Define gamete and zygote. What number of chromosomes does each have?
Answers
Answer:
Gametes (23) reproductive cell produced during meiosis that has the haploid number of chromosomes
Zygote (46) diploid cells
Related Questions
The diagram shows cellular activity across a cell membrane.
Which two processes does this diagram most directly model?
Answers
Answer:homeostasis and transport of molecules
Explanation:
which cellular component of our body are involved in developing infection
Answers
Answer:
the white blood cells or leucocytes
The channels in cell membranes that help substances to move in and out 20 poll
of cells during active transport are made of
A. protein.
B. chlorophyll.
C. cytoplasm
D. carbohydrates
NEED ASAP
Answers
Answer: C. cytoplasm
Explanation:
Mark as brainliest if you want ;)
first to answer correctly gets a brainly.

Answers
Answer:
8) possible genotypes
DD: 0%
Dd: 50%
dd: 50%
possible phenotypes
deaf pups 50%
hearing pups 50%
Dna strands are called antiparallel because of _______________.
Answers
DNA strands are called antiparallel because they are oriented in opposite directions. DNA, which stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, is a double-stranded molecule consisting of nucleotide monomers.
The DNA strands are complementary and run in opposite directions, which is known as antiparallel, as a result of the arrangement of these nucleotides. The phosphate group of one nucleotide is linked to the 3′ carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide by a covalent bond in the backbone of the DNA chain.
The resulting phosphate-sugar bond creates a sugar-phosphate backbone that runs in opposite directions, forming an antiparallel structure. The base pairs in the DNA molecule run in opposite directions, with one strand running from the 5′ end to the 3′ end, while the other runs in the opposite direction from the 3′ end to the 5′ end. As a result, the two strands run in opposite directions. In a DNA double helix, the two strands are complementary, with adenine always pairing with thymine and guanine always pairing with cytosine. Because of this, DNA replication is semi-conservative, with each newly synthesized DNA molecule consisting of one old and one new strand.
To know more about antiparallel visit:
https://brainly.com/question/30217797
#SPJ11
cell division that reduces chromosome number from diploid to haploid, reduction division
A Mitosis
B Meiosis
C Amitosis
D Fision
Answers
Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces chromosome number from diploid to haploid.
What do you mean by meiosis?
Meiosis, also called reduction division, division of a germ cell involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to four gametes, or sex cells, each possessing half the number of chromosomes of the original cell.
The process of meiosis is characteristic of organisms that reproduce sexually. Such species have in the nucleus of each cell a diploid (double) set of chromosomes, consisting of two haploid sets (one inherited from each parent). These haploid sets are homologous—i.e., they contain the same kinds of genes, but not necessarily in the same form.
To know more about meiosis from the given link:
https://brainly.com/question/15475960
#SPJ4
Meiosis is the division of a cell that reduces the number of chromosomes from a diploid (2n) state to a haploid (n) state.
What is diploid?
Diploid is a term used in genetics to refer to a cell or organism that has two sets of chromosomes. In humans, the diploid number of chromosomes is 46, which is two sets of 23. This means that any human cell contains two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent. Diploid cells are found in multicellular organisms, and are the most common form of cells in the human body. Diploidy is important for genetic diversity, as it allows for the exchange of genetic material between the two sets of chromosomes. This helps create genetic variation, which is necessary for evolution to occur.
This occurs in sex cells during the process of gamete formation, and is essential for sexual reproduction. During meiosis, two consecutive nuclear divisions (meiosis I and meiosis II) reduce the number of chromosomes by half. This process also involves cell division, which results in four haploid daughter cells. Each daughter cell contains one set of chromosomes, which is a combination of the maternal and paternal chromosomes of the original cell.
To learn more about diploid
https://brainly.com/question/27833793
#SPJ4
Why do scientists think that the chemicals found on Mars might have come from something that used to be alive?
Answers
Imagine that you live on a farm and grow all your own food. In four to eight sentences, trace the flow of carbohydrate macromolecules through your farm. State how the macromolecules are produced, how they are passed along, and what they are eventually used for. In your answer, give specific examples of macromolecules and processes
Answers
Carbohydrates are found in a wide array of both healthy and unhealthy foods—bread, beans, milk, popcorn, potatoes, cookies, spaghetti, soft drinks, corn, and cherry pie.
What is a carbohydrate?The carbohydrate which is a macro-molecule is produced by the producer such as trees and shrubs etc. in the process of photosynthesis. These carbohydrates transfer to the primary consumer such as monkey who eat these plants. When the secondary consumer such as jaguar eat these primary consumer, this carbohydrate again transfer from one organism to another organism.
How is energy stored?This carbohydrate is a source of energy which is broken down in the stomach into glucose and this glucose is absorbed by the cells and releases energy by mitochondria in the form of ATP. This energy is used in various activities such as walking, running and breathing etc. Carbohydrate, proteins and fats are the examples of macro-molecules.
To know more about mitochondria visit:-
brainly.com/question/10688306
#SPJ4
If a damaged cell is found, or produced, during the cell cycle, then that cell will undergo
O A. Division
B. Apoptosis
C. Growth
D. DNA synthesis
Answers
Answer:
D
Explanation:
DNA synthesis
If the damage is irreparable, the cell may undergo apoptosis, or programmed cell death 2. This self-destruction mechanism ensures that damaged DNA is not passed on to daughter cells and is important in preventing cancer.
where does the phosphorus thats used in ATP come from?
Answers
Answer:
Phosphorus in ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) comes from various sources, including food and cellular metabolic processes. Inorganic phosphate (Pi) is an essential nutrient in many foods, such as meat, fish, dairy, and whole grains. When we consume these foods, the phosphate is broken down and absorbed by the body, which can then be used to synthesize ATP in the cells.
Furthermore, the cellular metabolic processes, such as the breakdown of glucose, release Pi, which can be recycled to make more ATP. During cellular respiration, glucose is broken down into pyruvate, and Pi is released as a byproduct. This Pi is then used to replenish the phosphate groups in ATP, essential for energy transfer within the cells.
Hope it helps!
A single strand of mRNA is created by using DNA as a template. What is the correct sequence of events that occurs next during protein synthesis?
Responses
The mRNA combines with another strand to form double stranded RNA and then goes to a ribosome to make a protein
The mRNA combines with another strand to form double stranded RNA and then goes to a ribosome to make a protein
The mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to the golgi to be packaged and shipped to new cells
The mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to the golgi to be packaged and shipped to new cells
The mRNA leaves the nucleus to undergo translation into a protein at the mitochondria
The mRNA leaves the nucleus to undergo translation into a protein at the mitochondria
The mRNA goes to a ribosome after leaving the nucleus where codons and anticodons match up to string together changes of amino acids
Answers
Answer:
The correct sequence of events for protein synthesis after mRNA is created is:
The mRNA goes to a ribosome after leaving the nucleus where codons and anticodons match up to string together changes of amino acids
The key steps are:
DNA is used as a template to create mRNA strands in the nucleus.
The mRNA then leaves the nucleus.
The mRNA goes to ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
At the ribosomes, the mRNA codons pair with tRNA anticodons to recruit amino acids.
The amino acids are strung together into a polypeptide chain.
The polypeptide chain then folds into a functional 3D protein.
The other options are incorrect:
The mRNA does not combine with another strand to form double stranded RNA. It remains single stranded.
The mRNA does not go to the golgi apparatus. It goes directly from the nucleus to ribosomes.
The proteins are not synthesized in the mitochondria. They are synthesized on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
So in summary, the key stages after mRNA creation are: transcription to mRNA in nucleus → mRNA transport to cytoplasm → translation into proteins at ribosomes.
Explanation:
Answer:
The correct sequence of events that occurs next during protein synthesis is that the mRNA goes to a ribosome after leaving the nucleus where codons and anticodons match up to string together chains of amino acids, ultimately forming a protein. The ribosome acts as the site of protein synthesis and reads the sequence of codons on the mRNA, each of which corresponds to a specific amino acid. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) carrying the appropriate anticodon sequence then bring the corresponding amino acids to the ribosome, where they are linked together to form a growing peptide chain until the entire protein is complete. The completed protein may then undergo additional processing or folding before it can perform its cellular function.
West nile virus is transmitted by mosquitoes as they take a blood meal. flies can also transmit pathogens, but not in the process of taking a blood meal. differentiate the ways in which flies and mosquitoes acquire and transmit infectious agents, and suggest 1-2 ways in which these methods might be disrupted.
Answers
Mosquitoes acquire pathogens from infected hosts through blood meals, while flies acquire pathogens from contaminated surfaces and can transmit them through direct contact or regurgitation.
To disrupt the transmission of pathogens by mosquitoes, several strategies can be employed, including the use of insecticides to kill adult mosquitoes or larvicides to prevent the development of mosquito larvae in water sources.
Mosquito nets can also be used to physically block mosquitoes from accessing humans, and vaccination of humans or animals can provide immunity against certain mosquito-borne diseases.
In the case of fly-borne pathogens, sanitation measures such as proper waste disposal and cleaning can reduce the availability of contaminated surfaces. Additionally, using physical barriers such as screens or protective clothing can prevent direct contact between flies and hosts.
Educating individuals on proper hygiene practices, such as hand washing and food preparation, can also reduce the spread of fly-borne illnesses.
To know more about pathogens, refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/30654336#
#SPJ11
what is the path of blood from the heart to the right little finger (pinky) and back to the heart?
Answers
Blood is pumped out of the heart through the aorta, the largest artery in the body.
The aorta branches into smaller arteries, and eventually reaches the brachial artery in the arm. From there, the blood flows through the ulnar artery, which supplies the hand and fingers, including the little finger.
Once the blood has delivered oxygen and nutrients to the tissues of the little finger, it is collected by the venous system. The blood from the little finger drains into the ulnar vein, which joins with other veins to form the brachial vein.
The brachial vein then joins with the axillary vein, which merges with the subclavian vein to form the superior vena cava, which returns blood to the heart.
To know more about aorta , refer here :
https://brainly.com/question/31721645#
#SPJ11
Which plants utilize a specialized carbon fixation enzyme and a unique cell structure to reduce the problems of photorespiration?.
Answers
C4 plants uses carbon fixation enzyme and a unique cell structure to reduce the problems of photorespiration.
Photorespiration does not occur because they have a mechanism that increases the concentration of CO2 at the enzyme site.
C4 plants are corn, sorghum, sugarcane, and switchgrass. However, the In C4 plants require anatomical and biochemical adaptations and also additional plant energy and resources than C3 photosynthesis, This is the reason why in cooler environments, C3 plants are typically more photosynthetically efficient and productive.
To learn more about Photorespiration , here
brainly.com/question/13433623
#SPJ4
The melting of sea ice ______ (increases) (does not affect) (decreases) the density of the surrounding ocean water.
Answers
The melting of sea ice decreases the density of the surrounding ocean water.
What is the most likely reason sphingomyelinase can quickly respond to a toxin that facilitates calcium entry into the cell? Sphingomyelinase is recruited to the membrane by specific phospholipids Sph
Answers
This recruitment allows the enzyme to be readily available at the membrane, where it can interact with its substrate and initiate cellular signaling pathways in response to the toxin-induced calcium influx.
The most likely reason that sphingomyelinase can quickly respond to a toxin that facilitates calcium entry into the cell is due to its recruitment to the membrane by specific phospholipids called sphingomyelins.
Sphingomyelinase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes sphingomyelin, a specific type of sphingolipid found in cell membranes. Sphingomyelinase activation can be triggered by various factors, including cellular stress, pathogens, or toxins.
When a toxin facilitates calcium entry into the cell, it can disrupt the normal calcium homeostasis, leading to an increase in intracellular calcium levels. This increase in calcium can serve as a signaling mechanism to activate sphingomyelinase.
Specific phospholipids, such as sphingomyelins, play a crucial role in recruiting sphingomyelinase to the cell membrane. These phospholipids act as binding sites for sphingomyelinase and help localize the enzyme to the appropriate cellular compartments. Therefore, when the toxin-induced calcium entry occurs, sphingomyelinase can quickly respond by being readily available at the membrane to interact with its substrate, sphingomyelin.
Once activated, sphingomyelinase catalyzes the hydrolysis of sphingomyelin into ceramide and phosphorylcholine. This reaction generates ceramide, a bioactive lipid involved in various cellular processes, including cell signaling, apoptosis (programmed cell death), and inflammation. The rapid response of sphingomyelinase to a toxin-induced increase in intracellular calcium levels allows for the timely production of ceramide, facilitating downstream signaling events and cellular responses to the toxin.
In summary, sphingomyelinase can quickly respond to a toxin that facilitates calcium entry into the cell due to its recruitment to the membrane by specific phospholipids, such as sphingomyelins. This recruitment allows the enzyme to be readily available at the membrane, where it can interact with its substrate and initiate cellular signaling pathways in response to the toxin-induced calcium influx.
To know more about cell click-
brainly.com/question/3142913
#SPJ11
Which term describes the relationship in which one organism lives inside the other one. Check ih correct answer
Answers
Answer:
The term that describes the relationship in which one organism lives inside the other one is endosymbiosis.
Explanation:
explain what happens when a lipid ligand reaches a target cell and how the lipid ligand acts out a cellular response
Answers
when lipid ligand binds to the receptors, some conformational changes takes place which leads to responses.
This lipid ligand binding leads to signal transduction
lipid soluble hormones when diffuse through membrane they bind with receptors which is there in cytoplasm. the lipid receptor complex will now binds with gene this process is direct gene activation.
eg, steroid hormones
mrna is generated it enter cytoplasm and makes the protein.
lipid insoluble these do not bind directly to cell wall as they are insoluble therefore they bind to the secondary messenger which then bins to DNA the mrna is formed which leads to formation of proteins.
eg , peptide hormones
To know more about lipids,
https://brainly.com/question/29853349
#SPJ4
A 76-year-old female was diagnosed with osteoporosis by radiologic exam. She is at high risk for:
a.
Bone infections
b.
Joint injuries
c.
Pathologic bone fractures
d.
Ssteomalacia
Answers
b.
joint injuries
Explanation:
The word ‘osteoporosis’ means ‘porous bone.’ It is a disease that weakens bones. Osteoporosis means that you have less bone mass and strength. The disease often develops without any symptoms or pain, and it is usually not discovered until the weakened bones cause painful fractures. Most of these are fractures of the hip, wrist and spine.
Which one of the following is the first in allopatric speciation?
Geographic IsolationHybridizationGenetic DriftPolyploidy
Answers
Geographic isolation is the first step in allopatric speciation.
Allopatric speciation occurs when a population is separated by a physical or geographic barrier, such as a mountain range, river, or ocean. Once separated, the two populations may evolve independently due to differences in their environments, genetic drift, mutation, or natural selection. Over time, these differences can accumulate and lead to the formation of two distinct species.
Geographic isolation is the first step in this process, as it physically separates the population and prevents gene flow between them. Without gene flow, the two populations can accumulate genetic differences and eventually become reproductively isolated from each other, meaning they can no longer interbreed and produce viable offspring. At this point, they are considered to be separate species.
To know more about allopatric speciation:
https://brainly.com/question/4493180
#SPJ4
Which of the claims about the burning of wood is supported by Joan’s model?
Answers
The claims about the burning of wood that are supported by Joan's model are:
A. Matter is conserved during the burning of wood.E. Burning wood involves oxygen as well as carbon.What is Joan's model about?Joan's model shows that the burning of wood is a chemical reaction that involves the combination of oxygen and carbon. The reaction produces carbon dioxide and water vapor.
The model also shows that the reaction is reversible, meaning that it can occur in both the forward and reverse directions. However, the reverse reaction is much slower than the forward reaction, so it is not typically observed.
Find out more on burning of wood here: https://brainly.com/question/1537286
#SPJ1
Complete question:
Which of the claims about the burning of wood is supported by Joan's model? Select all the claims that are
supported.
A. Matter is conserved during the burning of wood.
B. Chemical energy is conserved during the burning of wood.
C. Burning wood involves a series of chemical reactions that occur in one direction only.
D. Burning wood involves a series of chemical reactions that occur in both the forward and reverse directions.
E. Burning wood involves oxygen as well as carbon.
what do animals ranging from corals to monkeys have in commona mouth and an anus number of embryonic tissue layerstype of body symmetrypresence of hox genes
Answers
Animals ranging from corals to monkeys share several key characteristics, including having a mouth and an anus, a specific number of embryonic tissue layers, a type of body symmetry, and the presence of hox genes.
Animals ranging from corals to monkeys have several characteristics in common. These shared features include having a mouth and an anus, a specific number of embryonic tissue layers, a type of body symmetry, and the presence of hox genes.
Having a mouth and an anus is a characteristic shared by all animals. This is because animals are heterotrophic organisms, meaning that they need to consume other organisms for energy. The mouth allows them to ingest food, while the anus is used to eliminate waste.
Animals also have a specific number of embryonic tissue layers. These layers are the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. These layers give rise to various organs and tissues during development.
The type of body symmetry is another shared characteristic among animals. Bilateral symmetry, where the animal can be divided into two mirror-image halves along a central axis, is the most common type of symmetry among animals. This symmetry allows animals to have a distinct head and tail region, as well as a front and back.
To learn more about tissue layers
https://brainly.com/question/30507706
#SPJ4
what is the substrate molecule that initiates this metabolic pathway? b. what is the inhibitor molecule c. what type of inhibitor is it? d. when does it have the most significant regulatory effect? e. what is this type of metabolic control called?
Answers
The substrate molecule that starts this metabolic pathway is threonine. The molecule of inhibition is isoleucine. It comes under non-competitive inhibition
When does it have significant regulatory effect?when it connects to an allosteric site, it has the most substantial regulatory impact. The non-active site of an enzyme is in which the allosteric inhibitor interacts. The active site's architecture is altered to prevent the enzyme from binding to its substrate.
What is the name of this kind of metabolic regulation?Through feedback inhibition, isoleucine inhibits threonine deaminase from working. Noncompetitive inhibitors are used in a common biochemical process called feedback inhibition to modulate some enzyme activity. In this process, the finished item blocks the enzyme that catalyses the initial reaction in a chain of reactions.
Learn more about metabolic pathway here:
brainly.com/question/17486892
#SPJ4
• Different types of molecules do
things in a cell
Answers
Answer:
I dont get what you are trynna ask so..
Explanation:
here are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell's mass.
Answer:
Your cells come from other cells dahhh stup!d
Explanation:
jk it's B
Mark me brainliest!
What is the Function of the Respiratory System?
Answers
Answer:
The respiratory system is a network of organisms and tissues that help you breathe. This system helps your body to absorb oxygen from the air so your organs work. It also cleans waste gases, such as carbon dioxide, from your blood
hope i helped
The process shown in the diagram below represents the copying of DNA during the S phase of the cell cycle.
DNA replication
What is the purpose of this process as it relates to cell division?
Question 1 options:
To make genetically different copies of DNA to produce genetically different cells during mitosis.
To make identical copies of DNA to produce identical daughter cells during mitosis.
To make identical copies of DNA to produce genetically different cells during mitosis.
To make genetically different copies of DNA to produce identical daughter cells during mitosis.

Answers
The goal of this procedure is to create identical DNA copies so that mitosis will result in identical daughter cells.
DNA replication happens during the S phase of the cell cycle to make sure the genetic material is replicated and passed on to the daughter cells. This mechanism makes sure that the daughter cells are similar to the parent cells and share their genetic makeup.
This is necessary for mitosis to be completed successfully and for the development of two daughter cells that share the same genetic material.
Learn more about mitosis at:
https://brainly.com/question/29768164
#SPJ1
58.The best description of the induced fit model of enzyme function isa. a cofactor must first bind to the active site, allowing the substrate to fit properly.b.a molecule not directly involved in the catalysis interacts with a site on the proteinfar from the active site, changing the shape of the active site to make it work.c. the active site, the substrate, or both change shape upon binding so that theactivation energy of the desired change is decreased.d. the active site has a definite, rigid shape that only fits one substrate molecule.a short protein chain that blocks access to the active site is chemically removed asthe substrate approaches.
Answers
Answer:
The correct answer is C:
the active site, the substrate, or both change shape upon binding so that the activation energy of the desired change is decreased.
The induced fit model for enzymed function describes how the substrate is able to induce the proper alignment of the active site of the enzyme. Both the active site of the enzyme and the substrate change in conformation until they are completly bound.
This theory explains why enzymes may exhibit broad specificity, that is that they can bind to a variety of molecules.
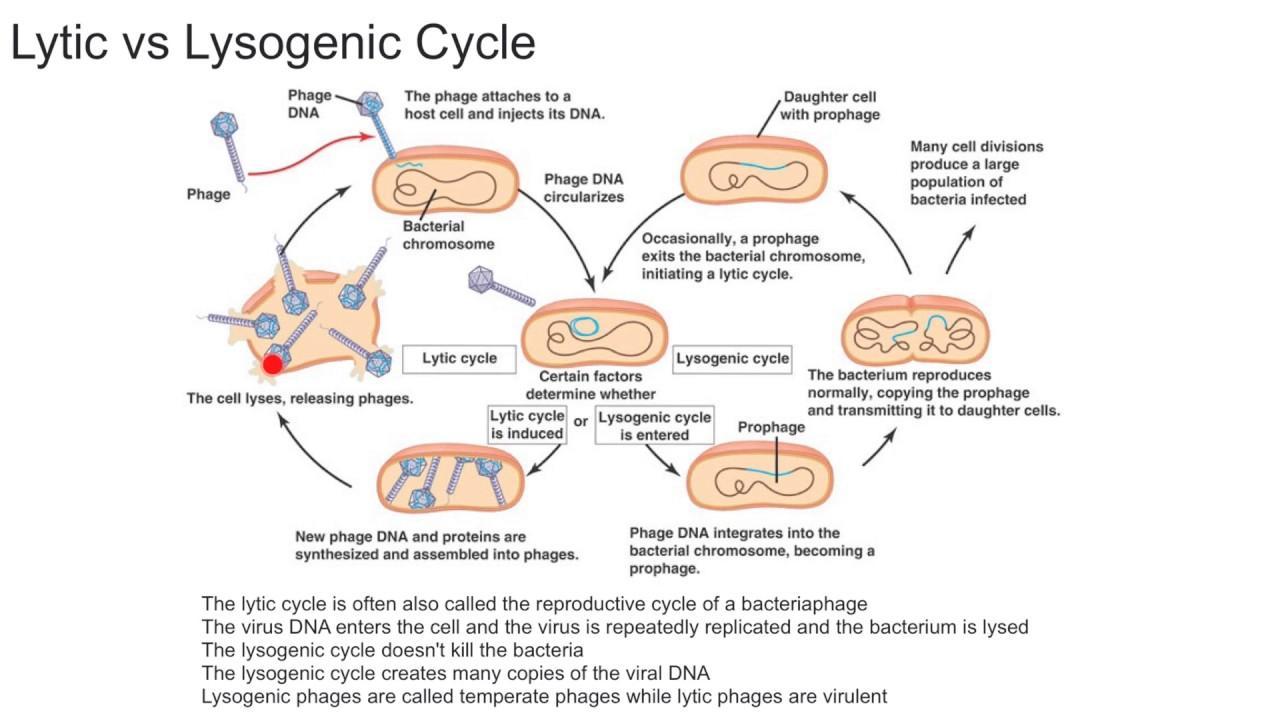
Lytic cycle or lysogenic cycle?: Infected cells have viral genes permanently.
Answers
Answer:
It is a lysogenic cycle.
Explanation:
In the lysogenic cycle, the viral DNA gets integrated into the host's DNA (see the picture attached).
Hope this will help :)
To maintain constant body temperature in a cold environment, a homeothermic animal uses which of the following physiological mechanisms
Answers
In order to maintain a constant body temperature in a cold environment, a homeothermic animal uses the following physiological mechanisms; Shivering and Non-Shivering Thermogenesis. These mechanisms allow the animal's body to regulate its body temperature in order to maintain a healthy and constant internal temperature.
Homeothermic animals are able to maintain their body temperature regardless of the external temperature of their environment.
Body temperature regulation is crucial in homeothermic animals since it has a direct impact on their physiological and metabolic processes.
As a result, when exposed to a cold environment, these animals utilize physiological mechanisms to produce heat and warm their body in order to prevent a decrease in their core temperature and hypothermia.
Non-shivering thermogenesis mechanism, in general, is usually activated in brown adipose tissue (BAT) during cold exposure, where it is responsible for the conversion of energy stored as triglycerides into heat.
BAT thermogenesis in non-shivering thermogenesis relies on the activation of the hormone-adipose tissue axis that stimulates lipolysis and thermogenic gene expression in brown adipocytes.
In contrast, shivering thermogenesis mechanism increases metabolic rate and produces heat by increasing muscle activity in response to cold. This mechanism requires shivering of skeletal muscles that helps generate heat as a result of the increased metabolic rate.
This is because muscles produce heat when they break down glucose. The heat generated is used to warm the body in cold environments.
To know more about temperature visit;
brainly.com/question/7510619
#SPJ11
A substance that provides nourshiment and growth or metabolism
O chromosome
O enzyme
O pathogen
о O
nutrient