Estimate the moment of inertia of a bicycle wheel 67.2 cm in diameter. The rim and tire have a combined mass of 1.25 kg. The mass of the hub (at the center) can be ignored.
Answers
Moment of Inertia of a Bicycle WheelThe moment of inertia of a bicycle wheel is the amount of force it takes to accelerate the wheel’s rotation about its central axis. The moment of inertia of a bicycle wheel can be determined by adding the moment of inertia of the rim and the tire, which are separate from each other.
It’s important to know the moment of inertia of a bicycle wheel because it’s essential in figuring out how much energy is required to accelerate the wheel, how quickly the wheel will rotate, and how much torque is needed to maintain a given angular velocity. If you want to estimate the moment of inertia of a bicycle wheel with a diameter of 67.2 cm, you’ll need to use a few equations.Moment of Inertia of a Thin RingTo determine the moment of inertia of a thin ring (or hoop), you can use the equation I = mr2, where I is the moment of inertia, m is the mass of the ring, and r is the radius of the ring. However, since we are given the diameter, we need to first find the radius. We know that the diameter of the bicycle wheel is 67.2 cm, so the radius is 33.6 cm or 0.336 m. Also, we are told that the mass of the rim and tire is 1.25 kg. Using the above equation, we can calculate the moment of inertia of the ring as:
I = mr2I
= (1.25 kg) (0.336 m)2I
= 0.150 kg
m2Moment of Inertia of a Solid DiscNext, we’ll need to find the moment of inertia of the solid disc that makes up the tire of the bicycle wheel. The equation for the moment of inertia of a solid disc is I = (1/2)mr2, where m is the mass of the disc and r is the radius of the disc. We know that the radius of the disc is the same as the radius of the ring, which is 0.336 m. Since we are given the mass of the rim and tire, and we know the mass of the rim, we can calculate the mass of the tire as follows:mass of tire = mass of rim and tire - mass of rimmass of tire
= 1.25 kg - 0.150 kgmass of tire
= 1.10 kg
Now we can calculate the moment of inertia of the disc as follows:
I = (1/2)mr2I
= (1/2)(1.10 kg)(0.336 m)2I
= 0.064 kg m2
Total Moment of InertiaFinally, we can add the moment of inertia of the ring and the moment of inertia of the disc to get the total moment of inertia of the bicycle wheel:
I(total) = I(ring) + I(disc)I(total)
= 0.150 kg m2 + 0.064 kg m2I(total)
= 0.214 kg m2
Therefore, the estimated moment of inertia of a bicycle wheel with a diameter of 67.2 cm is 0.214 kg m2.
For more information on Inertia visit:
brainly.com/question/3268780
#SPJ11
Related Questions
a medium has an index of refraction of 1.39. what is the critical angle of this medium with respect to air? [hint: during critical angle condition, angle of refraction is 90 degrees]. round your answer to two decimal places.
Answers
The critical angle of this medium with respect to air is 48.22 degrees.
The critical angle is the angle of incidence in a medium at which the angle of refraction in the surrounding medium becomes 90 degrees. It can be calculated using the formula:
critical angle = sin⁻¹(1/n)
Where n is the refractive index of the medium.
In this case, the refractive index of the medium is 1.39. Therefore, the critical angle can be calculated as:
critical angle = sin⁻¹(1/1.39) = 48.22 degrees
As a result, the critical angle of this medium in relation to air is 48.22 degrees.
The critical angle is an important concept in optics and is used in various applications such as fiber optics and total internal reflection. It occurs when light passes from a medium with a higher refractive index to a medium with a lower refractive index, such as from water to air. As the angle of incidence increases, the angle of refraction also increases, and at a certain angle, the angle of refraction becomes 90 degrees.
To know more about the Refraction, here
https://brainly.com/question/13819705
#SPJ4
HELP‼️‼️ A car horn creates a 595 Hz tone at rest. Two cars pass on the street, each going 20.0 m/s; the first car honks. What frequency does the other car hear before they pass each other?
Answers
The frequency of the other car is 669HZ
Let start off by writing out the parameters given in the question
frequency= 595 HZ
Speed of sound(v)= 343m/s
Speed of the car(vs)= 20m/s
Speed of the second car(vo) = 20m/s
The frequency of the other car can be calculated as follows
(v+vo/v-vs) f
= (343+20/343-20)595
= (363/323)595
= 1.1238(595)
= 669 HZ
Hence the frequency of the other car is 669 HZ
Learn more via the link below;
https://brainly.com/question/24338491?referrer=searchResults
If it actually hits the ground with a speed of 8. 50 m/s , what is the magnitude of the average force of air resistance exerted on it?
Answers
the magnitude of the average force of air resistance exerted on the object is approximately 1.05 N.
The magnitude of the average force of air resistance exerted on an object depends on various factors such as the shape, size, speed, and density of the object, as well as the density and viscosity of the air.
F = (1/2) * rho * Cd * A * v
we can estimate the density of air at sea level as 1.225 kg/m, and assume a drag coefficient of 0.5 for a spherical object.
F = (1/2) * rho * Cd * A * v
= (1/2) * 1.225 kg/m * 0.5 * pi * (0.1 m)* (8.50 m/s)
= 1.05 N (to two significant figures)
learn more about magnitude here:
https://brainly.com/question/29766788
#SPJ4
Draw simple electrical circuit using symbols of dry cell resistor voltmeter and switch
Answers
Explanation:
I hope this really can help you...
well done friend...



what is the period of a simple pendulum that is 1.00 m long in each of the following situations? a. in the physics lab b. in an elevator accelerating at 2.10 m/s 2 upward c. in an elevator accelerating at 2.10 m/s 2 downward d. in an elevator in free fall
Answers
a. T = 2.01 s
b. T = 1.84 s
c. T = 2.25 s
d. Pendulum does not oscillate in free fall due to zero effective acceleration.
The period of a simple pendulum depends on its length and the acceleration due to gravity. The formula for the period of a simple pendulum is:
T = 2π * √(L/g)
where T is the period, L is the length of the pendulum, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
a. In the physics lab, assuming that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s^2, the period of the pendulum would be:
T = 2π * √(1.00 m / 9.81 m/s^2) = 2.01 s
b. In an elevator accelerating at 2.10 m/s^2 upward, the effective acceleration due to gravity would be:
g' = g + a = 9.81 m/s^2 + 2.10 m/s^2 = 11.91 m/s^2
where a is the acceleration of the elevator. Using this effective acceleration, the period of the pendulum would be:
T = 2π * √(1.00 m / 11.91 m/s^2) = 1.84 s
c. In an elevator accelerating at 2.10 m/s^2 downward, the effective acceleration due to gravity would be:
g' = g - a = 9.81 m/s^2 - 2.10 m/s^2 = 7.71 m/s^2
Using this effective acceleration, the period of the pendulum would be:
T = 2π * √(1.00 m / 7.71 m/s^2) = 2.25 s
d. In an elevator in free fall, the effective acceleration due to gravity would be zero. In this case, the pendulum would not oscillate because there is no net force acting on it.
Visit to know more about Pendulum:-
brainly.com/question/26524032
#SPJ11
In what way could a random mutation provide an organism with an advantage? With a example please
Answers
Answer:
They are called beneficial mutations. They lead to new versions of proteins that help organisms adapt to changes in their environment. Beneficial mutations are essential for evolution to occur. They increase an organism's changes of surviving or reproducing, so they are likely to become more common over time.
Explanation:
Q.7. For a system with a transfer function of G(s)=- co² s² +2a+w² if the natural frequency is 0.5 and the damping ratio is 1.3, which of the following statements is correct regarding the unit step response of the system?
O A) Damped
O B) Undamped
O C) Underdamped
O D) Crittically Damped
O E) Overdamped
Answers
The system described by the transfer function G(s) = -co² s² + 2a + w², with a damping ratio of 1.3 and a natural frequency of 0.5, has an overdamped unit step response. So, the correct option is (E)
The transfer function of the system is given as G(s) = -co² s² + 2a + w², where co represents the damping ratio, a represents an arbitrary constant, and w represents the natural frequency of the system. We are given that the natural frequency is 0.5 and the damping ratio is 1.3.
To determine the type of unit step response, we need to analyze the damping ratio (co) in relation to the critical damping value (co_critical).
The critical damping ratio (co_critical) is defined as the value where the system is on the threshold between being overdamped and underdamped. It is given by the formula co_critical = 2 * sqrt(a * w²).
In our case, the natural frequency (w) is 0.5, so we can calculate co_critical as follows: co_critical = 2 * sqrt(a * 0.5²).
Since the damping ratio (co) is given as 1.3, we can compare it with co_critical to determine the type of unit step response.
If co > co_critical, the system is considered overdamped (Option E).
If co = co_critical, the system is considered critically damped (Option D).
If co < co_critical, the system is considered underdamped (Option C).
Based on the given values, we can determine that the system is overdamped (Option E) because the damping ratio (1.3) is greater than the critical damping ratio.
To know more about damping ratios, refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/31463018#
#SPJ11
A sample contains 16 g of a radioactive isotope. how much radioactive
isotope remains in the sample after 1 half-life?
Answers
After one half-life, 8 g of radioactive isotope will remain in the sample.
What is radioactivity?The act of producing radiation spontaneously is known as radioactivity. This is accomplished by an unstable atomic nucleus that want to give up some energy in order to move to a more stable form.
The following formula is used to compute the number of half lives elapsed:
\(\rm N=\frac{N_0}{2^n} \\\\ N=\frac{16}{2} \\\\ N= 8 \ gram\)
Hence,8 gram of radioactive isotope remains in the sample after 1 half-life.
To learn more about the radioactivity, refer to the link;
brainly.com/question/1770619
#SPJ1
Answer:
Answer is below
Explanation:
8 g

1. You will need to show how to preform parallel and serial dilution calculation. You can assume the stock concentration of the dye is to be 0.1 M. Depending on the molar absorptivity value of each dye, the concentrations you use may vary, you can use any concentration within the range of 0.01 M to 0.1 M. Prepare five different concentrations (total volume can range from 10-50 mL) using parallel and serial dilutions. 2. Describe how to use the UV-Vis spectrometer. What will you use as a blank
Answers
Parallel and Serial Dilution Calculations:
To perform parallel and serial dilutions, follow the steps below:
Parallel Dilutions:
Step 1: Determine the desired concentrations for the five dilutions. Let's assume the desired concentrations are as follows: 0.1 M, 0.05 M, 0.025 M, 0.0125 M, and 0.00625 M.
Step 2: Calculate the dilution factor (DF) for each dilution. The dilution factor represents the ratio of the final volume to the initial volume.
For example, if you want to prepare a 0.05 M dilution with a final volume of 25 mL, and you have a 0.1 M stock solution:
DF = (final volume)/(initial volume)
= 25 mL / 100 mL
= 0.25
Step 3: Calculate the volume of the stock solution required for each dilution. This can be determined using the following formula:
Volume of stock solution = (desired concentration) x (final volume) / (stock concentration)
or the example above:
Volume of stock solution = (0.05 M) x (25 mL) / (0.1 M)
= 12.5 mL
Step 4: Add the calculated volume of stock solution to an appropriate volume of diluent (e.g., water) to obtain the desired final volume.
Serial Dilutions:
Step 1: Determine the desired concentrations for the five dilutions, similar to the parallel dilutions.
Step 2: Choose a constant dilution factor for each subsequent dilution. For example, let's use a dilution factor of 10 for each step.
Step 3: Calculate the volume of stock solution and diluent for each dilution, following the same formula as in parallel dilutions.
For example, if you want to prepare a 0.05 M dilution with a final volume of 25 mL and a dilution factor of 10:
Volume of stock solution = (0.05 M) x (25 mL) / (0.1 M)
= 12.5 mL
Volume of diluent = final volume - volume of stock solution
= 25 mL - 12.5 mL
= 12.5 mL
Step 4: Transfer the calculated volume of stock solution to the first dilution tube and add the calculated volume of diluent. Mix thoroughly.
Step 5: Transfer the entire contents of the first dilution tube to the second dilution tube, and add the calculated volume of diluent. Mix thoroughly.
Repeat Step 5 for subsequent dilution tubes until you have prepared the desired number of dilutions.
Using the UV-Vis Spectrometer:
To use the UV-Vis spectrometer, follow these steps:
Step 1: Turn on the spectrometer and allow it to warm up for the recommended time specified by the manufacturer.
Step 2: Prepare a blank solution. A blank is a reference solution that contains all the components except the analyte of interest. It is used to calibrate the instrument and account for any background absorbance.
To prepare the blank, use the same solvent and volume as your sample solution but exclude the dye or analyte. For example, if your sample solution is prepared in a cuvette with 1 cm path length and contains the dye, prepare a blank solution in another cuvette with the same solvent and volume but without the dye
Step 3: Insert the blank cuvette into the spectrometer and close the lid to ensure proper alignment.
Step 4: Set the spectrometer to the appropriate wavelength range and select the desired wavelength for your analysis. This wavelength should correspond to the absorption maximum of the dye you are measuring.
Step 5: Zero the spectrometer by adjusting the instrument settings or pressing the "Zero" button. This establishes the baseline absorbance using the blank solution as a reference.
Step 6: Remove the blank cuvette and replace it with the cuvette containing your sample solution. Ensure that the cuvette is properly aligned and close the lid.
Step 7: Record the absorbance value displayed on the spectrometer for your sample solution.
Step 8: Repeat the process for each of your prepared dilutions, ensuring that you replace the cuvette with the appropriate solution for each measurement.
Remember to clean the cuvettes between measurements, use appropriate sample volumes for accurate readings, and follow any specific instructions provided by the spectrometer manufacturer.
For more such questions on serial dilution
https://brainly.com/question/14660275
#SPJ8
What average power would a 1000 kg speedboat need to go from rest to 20.0 m/s in 5.00 s, assuming the water exerts a constant drag force of magnitude fd = 500 N and the acceleration is constant.
Answers
The average power required by a 1000 kg speedboat to go from rest to 20.0 m/s in 5.00 s is 60000 Watts.
The average power required to accelerate an object is equal to the force required to overcome resistance multiplied by the velocity gained. In this case, the drag force fd opposes the acceleration of the speedboat, and so the net force on the boat is equal to the difference between the force applied to the boat and the drag force:
Fnet = Fapplied - fd = ma - fd
where m is the mass of the boat (1000 kg) and a is the acceleration. The acceleration can be calculated from the velocity gained and the time taken:
a = (vf - vi) / t = (20 m/s - 0 m/s) / 5.00 s = 4 m/s^2
So, the net force is:
Fnet = ma - fd = 1000 kg * 4 m/s^2 - 500 N = 3000 N
The power required to overcome the drag force and accelerate the speedboat is equal to the net force multiplied by the velocity gained:
P = Fnet * v = 3000 N * 20 m/s = 60000 Watts
Therefore, the average power required is 60000 Watts.
To know more about average power please refer:
https://brainly.com/question/17008088
#SPJ4
csggggresddgdfgthxefecdtvh
Answers
Answer:
csggggresdd
...........
Answer:
yes :)
Explanation:
how do you calculate the numerical value of physical quantity
Answers
The value of a physical quantity is normally expressed as an implied product of a numeric value and a unit of measurement.
There are three categories to consider:
There is no explicit unit of measurement included. Examples of this would include index of refraction of a medium and the specific gravity of a substance (which is ratio of the density of the material divided by the density of some reference material, usually water at some specified temperature). In this category, there is an implied measurement unit of 1 . It is usually not written because 1 times any number is that same number, so it is pointless to write the “times 1”. The value of an index of refraction is simply a number, and that number is all you write for the quantity value. That number is the numerical value of the physical quantity. It is only slightly more complicated for specific gravity, because you are dividing one density by another, and both values should be expressed in the same units of measurement, and the division of one by the other cancels out those units, leaving you with 1 as the overall measurement unit.
For plane angles, there is a relationship between the length s of the arc of a circle, the radius r of that circle, and the angle a subtended by the arc at the circle center:
a = s/r
with the angle a being measured in the unit of radians. (To write the formula for some other angular unit requires incorporating a numeric factor, which is basically a conversion factor from radians to degrees,) Thus, if you have a circle of radius 3 m and an arc of 6 m on that circle, the the angle subtended or formed is:
(6 m)/(3 m) = 2, but we said this is the number of radians, so it is 2 rad.
Notice, we are dividing a length by a length (both the arc length and the radius being lengths), so if we use the same measurement unit for both lengths (regardless that unit being meters, feet, parsecs, or anything else), the two units cancel each other out upon division. This means that the unit we are calling radian is like with specific gravity in #1—it has the value 1. Indeed, we see the formula gives us 2 and we know that it is 2 rad, and the only way we can have them be the same, 2 rad = 2, is if the unit radian is actually just a funny, special name for the number 1. Why do we give the number 1 a special name here, unlike in category #1? That is because some inexperienced people find the concept of radian to be strange and inconvenient. They would rather use degrees, or arcminutes, or arcseconds, or semicircles, or some other such unit, and they all have different sizes. For example, a full circle is 2π rad and it is also 360°. Therefore, since both equal one circle of rotation, they must be equal to each other:
360° = 2π rad. Divide both sides by 360 to get:
1° = (2π/360) rad = (π/180) rad. Now, we saw above that rad = 1, so:
1° = (π/180) rad = (π/180) × 1 = π/180.
Thus, like the radian, the degree is also a number—not 1 though, but rather π/180, which cannot be “thrown away” because π/180 times a number does not yield back the original number.
Thus, 30° = 30 × π/180 = π/6 = π/6 × 1 = π/6 rad.
This is the explanation as to when we express an angle in degrees, we must write the ° symbol or spell out degrees, whereas when we express the angle in radians, we may either explicitly write rad or we may leave it off. Unfortunately secondary school geometry textbooks do not seem to understand this point and typically leave off the mandatory ° symbol. That usually gets straightened out when radians are presented—typically later in the second year of algebra or in trigonometry, but it becomes something necessary for students to unlearn the incorrect and learn the correct. Thus, if an angular unit is included, you can convert that angular unit into a real number and multiply by the numeric part of the physical quantity value to the the numeric value of the physical quantity. (And absence of angular unit implies radians, which have numeric value 1, so the numeric value of the quantity is just the numeric value that is present.
Solid angles work similarly, involving area divided by area. The steradian (sr) is the unit that has value 1.
Which is an example of the force of attraction between two objects that have mass?
Magnetism
Gravity
Solar energy
Electricity
Answers
A kid pushes a stationary
merry-go-round, creating an
acceleration of 0.135 rad/s^2.
How much time does it take the
merry-go-round to complete
2.00 rotations?
(Unit = s)
Remember: CCW is +, CW is. 1 rev= 2*pi rad
Answers
The merry-go-round takes approximately 29.41 seconds to complete 2.00 rotations.
Given data:
Acceleration (α) = 0.135 rad/\(s^2\)
Number of rotations (θ) = 2.00
To find the time taken (t) for 2.00 rotations, we need to use the formula:
θ = 0.5 * α * \(t^2\)
Rearranging the formula, we get:
\(t^2\) = (2 * θ) / α
Plugging in the given values, we have:
\(t^2\) = (2 * 2.00) / 0.135
\(t^2\) = 29.63
Taking the square root of both sides, we find:
t ≈ √29.63
t ≈ 5.439
Therefore, the time taken for the merry-go-round to complete 2.00 rotations is approximately 5.439 seconds.
Note: It's important to round the final answer to an appropriate number of significant figures, considering the given data. In this case, we have used four significant figures in the final answer.
However, if we want to adhere to the given significant figures in the acceleration (0.135 rad/\(s^2\)), the answer should be rounded to three significant figures. In that case, the final answer would be approximately 5.44 seconds.
For more such questions on seconds, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/29813582
#SPJ8
Here's the screenshot

Answers
Animals and plants in a food web are on each other for survival. A. dependent B. suspending OC. superintendent D. interdependent
Answers
A. dependent
This is the answer
who was an inventor who helped design washington dc
Answers
Pierre Charles L'Enfant was an inventor and architect who is best known for designing the city plan of Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States.
What is inventor?An inventor is a person who creates new and useful ideas or devices that are often innovative and novel. Inventors can work in a wide range of fields, from technology and engineering to medicine and the arts. Their ideas and inventions can be revolutionary and can have a significant impact on society and the economy. The process of inventing typically involves identifying a problem or need, and then developing and testing a solution or device to address that problem. Inventors may work alone or as part of a team, and they may collaborate with other professionals, such as engineers, scientists, or designers, to bring their ideas to fruition.
Here,
L'Enfant was born in France in 1754 and received his training as an engineer and military officer. He served in the Continental Army during the American Revolution and later worked as a city planner and surveyor.
To know more about inventor,
https://brainly.com/question/30555639
#SPJ4
Which nucleus completes the following equation?
Cle+?
OA. S
OB. S
16
OC. Ar
18
OD. 39 y
18

Answers
The equation below is completed by the chromium nucleus.
Where can one locate chrome?Chromium is mostly found in chromite. The locations where this ore can be found include South Africa, India, Kazakhstan, and Turkey. In an electric arc furnace, chromite is often reduced with carbon to generate chromium metal, as is chromium(III) oxide when it is reduced with silicon or aluminum.
Why is chromium necessary?An important mineral called chromium helps insulin work properly in the body by regulating blood sugar levels. Your body uses the hormone insulin to convert sugar, starchy carbs, and other foods into the energy you require for daily activities.
To know more about chromium nucleus visit:
https://brainly.com/question/681602
#SPJ1
Which type of energy is the result when a drum is hit with a drumstick?
OA. electrical energy
OB. light energy
OC.
sound energy
OD.
all of these
Reset
Submit
Answers
Answer:
That drummer has mechanical energy as he moves the drumsticks to hit the drums and cymbals. So I'm pretty sure it's OD. sound energy.
¯\_(ツ)_/¯¯
help me please oml 2 one



Answers
Color: Both the bromine gas and steak have a brownish color.
What is bromine gas?Bromine gas is a reddish-brown, nonflammable, and highly toxic gas with a very strong, unpleasant odor. It is composed of two heavy, diatomic, halogen molecules, Br2, and is the only nonmetal element that exists as a liquid at room temperature. Bromine gas is denser than air and is soluble in water and organic solvents.
Texture: The bromine gas is a gas and therefore has no texture, while the steak is solid and has a firm texture.
Temperature: The bromine gas is a gas and therefore has a lower temperature than the steak, which is at room temperature.
Bromine Gas and Juice:
Color: The bromine gas is brownish and the juice is a yellowish or orange color.
Texture: The bromine gas is a gas and therefore has no texture, while the juice is a liquid and has a smooth texture.
Temperature: The bromine gas is a gas and therefore has a lower temperature than the juice, which is at room temperature.
To learn more about bromine gas
https://brainly.com/question/1126306
#SPJ1
Which is the best example of muscular endurance
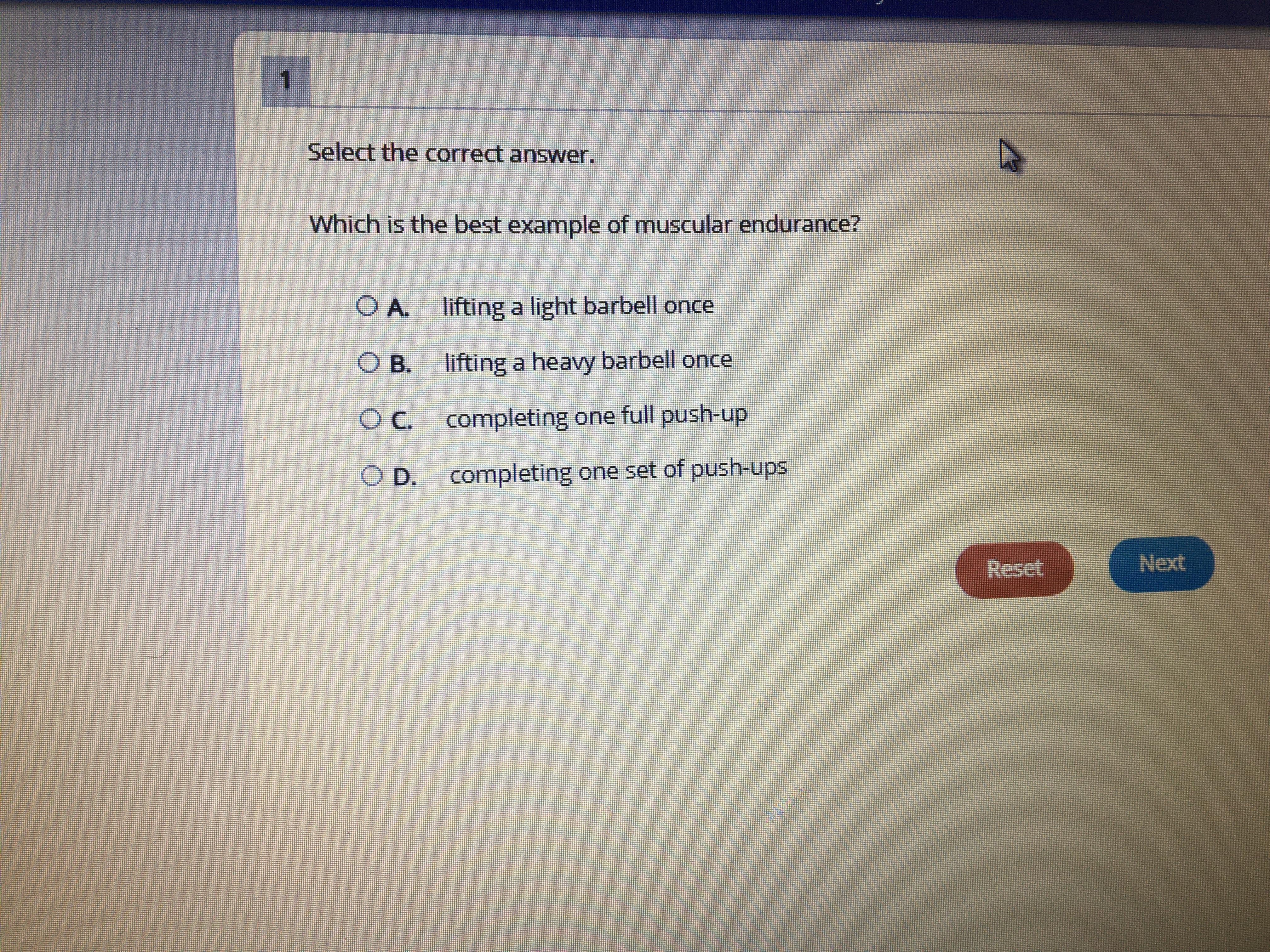
Answers
Answer:
personally I'd say C by do not know if that is the exact answer
The Integrated circuit (microelectronic circuit on a chip) was first invented/developed in 1958 with milli-meter (1/1000 of a meter) device dimensions. Today, integrated circuits use 5 nano-meter (5/1000,000,000 of a meter) device dimensions. What have been the implications on computing and communications resulting from this million times shrinking of device dimensions over the past 6 decades. Be specific, like the impact on speed of computing, and sophistication of circuit functions, etc. 20 points
Answers
The shrinking of integrated circuit device dimensions over six decades led to faster computing, advanced circuit functions, improved power efficiency, and widespread advanced electronic devices.
Increased Computing Speed: As device dimensions have shrunk, the distance between transistors on a chip has decreased, enabling faster electrical signal propagation. This has led to increased clock speeds and faster processing capabilities, allowing for more complex computations and faster data processing.
Enhanced Circuit Functionality: With smaller device dimensions, more transistors can be integrated into a single chip. This has enabled the development of highly sophisticated and complex circuits, such as microprocessors, capable of performing intricate tasks.
The increased number of transistors has also facilitated the integration of various functionalities, such as memory, graphics processing, and communication capabilities, onto a single chip, leading to more versatile and powerful computing devices.
Improved Power Efficiency: Smaller device dimensions have reduced the distance that electrical signals need to travel within a chip. This has minimized the power losses associated with signal propagation, resulting in improved power efficiency. Additionally, the miniaturization of components has allowed for the development of low-power transistors, enabling energy-efficient operation and longer battery life in portable electronic devices.
Proliferation of Advanced Electronic Devices: The million-fold reduction in device dimensions has made it possible to produce smaller, lighter, and more compact electronic devices. This has led to the widespread adoption of smartphones, tablets, wearables, and other portable devices that offer advanced computing, communication, and multimedia capabilities. The miniaturization of integrated circuits has also enabled the development of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smart sensors, and embedded systems, which have revolutionized various industries and aspects of everyday life.
Increased Integration and System Complexity: Shrinking device dimensions have allowed for greater integration of components and systems on a single chip. This has led to the development of system-on-chip (SoC) solutions, where multiple functions, such as processing, memory, and communication, are combined on a single integrated circuit. The increased integration and system complexity have contributed to the advancement of technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and autonomous systems.
Cost Reduction: The continual shrinking of device dimensions has resulted in increased transistor density on a chip. This has led to higher production yields per wafer, driving down the manufacturing cost per transistor. The cost reduction has made advanced computing and communication technologies more affordable and accessible to a wider range of users, fostering their widespread adoption.
Overall, the million times shrinking of device dimensions in integrated circuits over the past six decades has had a profound impact on computing and communications, revolutionizing the speed, functionality, power efficiency, and size of electronic devices while enabling the development of new technologies and driving economic growth in the digital era.
To learn more about integrated circuit click here:
brainly.com/question/14788296
#SPJ11
In which medium will waves travel the fastest?
Answers
The speed at which waves travel depends on the medium through which they are moving. In general, waves travel fastest through solids, followed by liquids, and then gases. This is because the molecules in solids are tightly packed and can transmit the waves more efficiently. Therefore, in general, waves will travel the fastest through a medium that is solid rather than liquid or gas.
For example, seismic waves travel fastest through solid rock, which is why earthquakes can be detected hundreds of miles away from their epicenter. Similarly, sound waves travel faster through water than through air, which is why underwater creatures can communicate over long distances.
In terms of electromagnetic waves, such as light and radio waves, travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, which is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second. However, when passing through a medium such as water or glass, their speed is reduced due to interactions with the molecules in the medium.
Therefore, in general, waves will travel the fastest through a medium that is solid rather than liquid or gas.
For more information on electromagnetic waves visit:
brainly.com/question/3101711
#SPJ11
A mountain climber has a mass of 80kg. Determine his loss of weight in going from the foot of Mount Everest at an altitude of 2440 meters to its top at an altitude of 8848m. Mount Everest has latitude of 280N, and the mean radius of the earth is 6371km
Answers
To determine the loss of weight for the mountain climber when ascending Mount Everest, we need to consider the change in gravitational force due to the change in altitude. The weight of an object can be calculated using the formula:
Weight = mass × acceleration due to gravity
The acceleration due to gravity varies with altitude due to the change in distance from the center of the Earth. The acceleration due to gravity at sea level (g₀) is approximately 9.8 m/s².
First, we need to calculate the acceleration due to gravity at the foot of Mount Everest:
g₁ = g₀ × (r₀ / (r₀ + h₁))²
where r₀ is the mean radius of the Earth and h₁ is the altitude at the foot of Mount Everest.
Next, calculate the acceleration due to gravity at the top of Mount Everest:
g₂ = g₀ × (r₀ / (r₀ + h₂))²
where h₂ is the altitude at the top of Mount Everest.
Now we can calculate the initial weight of the climber:
Weight₁ = mass × g₁
And the final weight of the climber:
Weight₂ = mass × g₂
Finally, calculate the loss of weight:
Loss of weight = Weight₁ - Weight₂
Given:
Mass of climber (m) = 80 kg
Altitude at foot of Mount Everest (h₁) = 2440 m
Altitude at top of Mount Everest (h₂) = 8848 m
Mean radius of the Earth (r₀) = 6371 km = 6371000 m
Acceleration due to gravity at sea level (g₀) = 9.8 m/s²
Let's plug in the values and calculate the loss of weight:
g₁ = 9.8 × (6371000 / (6371000 + 2440))² ≈ 9.8018 m/s²
g₂ = 9.8 × (6371000 / (6371000 + 8848))² ≈ 9.7827 m/s²
Weight₁ = 80 × 9.8018 ≈ 784.144 N
Weight₂ = 80 × 9.7827 ≈ 782.616 N
Loss of weight = 784.144 - 782.616 ≈ 1.528 N
Therefore, the loss of weight for the mountain climber in going from the foot of Mount Everest to its top is approximately 1.528 Newtons.
To know more about gravitational force visit :-
brainly.com/question/14762028
#SPJ11
Describe the motion of the box:
A)The box will not move because the forces acting on the box are balanced.
B)The box will move 75N to the right, because the forces are unbalanced.
C)The box will move 75N to the left, because the forces are unbalanced.

Answers
Answer:
B
Explanation:
because that's the answer
A motorcycle patrolman starts from rest at A two seconds after a car, speeding at the constant rate of 120km/h, passes point A. If the patrolman accelerates at the rate of 6m/s^2 until he reaches his maximum permissible speed of 150km/h, which he maintains, calculate the distance from point A to the point at which be overtakes the car
Answers
The distance from point A to the point at which the patrolman overtakes the car is 2700 meters.
The distance from point A to the point at which the motorcycle patrolman overtakes the car is 2700 meters. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of the calculations:
Step 1:
Distance covered by the car in 2 seconds:
Distance = Speed * Time
Speed = 120 km/hr = (120/3600) m/s = (1/30) m/s
Time = 2 seconds
Distance = (1/30) m/s * 2 s = 2/30 km = (2/30) * 1000 m = 66.67 m
Step 2:
Calculating the time taken by the motorcycle patrolman to reach a speed of 150 km/h:
Using the equation v = u + at
Initial velocity (u) = 0 m/s
Final velocity (v) = 150 km/h = (150000/3600) m/s = (125/3) m/s
Acceleration (a) = 6 m/s^2
(125/3) m/s = 0 m/s + 6 m/s^2 * t
Solving for t:
t = (125/3) / 6 sec = (125/3) * (1/6) sec = 125/18 sec
Step 3:
Calculating the distance covered by the motorcycle patrolman in the first (125/18) seconds:
Using the equation s = ut + (1/2)at^2
Initial velocity (u) = 0 m/s
Acceleration (a) = 6 m/s^2
Time (t) = 125/18 sec
s = 0 * (125/18) + (1/2) * 6 * ((125/18)^2) = 1562.5/9 m
Step 4:
Calculating the time taken by the motorcycle patrolman to overtake the car:
Let the time taken be t sec
Speed of the car = 120 km/hr = (100/3) m/s
Distance covered by the car in time t = (100/3) m/s * t
Distance covered by the motorcycle patrolman in time t = Distance covered by the car in time t + Distance covered by the motorcycle patrolman in the first (125/18) sec
Time taken = (Distance to be covered) / (Speed of the motorcycle patrolman)
= (Distance covered by the motorcycle patrolman in time t - Distance covered by the motorcycle patrolman in the first (125/18) sec) / [(150000/3600) m/s]
= [(100/3) * t + 1562.5/9 - 1562.5/9] / [(150000/3600)] sec
= [(100/3) * t] / [(150000/3600)] sec
= (1/45) * t sec
The two times should be equal, so we can set up the equation:
(100/3) * t + 1562.5/9 = (1/45) * t
Solving for t:
(3200/45) * t + 1562.5/9 = t
[(3200/45) - (1/45)] * t = 1562.5/9
t = (1562.5 * 45) / (9 * 3199) sec
Step 5:
Distance from point A to the point at which the motorcycle patrolman overtakes the car:
Distance = Distance covered by the motorcycle patrolman in the first (125/18) sec + Distance covered by the motorcycle patrolman in time t
Distance = 1562.5
/9 + [(100/3) * t + 1562.5/9 - 1562.5/9] m
= 1562.5/9 + (100/3) * (1562.5 * 45) / (9 * 3199) m
= 1562.5/9 + 10425/3199 m
= [(1562.5 * 3199) + 10425] / 28791 m
= 2700 m
Therefore, the distance from point A to the point at which the motorcycle patrolman overtakes the car is 2700 meters.
Learn more about distance here :-
https://brainly.com/question/31713805
#SPJ11
a child with a mass of 30 kg is standing on a spring scale in an elevator. if the spring scale reads 360 n, what are the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the elevator at this time? the acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/s2 .
Answers
The acceleration of the elevator at this time was 2m/s² and the elevator was accelerating the upward direction.
The mass of the child standing on a spring scale in an elevator is 30 kg the elevator is showing a reading of 360 Newtons.
The reading note by the elevator is given by radiation,
W = M(g+a)
Where w is the reading of the spring scale,
M is the mass of the child,
g is the gravitational acceleration which is given to be 10m/s² and a is the acceleration of the elevator.
Putting values,
360 = 30(10+a)
12 = 10+a
a = 2m/s²
As you can see from the above result that the acceleration of the lift is 2m/s² and because it is positive it means that the elevator is accelerating in the upward direction.
To know more about acceleration due to gravity, visit,
https://brainly.com/question/605631
#SPJ4
A force of 24 N will stretch a rubber band 12 cm(0.12 m) Assuming that Hooke's faw applies, how lar will a 20 - N lorce stretch the rubber band? How much wokk does if take fo stretch the nubber band this far? How lar will a 20.N torce stretch the rubber band? B) (Sirnplify your answed) How mach work does ia take la stretch the rubber band this far? (Stmplify your answer)
Answers
Work required to stretch the rubber band by 0.10 meters will be negative, indicating that work needs to be done against the force applied to stretch the rubber band.
To determine how much the rubber band will stretch under a 20 N force and the work required to stretch it, we need to apply Hooke's Law. Hooke's Law states that the force applied to a spring or elastic material is directly proportional to the displacement it undergoes.
We can set up a proportion to find the stretch under Force 2:
(F1 / S1) = (F2 / S2)
Substituting the given values:
(24 N / 0.12 m) = (20 N / S2)
To find S2, we can rearrange the equation:
S2 = (20 N * 0.12 m) / 24 N
Simplifying:
S2 = 0.10 m
Therefore, a 20 N force will stretch the rubber band by 0.10 meters.
Now, let's calculate the work required to stretch the rubber band this far. The work (W) can be calculated using the formula:
W = (1/2) * k * (S2^2 - S1^2)
Where k is the spring constant.
However, we don't have the spring constant (k) given in the problem. So, we cannot determine the exact work without that information.
But, if we assume that the rubber band behaves as a linear spring and Hooke's Law applies, we can simplify the equation. Hooke's Law states that the force applied to a spring is equal to the spring constant (k) multiplied by the displacement (S).
F = k * S
Rearranging the equation:
S = F / k
Since the stretch (S) is directly proportional to the force (F), we can approximate the work required by assuming a constant k value:
W ≈ (1/2) * k * (S2^2 - S1^2)
W ≈ (1/2) * k * [(0.10 m)^2 - (0.12 m)^2]
Simplifying:
W ≈ (1/2) * k * (0.01 m^2 - 0.0144 m^2)
W ≈ (1/2) * k * (-0.0044 m^2)
Without the exact value of the spring constant, we cannot calculate the work precisely. However, we can still conclude that the work required to stretch the rubber band by 0.10 meters will be negative, indicating that work needs to be done against the force applied to stretch the rubber band.
Learn more about spring constant (k) from :
https://brainly.com/question/1616151
#SPJ11
A vector points 12.0 units along the x-axis, and 9.00 units along the y-axis.
Find the direction of the vector.
Answers
Answer:
15 units NE
Explanation:
Assuming the coordinate plane is a compass with N being the positive y-axis, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of the vector. Since the vector is going up by 12 and right by 9 at the same time, it should form a diagonal line, aka the hypotenuse of a triangle. This triangle has both of its leg units as 12, and 9. Pythagorean theorem states that a^2 + b^2 = c^2, that is both of their legs squared is the hypotenuse of the triangle squared. 12^2 + 9^2 = c^2. c = 15. Now that we know the magnitude, let's go back to the quadrants as the compass. Since both units are positive, the vector goes in the positive direction on both sides, which is Quadrant 1. North and East would be the appropriate say for the vector's direction, thus the vector's direction will be 15 units North East.
Which of the following is NOT a way to increase the solubility of a solid in water?
A.
crushing the solid
B.
shaking the mixture of solid and water
C.
raising the temperature of the water
D.
letting the mixture stand still a long time
Answers
Answer:
A. crushing the solid .
Answer:
A.) crushing the solid