Computers have the mineral _______________ in their motherboard.
Answers
Answer:
silica
Explanation:
Answer:
Silica
Explanation:
Hope this helps ^^
Related Questions
What is the answer:
C4H8+H2=
Answers
the [delta]g of formation of a substance is 0 for elements in their standard states the [delta]g of formation of a substance is 0 for elements in their standard states true false
Answers
The correct answer is True.
The statement "the ΔG of formation of a substance is 0 for elements in their standard states" is true.
The ΔG (Gibbs free energy) of formation refers to the change in free energy when a substance is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states.
For elements in their standard states, the ΔG of formation is defined as zero.
This is because the standard state of an element is considered to have no enthalpic or entropic contributions, and thus no change in free energy occurs when the element is formed in its standard state.
The standard Gibbs free energy of the formation of an element in its standard state is zero by definition.
This means that an element in its standard state is the most stable form of that element at standard conditions (25°C and 1 atm pressure).
For example, the standard state of carbon is graphite, so the standard Gibbs free energy of the formation of graphite is zero.
To know more about standard states, refer here
https://brainly.com/question/30319269#
#SPJ11
which is right
A.
B.
C.
D.

Answers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
because the glass contain the ice cubes
if you had 15 moles of Oxygen (O2), how many moles of water (H2O) would you be able to make?
Answers
Answer:
30 moles of water will produced.
Explanation:
Given data:
Number of moles of O₂ react = 15 mol
Number of moles of water formed = ?
Solution:
Chemical equation:
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
Now we will compare the moles of water with oxygen.
O₂ : H₂O
1 : 2
15 : 2×15 = 30 mol
30 moles of water will produced.
A gas at STP has a volume of 1.5 L. What will the pressure be if it is at 26° C occupying .75 L
Answers
Answer:
P₂ = 2.19 atm
Explanation:
Given data:
Initial volume = 1.5 L
Initial pressure =1 atm
Initial temperature = 273K
Final temperature = 26°C (26+273 = 299 K)
Final volume = 0.75 L
Final pressure = ?
Formula:
P₁V₁/T₁ = P₂V₂/T₂
P₁ = Initial pressure
V₁ = Initial volume
T₁ = Initial temperature
P₂ = Final pressure
V₂ = Final volume
T₂ = Final temperature
Solution:
P₂ = P₁V₁ T₂/ T₁ V₂
P₂ = 1 atm × 1.5 L × 299 K / 273 K × 0.75 L
P₂ = 448.5 atm .L. K / 204.75 K.L
P₂ = 2.19 atm
4. How are isotopes of the same element different? Select all that apply.
[]They have different masses.
[]They have different numbers of electrons.
[]They have different numbers of neutrons.
[]They have different numbers of protons.
Answers
\(\huge \bf༆ Answer ༄\)
The Correct choice is ~ A
Isotopes are the elements with same Atomic Number but different masses ~
what is the ratio of aluminum chloride to lithium sulfate
Answers
i neeeed helllllpppppsss

Answers
Answer:
1.0 g/cm3
Explanation:
yeah that's the density of water
Answer:
a 1 g/cm3
Explanation:
per google- A common unit of measurement for water's density is agram per milliliter (1 g/ml) or 1 gram per cubic centimeter (1 g/cm3)
Which form of energy does a plant store when light is transformed during photosynthesis?
A.chemical energy
B.thermal energy
C.mechanical energy
D.electrical energy
Answers
Answer:
A. chemical energy
Explanation:
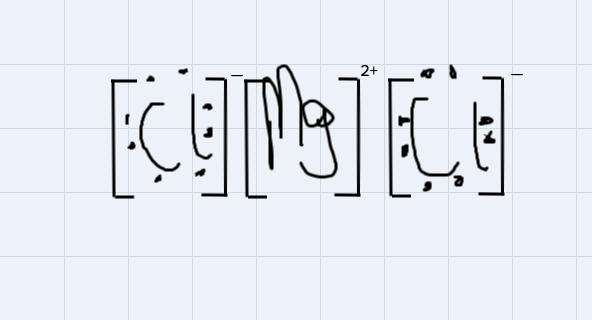
Use Lewis symbols to show how MgCl2 will be formed from Mg and Cl2.
Answers
This is a type of bonding that is formed from the from the attraction of oppositely charged ions in a compound.
For instance, MgCl2 is an ionic compound because the 2 positive ions wipossessed by the magnessium atom will attract each of the negtaive ion possessed by each of the chlorine atom to form the magnessium chloride compound
Using the Lewis symbol to demonstrate the bondng:
From the disgram, the negative ions on chlorine atoms will get attracted to the positive ions on the magnessium ion.
b. What is the atomic mass of the element in period 5, group 14?
Answers
Answer:
118.71 u
Explanation:
Tin. Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (for Latin: stannum) and atomic number 50. It is a main-group metal in group 14 of the periodic table.
Source: https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Period_5_element#:~:text=Tin,-Main%20article%3A%20Tin&text=Tin%20is%20a%20chemical%20element,14%20of%20the%20periodic%20table.
Is this statement true or false?
The products of a chemical reaction have the same properties as the reactants.
true
false
Answers
Hope this helps ❤️
Answer:
The answer is B. False
Explanation:
Find the period 2 elements (atomic numbers #3-10) and the period 3 elements (#11 - 18). Do period 2 and period 3 have the same trend?
Period 2 elements are Lithium (Li), Berillium (Be), Boron (B), Carbon (C), Nitrogen ( N), Oxygen (O), Fluorine (Fe), Neon (Ne). Period 3 elements are Sodium (Na), Magnesium (Mg), Aluminum (AI), Silicon (Si), Phosphorus (P), Sulfur (S), Chlorine (CI, Argon, (Ar)
do period 2 and period 3 have the same trend ? (if they do can you explain a bit ?)
(brainly !!)
Answers
Period 2 and period 3 elements do not have the same trend in terms of their electronic configurations. Period 2 elements have 2 electron shells and period 3 elements have 3 electron shells.
How does period 3 and period 2 elements differ?The elements in each period have one more electron shell than the elements in the previous period. As a result, the elements in each period have a different number of valence electrons, which affects their chemical properties.
As the period increases, the elements in the period become more metallic. The elements of Period 2 are generally non-metals, and the elements of Period 3 are generally metals.
Find out more on period 2 and 3 elements here: https://brainly.com/question/18878801
#SPJ1
what is the function of the cell membrane?
Answers
Answer:
Its the thin lining around the cell the moniters what gets in and out of the cell.
Explanation:
what is a metal and a non metal
Answers
Answer:
I assume you mean as in elements
A metal "A metal is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typically malleable or ductile." (wiki)
a non-metal "In chemistry, a nonmetal is a chemical element that mostly lacks the characteristics of a metal. Physically, a nonmetal tends to have a relatively low melting point, boiling point, and density. A nonmetal is typically brittle when solid and usually has poor thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity." (wiki)
Explanation:
Answer:
On the periodic table, the metals are usually on the left and middle side and nonmetals on the right side. nonmetals tend to be either a liquid or gas at room temperature and metals are usually solids at room temperature.
Explanation:
Según la Organización Mundial de la Salud, el nitrato de plata ( densidad = 4.35 g/cc ) es una sustancia con propiedades cáusticas, astringente, antiséptica y antiinfecciosa que apenas puede absorberse por la piel. Calcular la cantidad de agua necesaria para preparar 800 mL de una disolución 2 M de nitrato de plata. Ayuda porfavor
Answers
Answer:
737.52 mL de agua
Explanation:
En este caso solo debes usar la expresión de molaridad de una solución la cual es:
M = moles / V
Donde:
V: Volumen de solución.
Como queremos saber la cantidad de agua, queremos saber en otras palabras cual es la cantidad de solvente que se utilizó para preparar los 800 mL de disolución.
Una disolución se prepara con un soluto y solvente. El soluto lo tenemos, que es el nitrato de plata. Con la expresión de arriba, calculamos los moles de soluto, y luego su masa. Posteriormente, calculamos el volumen con la densidad, y finalmente podremos calcular el solvente de esta forma:
V ste = Vsol - Vsto
Primero calcularemos los moles de soluto:
moles = M * V
moles = 2 * 0.800 = 1.6 moles
Con estos moles, se calcula la masa usando el peso molecular reportado que es 169.87 g/mol:
m = moles * PM
m = 1.6 * 169.87 = 271.792 g
Ahora usando el valor de la densidad, calcularemos el volumen de soluto empleado:
d = m/V
V = m/d
V = 271.792 / 4.35
V = 62.48 mL
Finalmente, la cantidad de agua necesaria es:
V agua = 800 - 62.48
V agua = 737.52 mL
Which of the following is a change of state?
A. Chocolate melting when it is heated
B. Liquid water being absorbed by a dry sponge
O C. Wax becoming carbon dioxide and water when a candle burns
D. Bread dough rising when left out on a warm counter
SUES
Answers
Answer:
I think C. Hope this Helps!
Explanation:
A chemist titrates 190 ml of. 2412 nitrous acid solution with. 377 M KOH solution. Calculate the ph at equivalence. The pKa of nitrous acid is 3. 35
Answers
The equivalency solution has a pH of 2.624.
What is the procedure for making nitrous acid?Nitrous acid is frequently created by adding a mineral acid to aqueous sodium nitrite solutions. Typically, acidification is carried out at ice-cold temperatures, and HNO2 is consumed on-site. Nitrous acid in its free form is unstable and breaks down quickly.
In a neutralization process, weak nitrous acid (HNO2) reacts with strong basic KOH.
HNO2 + KOH → KNO2 + H2O
Then, we determine how many moles of KOH were used:
volume KOH x concentration equals moles KOH. KOH
moles KOH = 0.190 L x 0.377 mol/L
moles KOH = 0.07153 mol
Next, we calculate the initial concentration of HNO2:
concentration HNO2 = moles HNO2 / volume HNO2
concentration HNO2 = 0.07153 mol / 0.190 L
concentration HNO2 = 0.3765 M
[HNO2] = 0.5 x 0.3765 M
[HNO2] = 0.1883 M
The following equation can be used to model how nitrous acid dissociates in water:
HNO2 + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + NO2-
The following equation relates the pKa to the acid dissociation constant, Ka, for this reaction:
pKa = -log Ka
So we can find the Ka value from the given pKa:
pKa = -log Ka
3.35 = -log Ka
Ka = 10⁻³
Ka = 4.47 x 10⁻⁴
The relationship shown below is true for the concentrations of the species involved at equilibrium:
Ka = [H3O+][NO2-] / [HNO2]
Ka = [H3O+][NO2-] / [HNO2]
Ka = [H3O+] [HNO2]
Solving for [H3O+], we get:
[H3O+] = Ka / [HNO2]
[H3O+] = (4.47 x 10⁻⁴) / (0.1883 M)
[H3O+] = 0.002374 M
Finally, we can calculate the pH of the solution:
pH = -log[H3O+]
pH = -log(0.002374)
pH = 2.624
To know more about nitrous acid solution visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/17011556
#SPJ1
A sealed vessel contains 0. 200 mol of oxygen gas, 0. 100 mol of nitrogen gas, and 0. 200 mol of argon gas. The total pressure of the gas mixture is 5. 00 atm. The partial pressure of the argon is responses 0. 200 atm 0. 200 atm 0. 500 atm 0. 500 atm 1. 00 atm 1. 00 atm 2. 00 atm 2. 00 atm 5. 00 atm.
Answers
Answer:
Below
Explanation:
Each exerts pressure proportional to its fraction of the total
total = .200 + .100 + .200 = .500 mol
argon is .200 of this
.200 / .500 * 5 atm = 2 atm
The weather instruments: rain gauge can measure the amount of snow fall
True or false
Answers
Jamil invested $9,500 in an account he expects will earn 5% annually. Approximately how many years will it take for the account to double in value
Answers
It will take 14.4 years for Jamil's investment of $9,500 to double in value at a 5% annual interest rate.
To find out how long it will take for Jamil's investment to double in value, you can use the Rule of 72. The Rule of 72 is a formula used to estimate the number of years required to double the value of an investment with a fixed annual interest rate. The formula is:
Years to double = 72 / Annual Interest Rate
In this case, Jamil's annual interest rate is 5%. Plugging that into the formula:
Years to double = 72 / 5 = 14.4 years
Approximately, it will take 14.4 years for Jamil's investment to double in value.
Learn more about Rule of 72:
https://brainly.com/question/30197467
#SPJ11
Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.15 M in formic acid (HCOOH) and 0.20 M in sodium formate! (HCOONa). The Ka of formic acid is Ka = 1.8*10-4 (A) 9.21 (B) 7.00 (C)4.53 . (D) 3.87 (E) 1.15
Answers
The correct answer is (A) 9.21. We can then use the concentrations of formic acid and sodium formate in the solution to calculate the equilibrium concentrations of H3O+ and HCOO-.
To calculate the pH of the given solution, we need to first consider the ionization reaction of formic acid:
HCOOH + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + HCOO-
The Ka of formic acid, which is given, can be used to calculate the equilibrium constant (Keq) for the above reaction:
Keq = [H3O+][HCOO-]/[HCOOH] = Ka
We can then use the concentrations of formic acid and sodium formate in the solution to calculate the equilibrium concentrations of H3O+ and HCOO-. Assuming x is the concentration of H3O+ and HCOO- in the solution:
[H3O+] = x
[HCOO-] = 0.20 M - x
[HCOOH] = 0.15 M
Substituting these values in the Keq expression:
Ka = [H3O+][HCOO-]/[HCOOH]
1.8*10^-4 = x(0.20 - x)/0.15
Simplifying the equation, we get:
x^2 - 0.36x + 1.2*10^-4 = 0
Using the quadratic formula, we get:
x = 0.348 M
Therefore, the pH of the solution is:
pH = -log[H3O+] = -log(0.348) = 0.46
Therefore, the correct answer is (A) 9.21.
To know more about pH visit: https://brainly.com/question/2288405
#SPJ11
Mikayla says that air is an element since it has oxygen in it. Jose says that air is a mixture because each part of air keeps its properties. Grant says that both Mikayla and Jose are wrong, because air is a compound. Who is correct and why? Group of answer choices
Answers
Answer: Jose is correct because air is a mixture of gases ( both elements and compounds).
Explanation:
An element consist of only one type of atom and a compound made up of 2 or more types of elements joined together ( by ionic or covalent bonds).
Whereas air around us is a mixture of gases (both elements and compounds) like nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide, and very small amounts of other gases and water vapors
Hence, Jose is correct because air is a mixture of gases ( both elements and compounds).
I don't understand the concept of dynamic equlibrum and it shifting right and left depending on pressure concentration and temperature
Answers
Answer:
See below.
Explanation:
A dynamic equilibrium in chemistry refers to a situation in which the reaction of reactants to form product(s) in which the products can reverse the reaction by falling apart and back to the reactants. Reactions that go to completion are irreversible. In cases where reactants form products (in a forward reaction), but the products can change back into reactants (in a reverse reaction) are called reversible.
An example is the reaction of carbon dioxide with water to form carbonic acid (think soft drinks).
CO2(g)+H2O(l) ⇌ H2CO3(aq)
As anyone who has opened a warm can of soda knows, it can erupt suddenly and spray anyone nearby with a shower of bubbly, and sticky, soda. Carbonic acid is unstable and will happily decompose back to it's reactant molecules if given the chance.
Experience tells us what to expect when giving a brother or sister a can of warm soda that you've shaken hard for a minute. But if you are a chemist, such responses aren't always easy to predict with a new reaction. Equilibrium constants were developed to provide a means for presdicting the exstent of these reactions. They are used in equilibrium equations to predict the concentrations of products and reactants, given conditions of temperature and pressure, under defined conditions of temperature and pressure.
The equations themselves include concentrations as the key input. In the carbonic acid example, if one were to add excessive amounts of one of the reactants, one would expect the equilibrium to "shift to the right." This simply means that more carbonic acid would be made. The chances of the forward reaction increase as concentration increases. The amount of CO2 given off as a gas depends on the concentration of the CO2 in the gas phase, which is given by the partial pressure of the gas.
The space above the soda and the cap represents one place that the CO2(g) can escape the solution. The CO2 pressure in the gas phase is a measure of it's concentration. An equilbium calculation takes this concentration in account when decidng how much much of each component is present. Other compouns that are present may also impact the equilibrium since they may interfere with one of the reaction steps. Pressure and emperature either dirctly impact the concentration (e.g., gases) or they affect the "effective" concentrations of the compunds. A higher temperature creates more collisons between reactant molucules that may change the equilibrium constant..
12. what mass of glycerin (c3h8o3), a nonelectrolyte, must be dissolved in 200.0 g water to give a solution with a freezing point of -1.50 °c?
Answers
The mass of the glycerin, C₃H₈O₃ a nonelectrolyte, that must be dissolved in 200.0 g water to give a solution with the freezing point of -1.50 °C is 14.8 g.
Mass of solvent = 200.0 g
Depression at freezing point = - 1.50 °C
Kf = 1.86 °C / m
The molality is given as :
0 - ΔT = Kf × m × i
Where ,
ΔT = - 1.50 °C
Kf = 1.86 °C / m
m = molality = ?
i = 1
m = 1.50 / 1.86
m = 0.806 m
The molality = ( mass of solute × 1000) / ( molar mass of solute × mass of solvent)
Mass of solute =( 0.806 × 92 × 200 ) / 1000
Mass of the solute = 14.8 g
To learn more about freezing point here
https://brainly.com/question/13122709
#SPJ4
What happens in your cells with cellular respiration?
Answers
in a quasi-static isobaric expansion, 575 j of work are done by the gas. if the gas pressure is 0.40 atm, what is the fractional increase in the volume of the gas, assuming it was originally at 21.0 l?
Answers
A quasi-static isobaric expansion requires the gas to exert 575 j of work. suppose there is a 0.40 atm gas pressure the fractional increase in volume of the gas is 68.5
In a quasi-static isobaric expansion, the pressure of the gas remains constant, and the work done by the gas is given by:
W = PΔV
where W is the work done by the gas, P is the constant pressure of the gas, and ΔV is the change in volume of the gas. Rearranging this equation, we get:
ΔV = W/P
Substituting the given values, we have:
ΔV = 575 J / (0.40 atm) = 1437.5 L·atm
The fractional increase in volume is the ratio of the change in volume to the original volume:
ΔV/V = 1437.5 L·atm / (21.0 L x 1.00 atm) = 68.5
Therefore, the fractional increase in volume of the gas is 68.5, or 6750%.
Learn more about work done by the gas here:
https://brainly.com/question/29983272
#SPJ4
A reaction has an enthalpy change of − 71 kJ mol − 1 and an entropy change of − 58 J K − 1 mol − 1 . At what temperature does this exothermic reaction cease to be spontaneous?
Answers
To determine the temperature at which an exothermic reaction ceases to be spontaneous, we need to calculate the Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) and use the equation ΔG = ΔH - TΔS.
Given that ΔH = -71 kJ/mol and ΔS = -58 J/K·mol, we can calculate ΔG at different temperatures to determine the temperature at which the reaction becomes non-spontaneous.
At a temperature of 0 K, ΔG = ΔH, since TΔS = 0. Thus, ΔG = -71 kJ/mol.
As the temperature increases, TΔS becomes more negative, which means that ΔG becomes more negative, making the reaction more spontaneous.
At a certain temperature, however, ΔG will become positive, which means that the reaction is no longer spontaneous and will not proceed on its own. This temperature can be found by rearranging the equation ΔG = ΔH - TΔS to T = ΔH / ΔS, and substituting the known values for ΔH and ΔS:
T = ΔH / ΔS = -71 kJ/mol / (-58 J/K·mol) = 1230 K
So, the reaction will cease to be spontaneous at a temperature of approximately 1230 K.
14. The atoms of element X contains nineteen electrons. With which of the following elements will the chemistry of Z be similar? a Aluminum b) Bromine c) Lithium d) Magnesium
Answers
First of all, Z is unknown. I hope it is a mistake.
Now, it is given that the element X has nineteen electrons. This proves that X is actually Potassium.
As per the periodic table, both Potassium and Lithium belongs to group 1 as their valency is 1 because of the presence of only one electron in the outermost shell of electrons i.e., they lose an electron during a chemical reaction to form a stable compound. Furthermore, both are metallic.
Magnesium belongs to group 2 and hence its valency is two, which is different from potassium though it is metallic. Similiarly, bromine belongs to group 17 and gains one electron during a reaction in contrast to potassium.
( No internal links available for reference. For clarification, check the periodic table).
Why is ethylene an important raw material used in the production of plastics, but ethane is not?
Answers
Ethylene (C2H4) is an important raw material in the production of plastics due to its unique chemical properties and reactivity. Here are a few reasons why ethylene is favored over ethane:
Double Bond: Ethylene contains a double bond between the two carbon atoms, which provides it with increased reactivity compared to ethane. The presence of the double bond makes ethylene more suitable for undergoing polymerization reactions to form long-chain polymers.
Polymerization: Ethylene can undergo polymerization reactions where multiple ethylene molecules join together to form polyethylene, which is one of the most widely used plastics in various applications. The double bond in ethylene allows it to easily react with other ethylene molecules, leading to the formation of long polymer chains.
Versatility: Due to its ability to form polyethylene, ethylene serves as the building block for a wide range of plastic products, including packaging materials, bottles, containers, films, and pipes. Polyethylene can be modified and processed into different forms such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or low-density polyethylene (LDPE), each with distinct properties suited for various applications.
On the other hand, ethane (C2H6) lacks the double bond present in ethylene and therefore does not possess the same level of reactivity needed for polymerization reactions. Ethane is typically used as a feedstock for producing ethylene through processes like steam cracking, which involves breaking down larger hydrocarbons. Ethane itself is not directly used as a raw material in large-scale plastics production because it does not readily undergo the polymerization reactions required to form plastics.
learn more about Ethylene here
https://brainly.com/question/14797464
#SPJ11