Charlie bought three cantaloupes
for $7. How many
cantaloupes can he buy with $28?
Answers
Answer:
Charlie can buy 12 cantaloupes with $28
Step-by-step explanation:
If he is able to buy 3 cantaloupes with $7, the price per cantaloupe can be determined by dividing ou money spent by the number of cantaloupes:
$7/per 3 cantaloupes, this will give us a cost of $7/3 per cantaloupe.
With our single price, we can take the $28 we have and divide in by the unit price for the cantaloupes to determine how many we can buy:
$28/(7/3)=12 cantaloupes
Hi!
To solve this, we can set up a proportion.
First, we will make two ratios that we can set equal to each other.
If Charlie bought three cantaloupes for $7, our ratio would be 3:7 or \(\frac{3}{7} \).
Now, we want to know how many cantaloupes for $28, so our ratio would be x:28 or \(\frac{x}{28} \), where 'x' is the number of cantaloupes.
Now, we set those fractions equal to each other.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
\(\frac{x}{28} = \frac{3}{7} \)
Now, we can use cross-products to solve for x.
\(7x = 84\\ \)
Divide both sides by 7
\(x=12\)
Therefore, he can buy 12 cantaloupes with $28.
(See BELOW if you do not know what cross products are)

Related Questions
Find the inverse of the one-to-one function. F(x) = 7x - 6
Answers
Answer:
The inverse is (x+6)/7
Step-by-step explanation:
y = 7x-6
To find the inverse, exchange x and y
x = 7y-6
Solve for y
x+6 = 7y
Divide each side by 7
(x+6)/7 = y
The inverse is (x+6)/7
The drama club is selling short-sleeved shirts for $5 each, and long-sleeved shirts for $10 each. They hope to sell all of the shirts they ordered, to earn a total of $1,750. After the first week of the fundraiser, they sold StartFraction one-third EndFraction of the short-sleeved shirts and StartFraction one-half EndFraction of the long-sleeved shirts, for a total of 100 shirts. How many short-sleeved shirts were ordered?
How many long-sleeved shirts were ordered?
Answers
Answer:
150 short-sleeved shirts100 long-sleeved shirtsStep-by-step explanation:
Let S and L represent the numbers of short- and long-sleeved shirts ordered.
The expected earnings were ...
5S +10L = 1750
The number sold was ...
(1/3)S + (1/2)L = 100
We can multiply the first equation by 1/5 and the second equation by 6 to put the equations into standard form:
S +2L = 3502S +3L = 600Subtracting the second equation from twice the first gives ...
2(S +2L) -(2S +3L) = 2(350) -(600)
L = 100 . . . . . . simplify
2S +3(100) = 600
S = 150
150 short-sleeved and 100 long-sleeved shirts were ordered.
Answer:
b
Step-by-step explanation:
i did it on edge
Identify the factors in the expression 5(m - 1). O A. 5 and (m - 1) O B. 5 and 1 1 O C. 5 and m O D. mand 1

Answers
Answer:
A. 5 and (m - 1)Step-by-step explanation:
Given expression:
5(m - 1)It is the product of two factors, in other words it has two factors:
5 and (m - 1)Correct choice is A
Step-by-step explanation:
Given expression = 5(m - 1)
5(m - 1) = 0
So, the factors are
5 and (m - 1)
show all working convert the following improper fractions to mixed numbers in it's lowest terms. 96/7?
Answers
Answer:
13 5/7
Step-by-step explanation:
7 can fit into 96 13 times, So 96-(7x13) is 5. 5/7 is remaining.
Which of the following would you see on a circle graph?
OA. Percentages
OB. Bars
C. Points
OD. A y-axis
Answers
A, percentages
You would see percentages on a circle graph, because it's how many parts of the whole that they take up.
Happy to help, have a great day! :)
Question 2
No calculations are necessary to answer this question.
3/01
3/02
$1.7420 $1.7360
Date
July GBP Futures
Contract Price
O long; long
Based on the closing prices of July GBP Futures Contract over the 3-day period in March 20XX as shown above, you shou
position on 3/01 and a position on 3/02.
O long; short
O short; short
3/03
short; long
$1.7390
Answers
The given information does not provide any clear indication for determining the position that should be taken on 3/01 and 3/02. Without additional information, it is not possible to make a decision. The table only displays the closing prices of the July GBP Futures Contract on different days, and it is unclear what trading strategy or what scenario is being considered. Additional information about the goals and objectives, the market conditions, and other relevant factors would be necessary to make a decision about trading positions.
6. Journalise the following transactions
1. Bricks for Rs 60,000 and timber for Rs 35,000 purchased for
the construction of building. The payment was made by cheque.
2. Placed in fixed deposit account at bank by transfer from current
account Rs 13,000.
3. Appointed Mr. S.N. Rao as Accountant at Rs 300 p.m. and
Received Rs 1000 as security Deposit at 5% p.a. interest.
4. Sold goods to shruti for Rs 80,000 at 15% trade discount and
4% cash discount. Received 75% amount immediately through a
cheque.
5. Purchased goods from Richa for Rs 60,000 at 10% trade
discount and 5% cash discount. 60% amount paid by cheque
immediately.
6.
On 18th jan,Sold goods to shilpa at the list price of Rs 50,000
20% trade discount and 4% cash discount if the payment is made
within 7 days. 75% payment is received by cheque on Jan 23rd.
7. On 25th jan, sold goods to garima for Rs 1,00,000 allowed her
20% trade discount and 5% cash discount if the payment is made
within 15 days. She paid 1/4th of the amount by cheque on Feb 5th
and 60% of the remainder on 15th in cash.
8. Purchased land for Rs 2,00,000 and paid 1% as brokerage and
Rs 15,000 as registration charges on it. Entire payment is made by
cheque.
9. Goods worth Rs 25,000 and cash Rs 40,000 were taken away
by the proprietor for his personal use.
10. Sold goods costing Rs 1,20,000 to charu at a profit of 33% 3 %
on cost less 15% trade discount.
9
11. Paid rent of building Rs 60,000 by cheque. Half the building is
used by the proprietor for residential purpose.
12. Sold goods costing Rs 20,000 to sunil at a profit of 20% on
sales less 20% trade discount .
13. Purchased goods for Rs 1000 from nanda and supplied it to
helen for Rs 1300. Helen returned goods worth Rs 390, which in
turn were returned to nanda.
14. Received invoice at 10% trade discount from rohit and sons
and supplied these goods to madan, listed at Rs 3000.
Answers
1.Bricks and timber purchased for construction. (Debit: Bricks - Rs 60,000, Debit: Timber - Rs 35,000, Credit: Bank - Rs 95,000)
2.Transfer of Rs 13,000 to fixed deposit account. (Debit: Fixed Deposit - Rs 13,000, Credit: Current Account - Rs 13,000)
3.Appointment of Mr. S.N. Rao as Accountant. (Debit: Salary Expense - Rs 300, Debit: Security Deposit - Rs 1,000, Credit: Accountant - Rs 300)
4.Goods sold to Shruti with discounts. (Debit: Accounts Receivable - Shruti - Rs 80,000, Credit: Sales - Rs 80,000)
5.Goods purchased from Richa with discounts. (Debit: Purchases - Rs 60,000, Credit: Accounts Payable - Richa - Rs 60,000)
6.Goods sold to Shilpa with discounts and received payment. (Debit: Accounts Receivable - Shilpa - Rs 50,000, Credit: Sales - Rs 50,000)
7.Goods sold to Garima with discounts and received partial payment. (Debit: Accounts Receivable - Garima - Rs 1,00,000, Credit: Sales - Rs 1,00,000)
8.Purchase of land with additional charges. (Debit: Land - Rs 2,00,000, Debit: Brokerage Expense - Rs 2,000, Debit: Registration Charges - Rs 15,000, Credit: Bank - Rs 2,17,000)
9.Proprietor took goods and cash for personal use. (Debit: Proprietor's Drawings - Rs 65,000, Credit: Goods - Rs 25,000, Credit: Cash - Rs 40,000)
10.Goods sold to Charu with profit and discount. (Debit: Accounts Receivable - Charu - Rs 1,20,000, Credit: Sales - Rs 1,20,000)
11.Rent paid for the building. (Debit: Rent Expense - Rs 60,000, Credit: Bank - Rs 60,000)
12.Goods sold to Sunil with profit and discount. (Debit: Accounts Receivable - Sunil - Rs 24,000, Credit: Sales - Rs 24,000)
13.Purchased goods from Nanda and supplied to Helen. (Debit: Purchases - Rs 1,000, Debit: Accounts Payable - Nanda - Rs 1,000, Credit: Accounts Receivable - Helen - Rs 1,300, Credit: Sales - Rs 1,300)
14.Purchased goods from Rohit and Sons and supplied to Madan. (Debit: Purchases - Rs 2,700, Credit: Accounts Payable - Rohit and Sons - Rs 2,700, Debit: Accounts Receivable - Madan - Rs 3,000, Credit: Sales - Rs 3,000)
Here are the journal entries for the given transactions:
1. Bricks and timber purchased for construction:
Debit: Bricks (Asset) - Rs 60,000
Debit: Timber (Asset) - Rs 35,000
Credit: Bank (Liability) - Rs 95,000
2. Transfer to fixed deposit account:
Debit: Fixed Deposit (Asset) - Rs 13,000
Credit: Current Account (Asset) - Rs 13,000
3. Appointment of Mr. S.N. Rao as Accountant:
Debit: Salary Expense (Expense) - Rs 300
Debit: Security Deposit (Asset) - Rs 1,000
Credit: Accountant (Liability) - Rs 300
4. Goods sold to Shruti:
Debit: Accounts Receivable - Shruti (Asset) - Rs 80,000
Credit: Sales (Income) - Rs 80,000
5. Goods purchased from Richa:
Debit: Purchases (Expense) - Rs 60,000
Credit: Accounts Payable - Richa (Liability) - Rs 60,000
6. Goods sold to Shilpa:
Debit: Accounts Receivable - Shilpa (Asset) - Rs 50,000
Credit: Sales (Income) - Rs 50,000
7. Goods sold to Garima:
Debit: Accounts Receivable - Garima (Asset) - Rs 1,00,000
Credit: Sales (Income) - Rs 1,00,000
8.Purchase of land:
Debit: Land (Asset) - Rs 2,00,000
Debit: Brokerage Expense (Expense) - Rs 2,000
Debit: Registration Charges (Expense) - Rs 15,000
Credit: Bank (Liability) - Rs 2,17,000
9. Goods and cash taken away by proprietor:
Debit: Proprietor's Drawings (Equity) - Rs 65,000
Credit: Goods (Asset) - Rs 25,000
Credit: Cash (Asset) - Rs 40,000
10. Goods sold to Charu:
Debit: Accounts Receivable - Charu (Asset) - Rs 1,20,000
Credit: Sales (Income) - Rs 1,20,000
Credit: Cost of Goods Sold (Expense) - Rs 80,000
Credit: Profit on Sales (Income) - Rs 40,000
11. Rent paid for the building:
Debit: Rent Expense (Expense) - Rs 60,000
Credit: Bank (Liability) - Rs 60,000
12. Goods sold to Sunil:
Debit: Accounts Receivable - Sunil (Asset) - Rs 24,000
Credit: Sales (Income) - Rs 24,000
Credit: Cost of Goods Sold (Expense) - Rs 20,000
Credit: Profit on Sales (Income) - Rs 4,000
13. Goods purchased from Nanda and supplied to Helen:
Debit: Purchases (Expense) - Rs 1,000
Debit: Accounts Payable - Nanda (Liability) - Rs 1,000
Credit: Accounts Receivable - Helen (Asset) - Rs 1,300
Credit: Sales (Income) - Rs 1,300
14. Goods received from Rohit and Sons and supplied to Madan:
Debit: Purchases (Expense) - Rs 2,700 (after 10% trade discount)
Credit: Accounts Payable - Rohit and Sons (Liability) - Rs 2,700
Debit: Accounts Receivable - Madan (Asset) - Rs 3,000
Credit: Sales (Income) - Rs 3,000
for such more question on journal entries
https://brainly.com/question/28390337
#SPJ8
42,000 divided by 10'3 (ASAP)
Answers
Answer:407.7669
Step-by-step explanation:
42,000 divided by 1000 would be simplified to 42 divide if you take away the zeros from it hoped this help
A dishwasher uses 65 gallons of water to wash 5 loads of dishes. How many gallons of water would be used to wash 14 loads?
Answers
With the help of a linear equation, we know that 182 gallons of water would be used to wash 14 loads.
What is a linear equation?A mathematical expression for an equation with just one variable is a linear equation in one variable.A and B can be any two real numbers, while x is a confusing variable with only one potential value. This equation is Ax + B = 0.An illustration of a linear equation with only one variable is 9x + 78 = 18.So, gallons of water used to wash 14 loads are:
Gallons of water=65×14/5Gallons of water= 910/5 gallonsGallons of water= 182 gallonsTherefore, with the help of a linear equation, we know that 182 gallons of water would be used to wash 14 loads.
Learn more about linear equations:
brainly.com/question/11897796
#SPJ13
Which of the following are solutions to the inequality below? Select all that apply. 89 < 12 h
Answers
Answer:
7.4 < h
Step-by-step explanation:
89 < 12h
Divided both sides by 12
7.4 < h
The answer is:
⇨ h > 7.417Work/explanation:
The objective of this problem is to isolate the variable. So in the inequality \(\bf{89 < 12h}\), we should isolate h.
So I divide each side by 12
\(\bf{7.417 < h}\)
Hence, h > 7.417Suppose 150 mL (milliliters) of a medication is administered to an infected patient. It is estimated that 8%
of this person’s cells are infected with a virus.
1. Suppose 2 mL of the medication contains 2.3 × 103 antiviral proteins. How many antiviral proteins were
injected into this person? Express your answer in scientific notation.
2. There are about 1 × 1014 cells in the average adult human body. What percentage of this person’s cells
can be affected by the administered medication?
3. How many mL of medication would need to be administered to the patient in order to have 1 antiviral
protein for every infected cell? How many liters is this equivalent to?
Answers
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
To find the number of antiviral proteins injected into the person, we can set up a proportion:
2 mL contains 2.3 × 10^3 antiviral proteins
x mL contains how many antiviral proteins?
The proportion can be written as:
2 mL / 2.3 × 10^3 = x mL / (unknown number of antiviral proteins)
We can solve this proportion by cross-multiplication:
2 mL * (unknown number of antiviral proteins) = 2.3 × 10^3 antiviral proteins * x mL
x = (2.3 × 10^3 antiviral proteins * x mL) / 2 mL
Simplifying, we get:
x = 1.15 × 10^3 * x mL
Therefore, the number of antiviral proteins injected into the person is 1.15 × 10^3.
The total number of cells in the person's body is approximately 1 × 10^14. If 8% of the person's cells are infected with the virus, we can calculate the percentage of cells that can be affected by the medication:
Percentage of cells affected = (Number of infected cells / Total number of cells) * 100
Number of infected cells = 8% of 1 × 10^14 cells
Number of infected cells = (8/100) * 1 × 10^14
Number of infected cells = 8 × 10^12
Percentage of cells affected = (8 × 10^12 / 1 × 10^14) * 100
Percentage of cells affected = 8 × 10^-2 * 100
Percentage of cells affected = 8%
Therefore, the administered medication can affect 8% of the person's cells.
To find the amount of medication needed to have 1 antiviral protein for every infected cell, we can set up a proportion:
2.3 × 10^3 antiviral proteins in 2 mL
1 antiviral protein in x mL
The proportion can be written as:
2.3 × 10^3 antiviral proteins / 2 mL = 1 antiviral protein / x mL
We can solve this proportion by cross-multiplication:
(2.3 × 10^3 antiviral proteins) * x mL = 2 mL * 1 antiviral protein
x = (2 mL * 1 antiviral protein) / (2.3 × 10^3 antiviral proteins)
Simplifying, we get:
x = 0.8696 mL
Therefore, to have 1 antiviral protein for every infected cell, approximately 0.8696 mL of medication needs to be administered. This is equivalent to 0.0008696 liters.
Lane high school has 5 times as many students as park elementary. How many more students attend lane high school than park high school
Answers
Answer:
5 times as many
BRAINLIEST, please!
Step-by-step explanation:
I'd need more information about how many students there are at one of the schools. For example, if there are 200 students at Park Elementary, then there are 1000 at Lane High School since 200 x 5 = 1000. 1000 - 200 is 800, so there would be 800 more students at Lane High.
y
4
Solve for y.
Then, find the side lengths of the
largest triangle.
Fill in the green blank.
8
X
2
+
2
8
y
y
[?]
X
Enter
Help
Skip
![y4Solve for y.Then, find the side lengths of thelargest triangle.Fill in the green blank.8X2+28yy[?]XEnterHelpSkip](https://i5t5.c14.e2-1.dev/h-images-qa/contents/attachments/JuNdEokRZtVGhxu7UhDawqCUE5XDy8Kf.png)
Answers
Answer:
y = 4\(\sqrt{5}\) , ? = 10
Step-by-step explanation:
using Pythagoras' identity on the smallest right triangle
x² = 4² + 2² = 16 + 4 = 20 ( take square root of both sides )
x = \(\sqrt{20}\) = \(\sqrt{4(5)}\) = \(\sqrt{4}\) × \(\sqrt{5}\) = 2\(\sqrt{5}\)
using Pythagoras' identity on the middle right triangle
y² = 8² + 4² = 64 + 16 = 80 ( take square root of both sides )
y = \(\sqrt{80}\) = \(\sqrt{16(5)}\) = \(\sqrt{16}\) × \(\sqrt{5}\) = 4\(\sqrt{5}\)
using Pythagoras' identity on the largest right triangle
?² = x² + y² = (2\(\sqrt{5}\) )² + (4\(\sqrt{5}\) )² = 20 + 80 = 100
Take square root of both sides
? = \(\sqrt{100}\) = 10
8+3(p-9)
Pleaseeee helppp
Answers
Answer:
3p - 19
Step-by-step explanation:
8 + 3(p - 9)
Distribute;
8 + 3p - 27
Collect like terms;
-19 + 3p
3p-19 by using addition and the distributive property

Can someone answer this because this one is confusing and I need help.
Answers
A.280 cubic inches
B.1,800 cubic inches
C.180 cubic inches
D.600 cubic inches
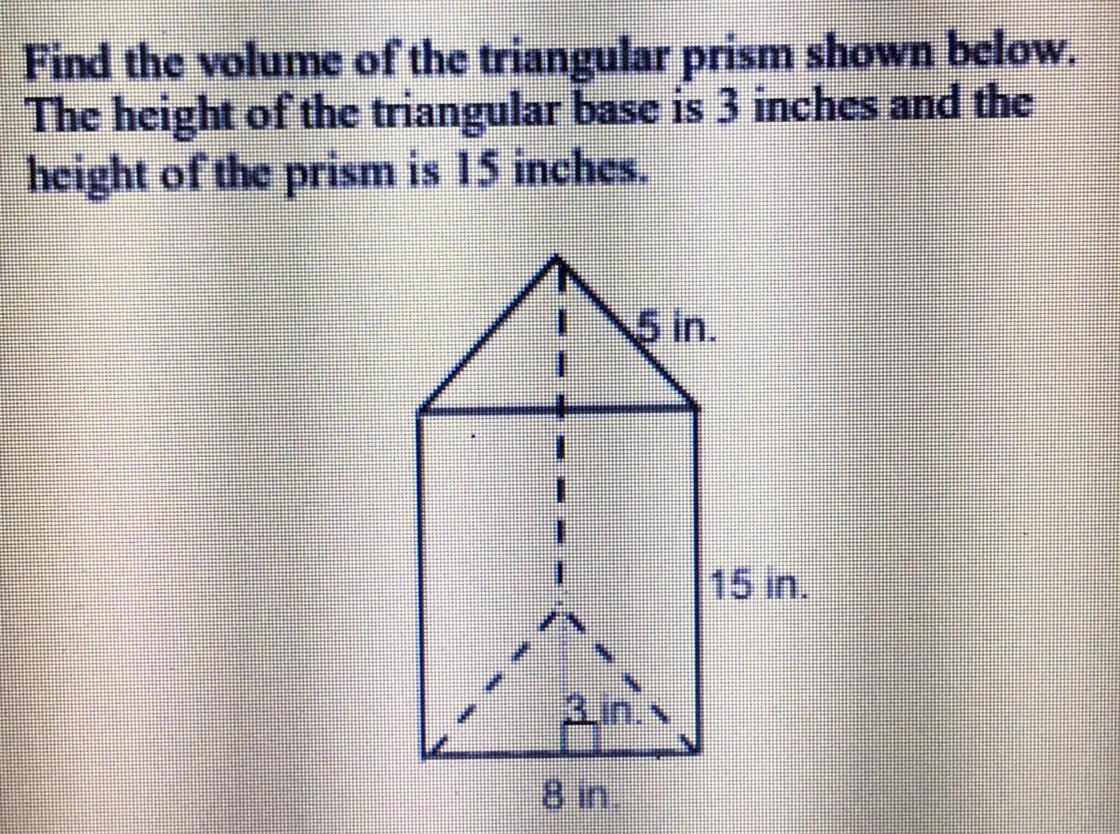
Answers
your answer would be 180 cubic inches which is option C
Type the answer in standard form below.
2,000,000+600,000+
30+8
Answers
Answer:
2,600,038
Step-by-step explanation:
If you horizontally stretch the quadratic parent function, f(x) = x2, by a factor
of 3, what is the equation of the new function?
O A. g(x) = x²
O B. g(x) = (3x)2
C. g(x) = 3x2
O D. g(x) = (3x)2

Answers
Answer:
g(x)=(1/3x)² .................
District size in 1790
The U.S. population in 1790 was 3,615,920, and the House size was set at 105.
The ideal congressional district size (Standard Divisor) in 1790 was [answer].
(Give your answer rounded to one decimal place.)
Answers
The ideal congressional district size (Standard Divisor) in 1790 was 34437.33.
What is Standard divisor?The number of persons each House of Representatives seat represents is known as the "Standard Divisor" (SD). By dividing the total population of all the states by the total number of seats available for voting, the SD is determined. SD is calculated as Total U.S. Population / Total Number of Voting Seats.
The ratio of the entire population to the available seats (or other allocations) is known as the standard divisor. • The Hamilton system divides up any extra seats among the states with the largest fractional parts after allocating each state its lower quota initially.
Given,
population in 1790 was 3,615,920,
number of objects = 105
⇒ Standard divisor = total population / number of objects
⇒ Standard divisor = 3,615,920 / 105
⇒ Standard Divisor = 34437.33
To learn more about Standard divisor from given link
https://brainly.com/question/17112402
#SPJ1
Si: F(x) = 2x + 4 ; R(x) = x ; calcula : R(F(0))
Answers
Answer: 4
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
\(F(x)=2x+4\)
\(R(x)=x\)
We need to find \(R(F(x))\) at \(x=0\)
\(R(F(x))=[2x+4]\)
\(R(F(x))=2x+4\)
\(R(F(0))=2\times 1+4=4\)
\(R(F(0))=4\)
Where does the line through A(−3, 1, 0) and B(−1, 5, 6) intersect the plane 2x + y − z + 2 = 0? Justify all your steps
Answers
Answer:
(0, 7, 9)
Step-by-step explanation:
The direction vector (a, b, c) is given by B - A
(a, b, c) = (−1, 5, 6) - (-3, 1, 0) = (2, 4, 6)
(a, b, c) = (2, 4, 6)
Let us use point A as \((x_o,y_o,z_o)\), therefore (-3, 1, 0) = \((x_o,y_o,z_o)\)
\(x=x_o+at\\\\x=-3+2t\\\\y=y_o+bt\\\\y=1+4t\\\\z=z_o+ct\\\\z=0+6t\)
Substituting the value of x, y and z into the plane equation:
2x + y − z + 2 = 0
2(-3+2t) + (1 + 4t) - (6t) + 2 = 0
-6 + 4t + 1 + 4t - 6t + 2 = 0
2t -3 = 0
2t = 3
\(\x=-3+2t\\\\x=-3+2(3/2)=0\\\\y=1+4t\\\\y=1+4(3/2)=7\\\\z=0+6t\\\\z=6(3/2)=9\\\\x=0,y=7,z=9\\\\(0,7,9)\)
t = 3/2
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
A grasshopper covered a distance of 6 yards in 10 equal hops How many yards did the grasshopper travel on each hop?
Answers
Answer:
0.6 yards
Step-by-step explanation:
6 yards/10 hops = 0.6 yards per hop
Which inequality will have a shaded area below the boundary line?
A.
y – x > 5
B.
2x - 3y ≤ 3
C.
2x – 3y
D.
7x + 2y ≤ 2
E.
3x + 4y > 12
Answers
Option c) 2x-3y ≥ 3 is correct inequality which has a shaded area below the boundary line.
Attempting all the equation on the graph to get the solutions
Inequality can be define as the relation of equation contains the symbol of ( ≤, ≥, <, >) instead of equal sign in an equation.
Since, while attempting all the option on graph. The one equation that satisfies the condition is 2x-3y ≥ 3 of having shaded area below the boundary line.
Thus, the option c) 2x-3y ≥ 3 is correct implification on graph which shows the shaded area below the boundary line.
Learn more about inequality here:
https://brainly.com/question/14098842
#SPJ1

Could use help on this thank you in advance!

Answers
Answer:
what exactly do i need to do ?????
Step-by-step explanation:
Heights of females are known to follow a normal distribution with mean 64.5 inches and standard deviation of 2.8 inches. Find the probability that a randomly selected female is taller than 67 inches.
Answers
The probability that a randomly selected female is taller than 67 inches is 0.8133, or approximately 81%.
To calculate this probability, we need to standardize the height of 67 inches using the formula:
z = (x - mu) / sigma
where x is the height we're interested in, mu is the mean, and sigma is the standard deviation.
z = (67 - 64.5) / 2.8 = 0.8929.
Then, we can look up the area to the right of z = 0.8929 in the standard normal distribution table, which is 0.1867.
Finally, we subtract this value from 1 to get the probability that a randomly selected female is taller than 67 inches:
P(X > 67) = 1 - 0.1867
P(X > 67) = 0.8133
So, the probability that a randomly selected female is taller than 67 inches is 0.8133, or approximately 81%.
To learn more about probability visit: https://brainly.com/question/13604758
#SPJ4
PLEASE HELP!!!!!! IMPORTANT!
THE ANSWER ISN'T THAT I ACCIDENTALLY HIT IT!

Answers
Answer:
C
Step-by-step explanation:
I took the quiz before:3
g(x) = -2x + 1
Find g(-7).
Answers
Answer:
g(-7) = -2(-7) + 1 = 15
Step-by-step explanation:
How to solve adjacent angles?

Answers
Answer:
D
Step-by-step explanation:
1 + 4x and 57° are corresponding angles and are congruent , so
1 + 4x = 57 ( subtract 1 from both sides )
4x = 56 ( divide both sides by 4 )
x = 14
Dilacey takes out a loan from the bank that charges a 10% interest rate. After 18 months,
she accrues $420 in simple interest. How much was the loan that Dilacey took out?
Answers
Answer:
Dilacey took a loan of $2800
Step-by-step explanation:
P=(Simple Interest×100)/R×T
P=$420×100/10×1½
P=$42000/15
P=$2800
show more notes w. heieie you can do it for
Answers
Answer:
Scallops
Step-by-step explanation:
What is the present value of R13 000 p.a. invested at the beginning of each year for 8years at 10%p.a. compound interest? (NB Use the compound interest tables provided or work to three decimal places only.)
Answers
Given statement solution is :- The present value of R13,000 per year invested for 8 years at 10% compound interest is approximately R69,776.60.
To calculate the present value of an investment with compound interest, we can use the formula for the present value of an annuity:
PV = A *\((1 - (1 + r)^(-n)) / r\)
Where:
PV = Present value
A = Annual payment or cash flow
r = Interest rate per period
n = Number of periods
In this case, the annual payment (A) is R13,000, the interest rate (r) is 10% per year, and the investment is made for 8 years (n).
Using the formula and substituting the given values, we can calculate the present value:
PV = \(13000 * (1 - (1 + 0.10)^(-8)) / 0.10\)
Calculating this expression:
PV = \(13000 * (1 - 1.10^(-8)) / 0.10\)
= 13000 * (1 - 0.46318) / 0.10
= 13000 * 0.53682 / 0.10
= 6977.66 / 0.10
= 69776.6
Therefore, the present value of R13,000 per year invested for 8 years at 10% compound interest is approximately R69,776.60.
For such more questions on present value
https://brainly.com/question/30390056
#SPJ8