Find the ratio of kinetic energy to momentum of a 3500 kg car traveling at 40 m/s.
Answers
The ratio of kinetic energy to momentum of a 3500 kg car traveling at 40 m/s is 20 J·s/m.
The kinetic energy (KE) of an object is given by the formula,
KE = 1/2mv², mass of the object is m and its velocity is v
The momentum (p) of an object is given by the formula,
p = mv
So, for a 3500 kg car traveling at 40 m/s, we have,
KE = 1/2 x 3500 kg(40 m/s)²
KE = 2,800,000 J
p = 3500 kg x 40 m/s
p = 140,000 kg·m/s
The ratio of kinetic energy to momentum is simply KE/p, which gives,
KE/p = 2,800,000 J / 140,000 kg·m/s
KE/p = 20 J·s/m
Therefore, the ratio of kinetic energy to momentum of the car is 20 J·s/m.
To know more about kinetic energy and momentum, visit,
https://brainly.com/question/29200829
#SPJ1
Related Questions
Suppose an object's acceleration is negative. Use the formula for
acceleration to explain what this implies about the initial and
final velocities.
Answers
Explanation:
Vi>Vf
so the initial is greater than from the final
hope it helps u have a great day
You look at a rope coiled on a beach and are able to perceive it as a single strand because of the law of.
Answers
You are able to perceive it as a single strand because of the principle of : Good continuation
Principle of good continuationPrinciple of Good continuation states that objects with very smooth edges are easily seen as been continuous ( i.e as a single strand ) rather than objects or materials with rough edges.
The rope coiled on a beach has very smooth edges therefore can be seen as a continuous strand and this is possible due to the principle of good continuation.
Hence we can conclude that You are able to perceive it as a single strand because of the principle of : Good continuation.
Learn more about principle of good continuation : https://brainly.com/question/9280179
what is the name of the part of the microscope that the objectives are attached to? (choose the best answer)
Answers
The part of the microscope that the objectives are attached to is called the (C) nosepiece.
The nosepiece is a rotating mechanism located below the microscope's body tube. It holds the objectives, which are the lenses responsible for magnifying the specimen. The nosepiece typically has multiple positions, allowing the user to switch between different objective lenses for varying levels of magnification.
This convenient feature eliminates the need to manually remove and replace objectives when changing magnification. By rotating the nosepiece, different objectives can be brought into position above the specimen. This allows for quick and efficient adjustments in magnification without disrupting the viewing process.
Hence, the nosepiece plays a critical role in the microscope's functionality by providing a convenient way to switch between objectives and adjust the magnification level.
Learn more about nosepiece here:
https://brainly.com/question/30515439
#SPJ11
Here is the complete question:
What is the name of the part of the microscope that the objectives are attached to? (Choose the best answer)
A. Ocular
B. Stage
C. Nosepiece
D. Arm
if 20.0 liters of nitrogen at 200mm Hg are compressed to 100 mm Hg at a constant temperature. what is the new volume
Answers
These rules are described by specific examples of the ideal gas formula, PV = nRT, the new volume of nitrogen is approximately 23.2 L.
What purposes does nitrogen serve?The chemical industry needs nitrogen to function. It's utilized in the production of explosives, nylon, colors, nitric acid, and fertilizers. The Haber process carries this out.
Where does most of the nitrogen come from?The atmosphere is the principal single source of nitrogen. An odorless, colorless, harmless gas, which makes up 78% of it, is present in it. Although nitrogen is present in the atmosphere, plants cannot utilize it.
The problem can be solved using Boyle's law, which states that the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional at constant temperature. Mathematically, Boyle's law can be expressed as:
P1V1 = P2V2
where P1 and V1 are the initial pressure and volume, respectively, and P2 and V2 are the final pressure and volume, respectively.
We are given that the initial volume, V1, is 22.5 L, the initial pressure, P1, is 748 mmHg, and the final pressure, P2, is 725 mmHg. We can use Boyle's law to find the final volume, V2:
P1V1 = P2V2
748 mmHg x 22.5 L = 725 mmHg x V2
V2 = (748 mmHg x 22.5 L) / 725 mmHg
V2 ≈ 23.2 L
Therefore, the new volume is approximately 23.2 L.
To know more about Nitrogen visit:
brainly.com/question/19938608
#SPJ1
Determine the freezing point of a solution that contains 78.8 g of naphthalene (C10H8, molar mass = 128.16 g/mol) dissolved in 722 mL of benzene (d = 0.877 g/mL). Pure
Answers
The freezing point of a solution that contains 78.8 g of naphthalene: The freezing point of the solution is approximately -3.43°C.
To determine the freezing point of the solution, we need to calculate the freezing point depression caused by the presence of the solute, naphthalene, in the solvent, benzene. The freezing point depression is given by the equation: ∆T = K_f × m
where ∆T is the freezing point depression, K_f is the freezing point depression constant, and m is the molality of the solution.
First, we calculate the molality of the solution using the given data. We need to convert the mass of naphthalene to moles and the volume of benzene to kilograms:
moles of naphthalene = mass / molar mass = 78.8 g / 128.16 g/mol = 0.614 mol
mass of benzene = volume × density = 722 mL × 0.877 g/mL = 633.594 g = 0.633594 kg
Next, we calculate the molality: molality = moles of solute / mass of solvent (in kg) = 0.614 mol / 0.633594 kg = 0.969 mol/kg
Now we can calculate the freezing point depression: ∆T = K_f × m = 4.90°C/m × 0.969 mol/kg = 4.7433°C
Finally, we subtract the freezing point depression from the freezing point of pure benzene to find the freezing point of the solution: Freezing point = 5.50°C - 4.7433°C = -3.43°C
To know more about freezing point, refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/40140#
#SPJ11
Complete question:
Determine the freezing point of a solution that contains 78.8 g of naphthalene (C10H8, molar mass = 128.16 g/mol) dissolved in 722 mL of benzene (d = 0.877 g/mL). Pure benzene has a melting point of 5.50°C and a freezing point depression constant of 4.90°C/m.
What is nuclear power

Answers
Answer:
D. All of the statements describe nuclear powerWhat is NUCLEAR POWER?
➡️ is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity.
➡️ it can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions.
Hope it helps
An 18-year-old runner can complete a 10.0 km course with an average speed of 4.60 m/s. A 50-year-old runner can cover the same distance with an average speed of 4.13 m/s. How much later (in seconds) should the younger runner start in order to finish the course at the same time as the older runner?
Answers
Taking into account the definition of speed, the 18-year-old runner must start 247.3945 s after the 50-year-old runner in order to finish the course at the same time.
Definition of speedSpeed is a quantity that expresses the relationship between the space traveled by an object and the time used for it.
In other words, speed can be defined as the change of position of an object in space within a certain amount of time and can be calculated using the expression:
speed= distance traveled÷ time
Time in this caseIn this case, you know:
An 18-year-old runner can complete a 10 km (10000 m, being 1 km equals to 1000 m) course with an average speed of 4.60 m/s. A 50-year-old runner can cover the same distance (10 km) with an average speed of 4.13 m/s.Replacing these values in the speed definition, it is possible to obtain the time that each runner needs to complete the race:
18-year-old runner: 4.60 m/s= 10000 m÷time50-year-old runner: 4.13 m/s= 10000 m÷timeSolving:
18-year-old runner: 4.60 m/s×time= 10000 m → time= 10000 m÷ 4.60 m/s → time= 2173.9130 s50-year-old runner: 4.13 m/s× time= 10000 m → time= 10000 m÷ 4.13 m/s → time= 2421.3075 sTo know the amount of time after which the youngest runner must start to finish the course at the same time as the oldest runner, the difference between the time it takes each runner to finish the course must be made:
difference of time= time of the 50-year-old runner - time of 18-year-old runner
difference of time= 2421.3075 s - 2173.9130 s
difference of time= 247.3945 s
Finally, the 18-year-old runner must start 247.3945 s after the 50-year-old runner in order to finish the course at the same time.
Learn more about average speed:
brainly.com/question/15273551
brainly.com/question/9834403
#SPJ1
An electric over operates at 240V with a current of 28 amps. If it takes 2.6 hours to cook a turkey, and electricity costs $0.16 per KWh, how much does the electricity cost to cook the turkey? Give your answer in dollars and cents (e.g. 9.50).
Answers
The electricity cost to cook the turkey is $2.80 (rounded to the nearest cent).
To calculate the electricity cost to cook the turkey using an electric oven, you need to find the energy consumption and then multiply it by the cost per kWh.
First, find the power of the oven:
Power (W) = Voltage (V) × Current (A) = 240V × 28A = 6720W = 6.72kW
Next, find the energy consumption:
Energy (kWh) = Power (kW) × Time (hours) = 6.72kW × 2.6 hours = 17.472kWh
Finally, calculate the electricity cost:
Cost = Energy (kWh) × Cost per KWh = 17.472kWh × $0.16/kWh = $2.79552
Therefore, the electricity cost to cook the turkey is $2.80 (rounded to the nearest cent).
visit here to learn more about electricity cost:
https://brainly.com/question/28800300
#SPJ11
To calculate the cost of electricity to cook the turkey, we need to first find the total energy used in KWh.
Energy (KWh) = Power (KW) x Time (hours)
Power (KW) = Voltage (V) x Current (A) / 1000
Power (KW) = 240V x 28A / 1000 = 6.72 KW
Energy (KWh) = 6.72KW x 2.6 hours = 17.472 KWh
The cost of electricity is $0.16 per KWh, so:
Cost = Energy (KWh) x Cost per KWh
Cost = 17.472 KWh x $0.16/KWh = $2.79552
Therefore, the cost of electricity to cook the turkey is $2.80.
To calculate the cost of electricity to cook the turkey, follow these steps:
1. Find the power of the oven in watts: Power (W) = Voltage (V) × Current (A)
Power = 240V × 28 amps = 6720W
2. Convert the power from watts to kilowatts: Power (kW) = Power (W) ÷ 1000
Power = 6720W ÷ 1000 = 6.72kW
3. Calculate the energy consumption in kilowatt-hours: Energy (kWh) = Power (kW) × Time (hours)
Energy = 6.72kW × 2.6 hours = 17.472kWh
4. Calculate the cost of electricity: Cost = Energy (kWh) × Price per kWh
Cost = 17.472kWh × $0.16/kWh = $2.79552
Rounded to the nearest cent, the cost of electricity to cook the turkey is $2.80.
Learn more about cost of electricity here : brainly.com/question/28800300
#SPJ11
Basic design elements include (Check 7)
What are the 3 properties of color? Immersive Reader
depth, shade, fragrance
value, hue, depth
saturation, hue, chroma
hue, value, intensity
Answers
Answer: depth, shade, fragrance
Explanation:
Another switch allows one to adjust the magnetic field so that it is either nearly uniform at the center or has a strong gradient. The latter means that the magnitude of the field changes rapidly along the vertical direction near the center. How does this switoh change the current in the two coils?
Answers
The switch that adjusts the magnetic field to be either nearly uniform or have a strong gradient will affect the current in the two coils differently.
When the magnetic field is nearly uniform at the center, the current in both coils will remain relatively unchanged. The uniform field will not induce any significant voltage in the coils, so the current will flow through them as usual.
However, when the magnetic field has a strong gradient, the current in the two coils will be affected differently. The rapidly changing field will induce a voltage in the coils according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. This induced voltage will result in a change in the current flowing through the coils. The magnitude and direction of the induced current will depend on the specific characteristics of the coils and the magnetic field gradient.
In summary, the switch that changes the magnetic field from uniform to having a strong gradient will induce a change in the current flowing through the coils due to the induced voltage.
Learn more about magnetic field gradient.
https://brainly.com/question/31421539
#SPJ4
You have a 100 ohm resistor. How much resistance must you add in parallel to the 100 ohm resistor to create an equivalent resistance of 75.0 ohms?
Answers
Answer:
300 ohm
Explanation:
Acellus
when light travelling in a certain medium falls on the surface of another medium, a part of it turns back in the same medium. this phenomenon is called group of answer choices diffraction dispersion reflection refraction acoustics
Answers
When light travels in a certain medium and falls on the surface of another medium a part of it turns back in the same medium This phenomenon is called Reflection.
A wavefront may alter its course at an interface between two different media and return to the first medium, a phenomenon known as reflection. Common examples are the reflection of light, sound, and water waves.
Reflection of light refers to the occurrence where light strikes an item and bounces back off its surface. Examples: using a flat mirror to reflect. by a spherical mirror's reflection. There are essentially two types of reflection that apply to light. While diffuse reflection is caused by rough surfaces that tend to reflect light in all directions, specular reflection is described as light reflected off a smooth surface at a specific angle.
To learn more about Reflection visit here:
brainly.com/question/15487308
#SPJ4
what is the value of sin square 60
Answers
Explanation:
\( \sin(60) = \frac{ \sqrt{3} }{2} \\ \\ \sin(60 ) {}^{2} = ( \frac{ \sqrt{3} }{2} ) {}^{2} \\ \\ \sin(60 ) {}^{2} = \frac{3}{4} \)
Write two reasons for using mercury in a thermometer ️️
Answers
Answer:
my first reason is that Mercury is the only one in liquid state at room temperature and thermometers because it has high coefficient of expansion . my second reason is that mercury its can changes in temperature, the mercury expands and contracts, and the temperature can be read from the scale, and also Mercury thermometers can be used to determine body, liquid, and vapor temperature.
A conducting wire of 60cm long is moved at a constant speed of 5m/s perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. If thr EMF induced in the wire is 2volts, deduce the value of tge magnetic induction
Answers
The value of magnetic induction is 0.667 T.
The EMF induced in a conductor traveling through a magnetic field is given by:
EMF = B x L x v
where B is the magnetic induction (measured in Tesla), L is the conductor's length (in meters), and v is its speed (in meters per second)
What we have here is
L = 60 cm = 0.6 m (because the length of the wire is specified in centimeters) (since the length of the wire is given in centimeters)
v = 5 m/s
EMF = 2 V
When these values are inserted into the equation, we obtain the following:
2 V = B x 0.6 m x 5 m/s
Calculating for B, we obtain:
B = 2 V / (0.6 m x 5 m/s) = 0.666... T
Thus, the magnetic induction is 0.667 T, rounded to three significant numbers.
To learn more about Magnetic induction:
https://brainly.in/question/47035
A hot air balloon lifts 50 meters vertically into the air and then comes back down. What are the displacement and distance of the balloon’s flight?
The displacement is 100 meters and the distance is zero.
The displacement is 50 meters downward and the distance is 100 meters.
The displacement is zero and the distance is 100 meters
The displacement is 50 meters upward and the distance is 100 meters.
Answers
The displacement of the balloon is zero while the distance is 100 m
Displacement if the change in the position of an object. When an object is displaced and it returns to the same position, the displacement is zero.
Displacement is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude and direction.
Displacement of the balloon = 50 m Upward - 50 m downward = 0Distance is the measure of the total path traveled by object. When an object is released to certain position and it returns to the same position, the distance is the sum of the path covered by the object. Unlike displacement, distance is a scalar quantity, because it can represented by magnitude only.
The distance of the balloon = 50 m upward + 50 m downward = 100 mThus, the displacement of the balloon is zero while the distance is 100 m
Learn more here: https://brainly.com/question/17345815
Answer:
The displacement is zero and the distance is 100 meters.
Explanation:
An object moving with 108 km/h moves 400 m in 8 seconds. find the velocity attained by the object.
Answers
Answer:50ms-1
Explanation:use the formula v=d/t
in order to find the velocity,devide the distance with time taken.
since distance is 400 meters devide it with seconds whiuch gives us 50.
what makes something bouncy
Answers
Answer: The speed of the object traveling should be met with the opposite reaction, thus making something like a basketball bounce as high as the force applied to the ball, making both surfaces push off each other until kinetic energy ( form of energy that an object or a particle has by reason of its motion) is lost.
11. Which of these is a way to make an electromagnet stronger?
a putting a switch in the electrical circuit
b replacing the iron core with a copper core
© replacing the copper wire with plastic wire
wrapping the wire around the iron core more times
Answers
Answer:
wrapping around the wire around iron core several times
Explanation:
adding more turns to the coil. increasing the current flowing through the coil.
How is impact force and impact time related when describing the same impulse?
a) Inversely proportional
b) Directly proportional
c) They are opposite to each other
d) None of the above
Answers
Answer:
The correct option is (a)
Explanation:
Impulse is given by the product of force and time. It is denoted by J. So,
\(J=F\times t\)
or
\(F=\dfrac{J}{t}\)
It can be seen that the relation between the force and the impact time is inverse. Hence, the impact force and impact time possess inverse relation.
Which surface has the most friction? a An ice rink b A grassy field c A paved road
Answers
Answer:
An Ice Rink
Explanation:
Answer:
b
Explanation:
i remember this from a test
what is a recovery heart rate?
Answers
Answer:Recovery heart rate is simply your pulse rate after exercise. Some fitness specialists refer to it as the post-exercise heart rate. The pulse number is used for different reasons in different settings.
Explanation:
Answer:
Heart rate is the speed of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute.
Explanation:
pls the answer.........................................................................................................................


Answers
a) The motion of the motorcyclist is a uniform motion
b) The distance is 600 m
c) The speed is 20 m/s.
What is the motion?We now that motion has to do with the change in the position of an object with time. In this case, we have the graph that described the motion of the motorcyclist . It is clear that the distance is increasing in equal amounts, in equal time intervals thus this is a uniform motion.
Looking at the graph, we can see that the motorcyclist covers 600 meters of distance within 30 seconds.
We can obtain the speed as the ratio of the distance to the time or the slope of the graph. Hence the speed is obtained from;
Speed = distance / time
Using the slope concept;
\(y_{2} - y_{1} /x_{2} - x_{1}\)
= 600 - 0/30 - 0
= 20 m/s
Learn more about speed:https://brainly.com/question/28224010
#SPJ1
HELP I NEED THIS QUICK PLEASE
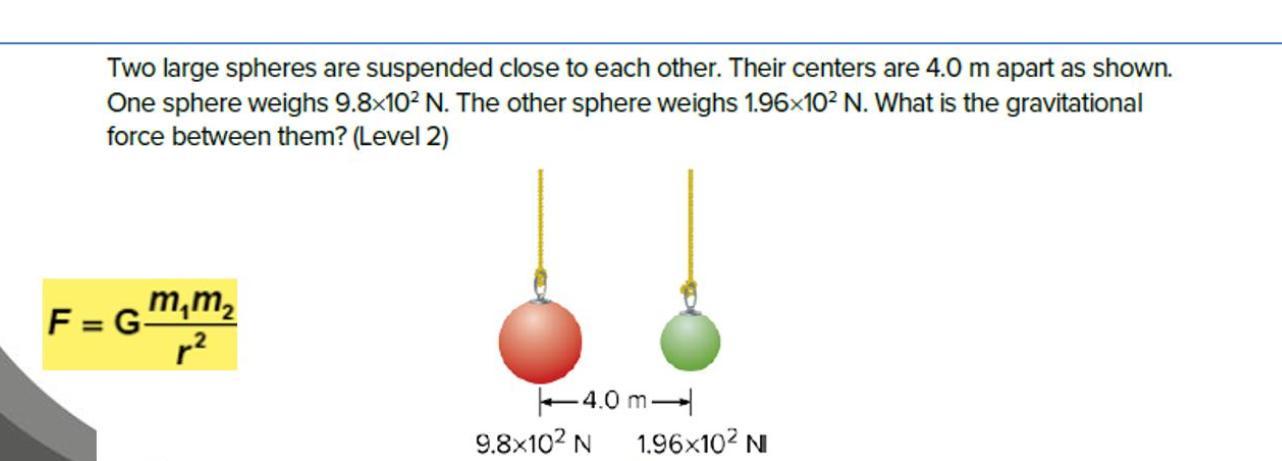
Answers
First let's see what the funny letters in the equation they gave us means.
F = Gravitational Force
G = Gravitational Constant
m1 = Mass of one of the spheres
m2 = Mass of the other sphere
r = Distance between the two spheres
Ok, now implement it.
\(\frac{9.8 x 10^{2} 1.96 x 10^{2} }{4^{2} }\)
To make it simpler
F = 980 x 196 = 192,080
192,080 ÷ 4²
192,080 ÷ 16
= 12005
F = 12,005N
the approach to motivation emphasizes the role of species-specific instincts in directing behavior.
Answers
The approach to motivation that emphasizes the role of species-specific instincts in directing behavior is called the Instinct Theory of Motivation.
This theory suggests that certain innate, fixed patterns of behavior, known as instincts, are responsible for motivating actions and reactions within specific species. These instincts have evolved over time due to their contribution to the survival and reproductive success of the species.
For example, the fight or flight response, which is a common instinct among many animals, helps protect them from predators and ensures their survival. Another example is the maternal instinct observed in many mammal species, which promotes nurturing and protective behaviors towards their offspring, ultimately benefiting their survival and reproduction.
Instinct Theory of Motivation has its roots in the work of early psychologists like William James and Sigmund Freud, who believed that instincts played a significant role in shaping human behavior. However, it is important to note that while instincts do influence motivation, they are not the only factors at play. Other approaches, such as the drive-reduction theory and cognitive theories, also contribute to our understanding of motivation and behavior.
To know more about Instinct Theory of Motivation, refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/31586201#
#SPJ11
Which has the greater mass?
a. king-size pillow
b. automobile battery
c. both about the same
Answers
Automobile battery has more mass than a king-size pillow. Compared to the batteries, the king-size pillow has a larger volume but less mass.
It takes more effort to set an automobile battery in motion. This demonstrates the battery's higher inertia and hence higher mass. Inertia is the ability of a moving object to resist changes in motion. An object's mass affects how much inertia it possesses.
To know more about Inertia go here:-
brainly.com/question/1358512
#SPJ4
Three particles with charges q1 = +10 µC, q2 = -20 µC, and q3 = +31 µC are positioned at the vertices of an isosceles triangle as shown in the figure. a = 10 cm and b = 6.0 cm.
(a) How much work must an external agent do to exchange the positions of q1 and q3?
(b) How much work must an external agent do to exchange the positions of q1 and q2, instead
Answers
No work is required to exchange the positions of q1 and q2, since their potential energies do not change.
Electric potential energy, which is U = kq1q2/r, where k is Coulomb's constant (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2), q1 and q2 are the charges of the particles, and r is the distance between them.
(a) To exchange the positions of q1 and q3, we need to move q1 to the position of q3, and vice versa. The distance between q1 and q3 is the length of the base of the isosceles triangle, which is 2b = 12 cm. The distance between q1 and q2 is the height of the triangle, which is h = sqrt(a^2 - b^2) = 8 cm.
The initial potential energy of the system is: U1 = kq1q2/h + kq2q3/2b + kq1q3/2b
we get:U1 = (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(+10 µC)(-20 µC)/8 cm + (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(-20 µC)(+31 µC)/12 cm + (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(+10 µC)(+31 µC)/12 cm
U1 = -34.9 mJ
To exchange the positions of q1 and q3, we need to move q1 to the position of q3, and vice versa. This involves doing work against the electric force between the particles. The work done is equal to the change in potential energy, which is: W = U2 - U1
where U2 is the final potential energy of the system after the particles have been exchanged.
When q1 and q3 are exchanged, the potential energy of the system changes to: U2 = kq3q2/h + kq2q1/2b + kq3q1/2b
Substituting the given values, we get:
U2 = (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(+31 µC)(-20 µC)/8 cm + (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(-20 µC)(+10 µC)/12 cm + (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(+31 µC)(+10 µC)/12 cm
U2 = -38.4 mJ
Therefore, the work done to exchange the positions of q1 and q3 is: W = U2 - U1 = -38.4 mJ - (-34.9 mJ) = -3.5 mJ
The negative sign indicates that work is done by the system, which means that an external agent must do positive work to exchange the positions of q1 and q3.
(b) To exchange the positions of q1 and q2, we need to move q1 to the position of q2, and vice versa. The distance between q1 and q2 is the height of the triangle, which is h = 8 cm. The distance between q1 and q3 is the length of the base of the triangle, which is 2b = 12 cm.
The initial potential energy of the system is: U1 = kq1q3/2b + kq2q3/h + kq1q2/h
Substituting the given values, we get: U1 = (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(+10 µC)(+31 µC)/12 cm + (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(-20 µC)(+31 µC)/8 cm + (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(+10 µC)(-20 µC)/8 cm
U1 = -52.4 mJ
To exchange the positions of q1 and q2, we need to move q1 to the position of q2, and vice versa. The work done is equal to the change in potential energy, which is:
W = U2 - U1
where U2 is the final potential energy of the system after the particles have been exchanged.
When q1 and q2 are exchanged, the potential energy of the system changes to: U2 = kq2q3/2b + kq1q3/h + kq1q2/h
Substituting the given values, we get:
U2 = (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(-20 µC)(+31 µC)/12 cm + (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(+10 µC)(+31 µC)/8 cm + (9.0 x 10^9 N*m^2/C^2)(+10 µC)(-20 µC)/8 cm
U2 = -52.4 mJ
Therefore, the work done to exchange the positions of q1 and q2 is:
W = U2 - U1 = -52.4 mJ - (-52.4 mJ) = 0
learn more about potential energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/24284560
#SPJ11
A ramp is 4 meters tall and has a mechanical advantage of 2.5 what is its length? HELP
Answers
We must use the mechanical advantage formula to determine the length of the ramp:
Output force minus Input force equals Mechanical Advantage (MA). In this instance, the input force is the force required to hoist the object in the absence of the ramp, and the output force is the weight of the object being raised up the ramp
How do you determine a ramp's mechanical advantage?By dividing the length of the slope by its height, you may calculate the optimal mechanical advantage of an inclined plane. The ideal mechanical advantage of a ramp, for instance, is 3 metres 1 metre, or 3 metres, if you are loading a truck that is 1 metre high utilising it.
How is the mechanical advantage determined?Basic Machines' Mechanical Advantage and Efficiency Calculated. The IMA is typically calculated as the resistance force (Fr) divided by the effort force (Fe). IMA is also equal to the product of the load's travel distance (d) and the distance over which the effort is applied (de).
To know more about mechanics visit:-
brainly.com/question/20885658
#SPJ1
Fill in the blanks below with the best answer from the options given.
Hot objects contain _____ energy and emit ______ photons at all wavelengths, compared to cool objects
Hot objects emit more energy at ________ frequencies and ________ wavelengths
Cool objects appear _______ in color than hot objects
Answer choices: more, less, higher, lower, longer, shorter, up, down, left, right, redder, greener, bluer, whiter
Answers
Hot objects contain more energy and emit photons at higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths compared to cool objects. Cool objects appear redder in color than hot objects.
Hot objects have a higher internal energy compared to cool objects. This higher energy is manifested in the form of increased thermal motion of particles within the object. As a result, hot objects emit more energy in the form of photons.
When it comes to the emission of photons, hot objects emit more photons at higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths. This is because the energy of individual photons is directly proportional to their frequency. Hotter objects have more energetic particles, leading to the emission of photons with higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths.
On the other hand, cool objects emit fewer photons and at lower frequencies and longer wavelengths. The lower energy of the particles in cool objects results in the emission of photons with lower frequencies and longer wavelengths.
In terms of color appearance, cool objects appear redder than hot objects. This is because cooler objects emit more photons in the red part of the electromagnetic spectrum, while hotter objects emit more photons in the blue part of the spectrum.
Learn more about frequencies here:
https://brainly.com/question/30333783
#SPJ11
what is the equation for finding the net torque on a dipole? Why does the dipole exhibit a torque?
Answers
The equation for finding the net torque on a dipole is given by τ = p × E, where τ represents the torque, p is the dipole moment, and E is the electric field.
A dipole exhibits a torque because it consists of two opposite charges separated by a distance, and when placed in an electric field, these charges experience forces in opposite directions, causing a rotational effect or torque. The torque tends to align the dipole moment with the direction of the electric field, and the strength of the torque depends on the magnitude of the dipole moment and the electric field, as well as the angle between them.
To learn more about torque https://brainly.com/question/20691242
#SPJ11