fg is the gravitational force, m is the mass of the rocket, and g is the acceleration due to gravity. The gravitational force acts to pull the rocket downward, opposing its upward motion.
2. Thrust Force: The thrust force is the force generated by the rocket's engines as they expel exhaust gases in the opposite direction. It acts upward and propels the rocket forward.
The magnitude of the thrust force depends on factors such as the design of the rocket engines, the amount of fuel burned, and the rate of exhaust gas expulsion. The thrust force must be greater than or equal to the gravitational force for the rocket to overcome Earth's gravity and achieve upward acceleration.
Initially, when the rocket is launched, the thrust force is at its maximum while the gravitational force remains constant. As the rocket gains altitude, the gravitational force decreases slightly due to the increasing distance from the Earth's center.
However, the thrust force continues to be the dominant force propelling the rocket upward.
It's important to note that other forces such as air resistance and wind may also act on the rocket, but immediately after leaving the launching pad, these forces are typically negligible compared to the gravitational force and thrust force.
for more questions on gravitational force
https://brainly.com/question/27943482
#SPJ8
A 2190 kg car moving east at 10.7 m/s collides with a 3210 kg car moving east. The cars stick together and move east as a unit after the collision at a velocity of 5.46 m/s. a) What is the decrease in kinetic energy during the collision
Answers
45152 Joules
Explanation
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.its formula is
\(\begin{gathered} E_k=\frac{1}{2}mv^2 \\ \text{where m is the mass of the object and v its sp}eed \end{gathered}\)also, A collision in which the objects stick together is sometimes called perfectly inelastic because it reduces internal kinetic energy more than does any other type of inelastic collision,
When two objects collide under inelastic colliition, the final velocity with which the object moves is given by
\(\begin{gathered} V=\frac{(M_1V_1+M_2V_2}{M_1+M_2} \\ \end{gathered}\)Where,
V= Final velocity
M1= mass of the first object in kgs
M2= mas of the second object in kgs
V1= initial velocity of the first object in m/s
V2= initial velocity of the second object in m/s
then, replace
\(\begin{gathered} V=\frac{(M_1V_1+M_2V_2}{M_1+M_2} \\ 5.46=\frac{(2190\cdot10.7)+(3210\cdot V_2)}{2190+3210} \\ 5.46=\frac{23433+(3210\cdot V_2)}{5400} \\ 5400\cdot5.46=23433+(3210\cdot V_2) \\ 29484=23433+(3210\cdot V_2) \\ 29484-23433=3210V_2 \\ 6051=3210V_2 \\ \frac{6051}{3210}=\frac{3210V_2}{3210} \\ 1.88=V_2 \end{gathered}\)it means the velocity of the second car is 1.88 m/s
Step 2
a)Now, let's find the total kinetic energy before the collition
\(\begin{gathered} E_k=\frac{1}{2}mv^2 \\ E_1=\frac{1}{2}(2190kg)(10.7)^2 \\ E_1=1252366\text{ Joules} \\ \text{now, the car 2} \\ E_2=\frac{1}{2}(3210)(1.88)^2 \\ E_2=5672 \end{gathered}\)so, the total is
\(\begin{gathered} E_{total\text{ }}\text{= 125366 Joules +5672.712 JOules} \\ E_{total\text{ }}\text{=131038} \end{gathered}\)b) now, the total energy after the collition
Let
m=m1+m2=2190+3210=5400kg
v=5.46
replace
\(\begin{gathered} E_k=\frac{1}{2}mv^2 \\ E_t=\frac{1}{2}(5400)(5.46)^2 \\ E_t=85885.92\text{ Joules} \end{gathered}\)C) finally, the decrease of kinetic energy is the difference to those values
\(\text{Decrease}=131038-85556=45152.08\text{ Joules}\)hence, the answer is 45152 Joules
I hope this helps you
(a) In Coulomb scattering of 7.50-MeV protons by a target of 'Li, what is the energy of the elastically scattered protons at 90°? (b) What is the energy of the inelastically scattered protons at 90° when the 'Li is left in its first excited state (0.477 MeV)?
Answers
Answer:
First the charge is given 7.50×10^-6
Explanation:
so that we have
\(90 \)
so that their is no cross sectional area of this anglethen the direction is one is left and other one is right so thats my hint



For every particle there is a corresponding ______________.
Answers
Answer:
Anti-Particle
The image blow shows a certain type of global wind:
What best describes these winds? Polar easterlies caused by air above poles being relatively warmer.
Polar easterlies caused by air above poles being relatively cooler.
Trade winds caused by air above equator being relatively warmer.
Trade winds caused by air above equator being relatively cooler.

Answers
Answer:
i got u its a
Explanation:
What are the vertical bars through the data points in this graph?
A. y-axis labels
B. error bars
C. chart junk
D. tick marks
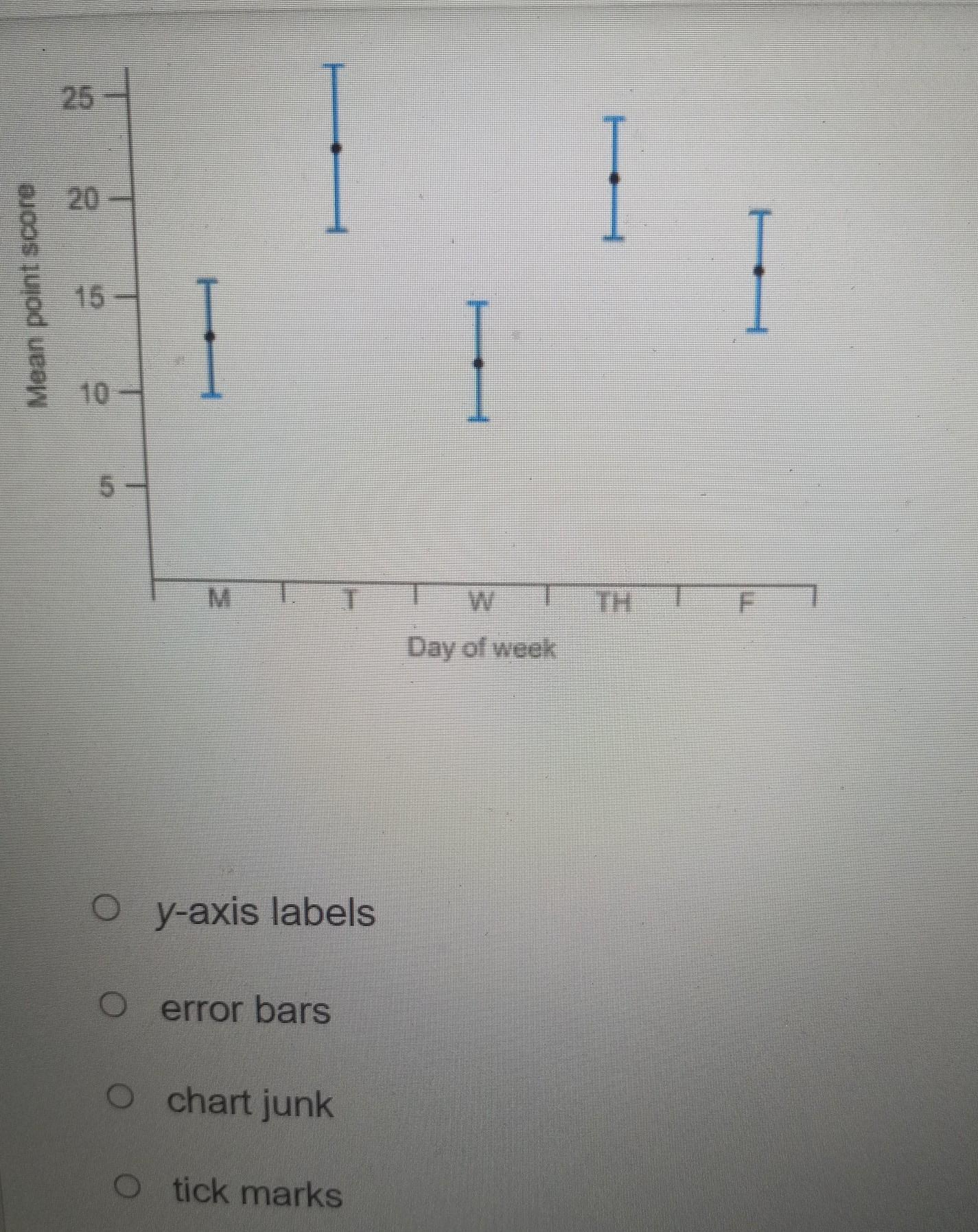
Answers
the characteristics of the graphs we can find that the correct answer is:
B. error bars
Graph is a method of grouping the experimental results in such a way that they can be easily analyzed, in the different types of graphs the experimental values of the points are plotted and if the errors of the measurements at each point are known.
The errors of each point are plotted in the form of bars bounded both by excess and by default, above each plotted point.
Let's analyze the different claims;
A. false The y-axis labels written on this axis
B. True. These are the error bar at each experimental point
C. False. They are not adornments or distractions, they are an important part of the information on the chart.
D. False. The division marks are on the y-axis
In conclusion, using the characteristics of the graphs, we were able to find the correct answer is:
B. Error bars
Learn more about error bars here:
https://brainly.com/question/15859938
A double slit experiment is conducted in air using a laser at 532nm and a slit separation of 20um. What happens to the fringe spacing if the entire experiment is now immersed in water?
A. The fringe spacing will remain the same
B. The fringe spacing will increase
C. The fringe spacing will decrease
Answers
Answer:
Option B - The fringe spacing will increase
Explanation:
We are given;
Wavelength; λ = 532nm
slit separation; d = 20um
For double-slit experiment, the fringe width is given by the expression;
β = λD/d
Where;
β is the fringe width
λ is the wavelength
D is the distance between the screen and the slit
d is the slit separation
Now, when immersed in water, the slit separation distance will decrease.
Now, from the fringe width equation, when "d" decreases, it means that we will have a bigger value of fringe width.
Thus, as slit separation decreases, the fringe width increases.
The image below shows sound waves traveling through air.
Which point is the source of the sound?

Answers
The point on the image that is the source of the sound / sound waves travelling would be B. 2.
Where do sound waves originate ?When a sound is produced, such as a musical note or spoken word, it initiates a disturbance at the source, which sets the surrounding particles in motion. As these particles oscillate back and forth, they generate regions of compression and rarefaction, resulting in the formation of longitudinal waves.
The propagation of sound waves emanates from a central source, radiating outward in a spherical pattern, thereby creating an expanding wavefront. This fundamental principle of wave behavior stems from the point-source nature of sound waves, wherein they originate from a central locus and disperse in all directions.
This central source in the image is 2.
Find out more on sound waves at https://brainly.com/question/15680946
#SPJ1
Consider the circuit in Figure 5 with e(t) = 12sin(120pit) V. When S1 and S2 are
open, i leads e by 30°. When SI is closed and S2 is open, i lags e by 30°. When S1 and S2 are closed, i has an amplitude 0.5A. What are R, L, and C?

Answers
Based on the information, it should be noted that the resistance R is 0.5 Ω.
How to calculate the resistanceWhen S1 and S2 are open, i leads e by 30°. In this case, the circuit consists of only the inductor (L) and the capacitor (C) in series. Therefore, the impedance of the circuit can be written as:
Z = jωL - 1/(jωC)
Since i leads e by 30°, we can express the phasor relationship as:
I = k * e^(j(ωt + θ))
Z = jωL - 1/(jωC) = j(120π)L - 1/(j(120π)C)
Re(Z) = 0
By equating the real parts, we get:
0 = 0 - 1/(120πC)
Let's assume that there is a resistance (R) in series with the inductor and capacitor. The impedance equation becomes:
Z = R + jωL - 1/(jωC)
Z = R + jωL
Im(Z) = ωL > 0
Substituting the angular frequency and rearranging the inequality, we have:
120πL > 0
L > 0
This condition implies that the inductance L must be greater than zero.
When S1 and S2 are closed, i has an amplitude of 0.5 A. In this case, the impedance is:
Z = R + jωL - 1/(jωC)
Since the amplitude of i is given as 0.5 A, we can express the phasor relationship as:
I = 0.5 * e^(j(ωt + θ))
By substituting this phasor relationship into the impedance equation, we can determine the value of R. The real part of the impedance must be equal to R:
Re(Z) = R
Since the amplitude of i is 0.5 A, the real part of the impedance must be equal to 0.5 A: 0.5 = R
Therefore, the resistance R is 0.5 Ω.
Learn more about resistance on
https://brainly.com/question/17563681
#SPJ1
A wheel accelerates from rest to 48 rad/s at a uniform rate of 57 rad/s^2. Through what angle (in radians) did the wheel turn while accelerating?
Answers
Answer:
θ = 20.21 radians
Explanation:
Using the expression to het the angle;
w² = wi² + 2∝θ
w is the final angular velocity
wi is the initial angular velocity
θ is the angle
∝ is the angular acceleration
Substitute the given values into the formula;
w² = wi² + 2∝θ
48² = 0² + 2(57)θ
2304 = 114θ
θ = 2304/114
θ = 20.21 radians
Which body system is responsible for preparing the body for fight or flight?
Answers
Answer:
The sympathetic nervous system, part of the autonomic nervous system, also known as the involuntary system, is in charge of the fight-or-flight response, a response to the stress that leads to a hormonal cascade that boosts alertness and heart rate to prepare the body to respond.
Explanation:
Answer:
Rapid heart rate and breathing: Heartbeat and respiration rate increase to provide the body with the energy and oxygen needed to fuel a rapid response to danger. 2 Trembling: The muscles tense and become primed for action, which can cause trembling or shaking.
A ball is thrown horizontally at a speed of 24 meters per second from the top of a cliff. If the ball hits the ground 6.0 seconds later, approximately how high is the cliff? ( EASY QUESTION.. PLZZ HELPPP MEEE I WILL MARK YOU THE BRAINLIEST PLZZ)
Answers
Answer:
144 meters
Explanation:
the ball is thrown with a speed of 24 meters per second right so if the ball reaches the ground in 6 seconds. the hight of the cliff must be S=v.t
S (height cliff)=24m/s×6s=144
The phase velocity of transverse waves in a crystal of atomic separation a is given byy = csin(ka/2) pka/2 1. What is the dispersion relation e(k)? 2. What is the group velocity as a function of k?
Answers
Answer:
a
e(k) = \frac{2a}{c} * sin (\frac{k*a}{2} )
b
G_{v} = \frac{d e(k ) }{dk } = \frac{a^2}{c} * cos (\frac{k* a}{2} )
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The velocity of transverse waves in a crystal of atomic separation is
\(b_y = c \frac{sin (\frac{k*a}{2} )}{\frac{k*a}{2} }\)
Generally the dispersion relation is mathematically represented as
\(e(k) = b_y * k\)
=> \(e(k) = c \frac{sin(\frac{k*a}{2} ) }{ \frac{k*a}{2} } * k\)
=> \(e(k) = c * \frac{sin (\frac{k_a}{2} )}{ \frac{a}{2} }\)
=> \(e(k) = \frac{2a}{c} * sin (\frac{k*a}{2} )\)
Generally the group velocity is mathematically represented as
\(G_{v} = \frac{d e(k ) }{dk } = \frac{a^2}{c} * cos (\frac{k* a}{2} ) \)
n unit-vector notation, what is the torque about the origin on a particle located at coordinates (0, −4.0 m, 3.0 m) if that torque is due to (a) force F1 with components F1x = 2.0 N, F1y = F1z = 0, and (b) force F2 with components F2x = 0, F2y = 2.0 N, F2z = 4.0 N?
Answers
n unit vector notation, -22j is the torque about the origin on a particle located at coordinate (o, -4.0m, 3.0m)
Torque is defined as the force that can cause an object to rotate along an axis is measured as torque. Estimate the angle between the vector connecting the force's application point and the pivot point and the direction of the applied force. You may calculate the torque by multiplying r by F and sin.
T=R (distance) x F (Force)
R=-4j+3k
F=2J
Hence, t= R x F vector product
=(-4j+3k)x2j
=-4x2x(y x J)
=+3x2y(k x r)
=-8x(-k)+6j
=(6j+8k) nm
b) F^2=2J+4K
Hence, t=r x f^2
=(-4j+3k)x(2j+4k)
=0-16( J x k)+6(K x J)+0
=-16j-6j
=-22j
To learn more about vector notation
https://brainly.com/question/28564974
#SPJ4
If you drop an egg off of the Empire State Building, which of the following things will happen first?
O The egg will appear to hover
O Gravity and drag will fall into balance
O Drag will increase
O The net force will be zero
Answers
O Gravity and drag will fall into balance.
Explanation:
When an object, such as an egg, is dropped from a height, the force of gravity causes it to accelerate downwards. As the egg falls, it experiences air resistance, which opposes its motion and slows it down. This air resistance is called drag. As the speed of the falling egg increases, so does the force of drag, until it eventually becomes equal to the force of gravity. At this point, the egg will stop accelerating and will fall at a constant speed.
So, the first thing that will happen is that gravity and drag will fall into balance. The egg will continue to fall at a constant speed until it reaches the ground, at which point it will experience a sudden stop and likely break due to the impact.
How many electron flow through a light bulb each second if the current flow through the light bulb 0.75A.The electric charge of one electron is 1.6 x 10-19C
Answers
Answer:
\(n=4.68\times 10^{18}\)
Explanation:
The current through the bulb, I = 0.75 A
We need to find the number of electrons flowing per second. We know that the electric current is given by :
\(I=\dfrac{ne}{t}\\\\n=\dfrac{It}{e}\\\\n=\dfrac{0.75\times 1}{1.6\times 10^{-19}}\\\\n=4.68\times 10^{18}\)
So, there are \(4.68\times 10^{18}\) electrons flowing per second.
There are "\(4.68\times 10^{18}\)" electron flowing per second.
Electric charge:Whenever retained inside an electric as well as the magnetic field, this same basic physical attribute of matter which thus permits it to perceive a force, is considered as Electric charge.
According to the question,
Current flow, I = 0.75 A
Electric charge of one electron, e = 1.6 x 10⁻¹⁹ C
As we know the relation,
Current, I = \(\frac{ne}{t}\)
or,
→ n = \(\frac{It}{e}\)
By substituting the given values in the above formula, we get
= \(\frac{0.75\times 1}{1.6\times 10^{-19}}\)
= \(4.68\times 10^{18}\)
Thus the approach above is appropriate.
Find out more information about electric charge here:
https://brainly.com/question/14372859
Suppose the same car had at one point an acceleration of 12m/s^2 and an initial velocity of 8m/s. After 2 seconds, what would be the car's final velocity
Answers
Answer: 32 m/s
Explanation: v = u + at
= 8 + 12*2
= 8 + 24
= 32 m/s
How can we show that air can do work?
Answers
Air can do work when it exerts a force on an object and causes it to undergo displacement. The ability of air to do work is evident in various phenomena, such as wind pushing sails, fans moving objects, and air pressure powering pneumatic systems.
Air can do work through its ability to exert a force over a distance. Work is defined as the transfer of energy that occurs when a force is applied to an object and it undergoes displacement in the direction of the force. When air is in motion, it possesses kinetic energy and can exert a force on objects in its path, thus performing work.
To understand how air can do work, we can consider the example of a moving fan. When a fan is turned on, the blades start to rotate, creating a flow of air. As the air moves, it carries kinetic energy. When the moving air encounters an object, such as a piece of paper, the air molecules collide with the paper's surface and exert a force on it. This force causes the paper to move and displaces it from its initial position.
The work done by the air can be calculated using the equation:
Work = Force * Distance * cos(θ)
Where Force is the magnitude of the force exerted by the air, Distance is the displacement of the object, and θ is the angle between the direction of the force and the displacement.
In the case of air doing work on an object, the force exerted by the air is perpendicular to the direction of motion, resulting in θ = 90 degrees. Since cos(90) = 0, the equation simplifies to:
Work = Force * Distance * 0
Therefore, the work done by the air on the object is zero when the force exerted by the air is perpendicular to the displacement.
However, if the force exerted by the air is not perpendicular to the displacement, such as when blowing air at an angle to move an object, then work is performed. The air exerts a force on the object and causes it to move in the direction of the force, resulting in the transfer of energy.
For more such information on: work
https://brainly.com/question/25573309
#SPJ8
what is the term for an object used to observe the state of rest or motion?
Answers
Answer:
im pretty sure it's inertia
Explanation:
When Jim lifts a (previously stationary) bowling ball using a constant 72 N (↑) Force, it rises 1.0 m in 3.0 s.
a) compute the ball’s acceleration.
Answers
Explanation:
By using the formula :
\(s = ut + \frac{1}{2} at {}^{2} \)
where;
S = distance
u = initial velocity
t = time taken
a = acceleration
Plug in all the information we have,
\(1 = 0 + \frac{1}{2} a(3) {}^{2} \)
therefore :
\(a = \frac{2}{9} ms {}^{ - 2} \)
a roller coaster weighs 2000 kg This ride includes an initial vertical drop of 59.3 m.
Assume that the roller coaster has a speed of nearly zero as it crests the top of the hill.
If the track was frictionless, find the speed of the roller coaster at the bottom of
the hill.
Answers
The speed of the roller coaster at the bottom of the hill if the track was frictionless is 34.04 m/s.
Given that the weight of the roller coaster is 2000 kg and the initial vertical drop of the ride is 59.3 m. We are to find the speed of the roller coaster at the bottom of the hill if the track was frictionless.We know that the roller coaster will lose potential energy due to the vertical drop. Assuming there is no friction, the potential energy will be converted into kinetic energy at the bottom of the hill.Considering the conservation of energy between the potential and kinetic energy, we can set the initial potential energy equal to the final kinetic energy. We can use the formula to calculate potential energy, which is PE = mgh where m = 2000 kg, g = 9.8 m/s², and h = 59.3 m. Therefore,PE = 2000 kg × 9.8 m/s² × 59.3 m = 1,157,924 JWe can use the formula to calculate kinetic energy, which is KE = 1/2mv² where m = 2000 kg and v is the final velocity. Therefore,KE = 1/2 × 2000 kg × v².The total energy remains constant as we know there is no friction. Therefore the final kinetic energy will be equal to the initial potential energy,1,157,924 J = 1/2 × 2000 kg × v²v² = (2 × 1,157,924 J) / 2000 kgv² = 1157.924v = √1157.924v = 34.04 m/s.
for such more questions on speed
https://brainly.com/question/13943409
#SPJ8
You serve a volleyball with a mass of 2.1 kg. The ball leaves your hand with a speed of 2.1 m/s. The
ball has ____
energy. Calculate it.
Answers
Answer:
4.6 Joules
Explanation:
K=1/2*MV^2
1/2 * 2.1kg * 2.1^2m/s
==4.6305 Joules
simplified to 4.6 Joules
Which scenario is an example of the transfer of thermal energy by
conduction?
A. Chicken eggs are warmed by an infrared lamp that is placed above
them.
B. A person swimming in a pool becomes become cooler.
OC. A hot sidewalk cools down at night as it warms the surrounding
air.
D. Warm water rises inside a tea kettle as cooler water sinks.
SUBMIT
Answers
The scenario that is an example of the transfer of thermal energy by conduction is D. Warm water ascends inside a tea pot as cooler water sinks.
Conduction is the transfer of heat through a material without the bulk motion of matter. In the case of a tea kettle, the heat source (such as a stove) heats the metal of the kettle, which then conducts the heat to the water inside the kettle.
The hot water molecules transfer their thermal energy to the cooler water molecules through direct contact, which causes the cooler water to become denser and sink while the warmer water becomes less dense and rises.
This creates a convection current, which further distributes the thermal energy within the water.
Option A describes the transfer of thermal energy by radiation, where electromagnetic waves (such as infrared light) transfer energy from the source to the eggs without any direct contact.
Option B describes the transfer of thermal energy by convection, where the cooler water in the pool sinks to the bottom and is replaced by warmer water rising to the surface.
Option C describes the transfer of thermal energy by radiation and convection, where the hot sidewalk radiates heat to the surrounding air, which then rises and is replaced by cooler air.
For more such questions on conduction, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/893656
#SPJ11
A paperboy rode his bike at 10 m/s. After being chased by a dog for 5 seconds, he was traveling 16m/s. What is his acceleration?
Answers
Answer:
1.2 m/s^2
Explanation:
acceleration = change in velocity / change in time
= 6 m/s / 5 sec = 1.2 m/s^2
What is the powder taking the shape of?
The magnetic field
The poles
A snowman
A star
Answers
The powder takes the shape of a magnetic field.
What is the particle shape of powder?Powder morphology is connected to the shape and size of powder particles and is strongly dependent on the manufacturing methods. For example, mechanical alloying or mechanical milling leads to unevenly shaped powder particles, while gas dissipation leads to spherically shaped particles.
Atomized metal powder particles come in two basic particle shapes: those that are almost superbly round called spherical, and those that have lopsided, rounded shapes, called spheroidal.
So we can conclude that Powders are a group of particles of different sizes.
Learn more about powder here: https://brainly.com/question/20628766
#SPJ1
Which kind of EM Radiation carries the most energy, microwaves
or IR?
Answers
Answer:
gamma-rays
Explanation:
he composition of the ancient atmosphere can be determined by analyzing bubbles of air trapped in amber, which is fossilized tree resin. (This is one way we know that the air in the time of the dinosaurs was richer in oxygen than our current atmosphere.) An air bubble appears to be 7.2 mm below the flat surface of a piece of amber, which has index of refraction 1.54. How long a needle is required to reach the bubble
Answers
Answer:
the needle must be 11.1 mm long to reach the bubble
Explanation:
Given that;
An air bubble appears to be 7.2 mm below the flat surface of a piece of amber
so Apparent depth = 7.2 mm
index of refraction = 1.54
we know that;
Refractive index = Real depth / Apparent depth
we substitute
1.54 = Real depth / 7.2 mm
Real depth = 1.54 × 7.2 mm
Real depth = 11.088 ≈ 11.1 mm
Therefore, the needle must be 11.1 mm long to reach the bubble
What is measurement???
knahi pani nepali ca jasto chaxenw
Answers
Explanation:
The comparison of an unknown physical quantity with the known standard quantity is called measurement....
Here are some tho.....