Answers
Answer: transverse wave.
Explanation:
In a wave motion rope, the particles of the rope move in the perpendicular direction to the actual wave, so this is a transverse wave. (we have a longitudinal wave when the movement of the particles is in the same direction than the wave propagation, an example of this is the waves in the surface of the water when you throw a rock in)
Now, the fact that he waved it only once does not mean that this is a pulse if the other end of the rope is connected to a fixed point when the wave reaches that point will be reflected (losing a bit of amplitude, but we still will have a wave)
so the correct option is a transverse wave.
Related Questions
Which is the best example of tropism in plants?
Answers
One example is the Shame Plant.
It exhibits Negative Thigmotropism.
When you touch the plant, its leaves will curl up,
Which of the following actions will increase the current induced in a wire by a
magnetic field?
Answers
Answer:
The induced current can be increased in the coil in the following ways: By increasing the strength of the magnet. By increasing the speed of the magnet through the coil.
Explanation:
A small box of mass m is placed on top of a larger box of mass 2m as shown
in the diagram at right. When a force F is applied to the large box, both boxes accelerate to the right with the same acceleration. If the coefficient of static friction between the lower block and the upper block is μs and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the lower block and the floor is μk, which two of the following statements must be true?
A) The force of friction between the blocks is smaller in magnitude than the force F.
B) The force of friction between the lower block and the floor is equal to 3μkmg.
C) The friction force on the upper block is directed towards the left.
D) The force of static friction acting on the system is greater than the force of kinetic friction acting on the system.

Answers
Answer: aaa
Explanation: a
aaa
what is the importance of antacid in human health
Answers
Answer:
it helps to get rid of gas. and can cut down heartburn.
Answer:
Explanation:
Antacids are medication that neutralize stomach acid to cut down on heartburn, sour stomach, acid indigestion, and stomach upset. Some antacids also contain simethicone, an ingredient that helps your body get rid of gas. Others have ingredients that can lead to diarrhea or constipation.
jerome pitches a baseball of mass 0.300 kg. the ball arrives at home plate with a speed of 40.0 m/s and is batted straight back to jerome with a return speed of 52.0 m/s. what is the magnitude of change in the ball's momentum?
Answers
The change in the momentum of the ball is 3.6 Kgm/s.
What is momentum?The term momentum has to do with the product in the velocity of a body and mass of the body. We have to recall at this point that rate of change of momentum is directly related to the impressed force and this is in accordance with the Newton second law of motion.
Now we have to look at the few pieces of information that we can be able to glean from the question;
Mass of the object = 0.300 kg
Initial speed of the object = 40.0 m/s
Final speed of the object = 52.0 m/s
Given that the change in the velocity of the object is given by;
m( v - u)
m = Mass of the object
v = Final speed of the object
u = Initial speed of the object
change in the velocity of the object = 0.300(52 - 40)
= 3.6 Kgm/s
Learn more about momentum:https://brainly.com/question/904448
#SPJ1
A sample of silver (with work function Φ=4.52 eV ) is exposed to an ultraviolet light source (????=200 nm), which results in the ejection of photoelectrons. What changes will be observed if:
1. The silver is replaced with copper (Φ= 5.10 eV)?
a. more energetic photoelectrons (on average)
b. no photoelectrons are emitted more photoelectrons ejected
c. less energetic photoelectrons (on average)
d. fewer photoelectrons ejected
2. A second (identical) light source also shines on the metal?
a. fewer photoelectrons ejected
b. no photoelectrons are emitted more
c. energetic photoelectrons (on average)
d. less energetic photoelectrons (on average)
e. more photoelectrons ejected
3. The ultraviolet source is replaced with an X-ray source that emits the same number of photons per unit time as the original ultraviolet source?
a. no photoelectrons are emitted
b. less energetic photoelectrons (on average)
c. fewer photoelectrons ejected
d. more energetic photoelectrons (on average)
e. more photoelectrons ejected
Answers
Answer:
1. c
2. e
3. d
Explanation:
1.
From Einstein's Photoelectric Equation, we know that:
Energy given up by photon = Work Function + K.E of Electron
hc/λ = φ + K.E
where,
h = Plank's Constant = 6.626 x 10⁻³⁴ J.s
c = speed of light = 3 x 10⁸ m/s
λ = wavelength of light source = 200 nm = 2 x 10⁻⁷ m
φ = (5.1 eV)(1.6 x 10⁻¹⁹ J/eV) = 8.16 x 10⁻¹⁹ J
Therefore,
(6.626 x 10⁻³⁴ J.s)(3 x 10⁸ m/s)/(2 x 10⁻⁷ m) - 8.16 x 10⁻¹⁹ = K.E
K.E = (9.939 - 8.16) x 10⁻¹⁹ J
K.E = 1.778 x 10⁻¹⁹ J
The positive answer shows that electrons will be emitted. Since it is clear from the equation the the K.E of electron decreases with the increase in work function. Therefore:
c. less energetic photo-electrons (on average)
2.
The increase in light sources means an increase in the intensity of light. The no. of photons are increased, due to increase of intensity. Thus, more photons hit the metal and they eject greater no. of electrons. Therefore,
e. more photo-electrons ejected
3.
X-rays have smaller wavelength and greater energy than ultraviolet rays. Thus, the photons with greater energy will strike the metal and as a result, electrons with higher energy will be ejected.
d. more energetic photo-electrons (on average)
Photoelectrons with a maximum speed of 8.00 • 106 m/sec are ejected froma surface in the presence of light with a frequency of 6.32 · 1014Hz. If themass of an electron is 9.10 . 10-31 kg, calculate the maximum kineticenergy of a single electron, in joules.a. 3.64 x 10-24 Jb. 2.88 x 10-16 Jc. 5.82 x 10-17 Jd. 2.91 x 10-17 J
Answers
The kinetic energy is given by:
\(K=\frac{1}{2}mv^2\)We know the mass and the maximum speed, plugging their values in the expression above we have:
\(\begin{gathered} K=\frac{1}{2}(9.1\times10^{-31})(8\times10^6)^2 \\ K=2.91\times10^{-17}\text{ J} \end{gathered}\)Therefore, the answer is d.
Packages having a mass of 6 kgkg slide down a smooth chute and land horizontally with a speed of 3 m/sm/s on the surface of a conveyor belt. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the belt and a package is
Answers
Answer:
t = 1.02 s
Explanation:
The computation of the time required is shown below:
The package speed for belt is
= 3 - 1
= 2 m/s
Moreover, the decelerative force would be acted on the block i.e u.m.g
So, the decelerative produced
= 0.2 × 9.81
= 1.962 m/s^2
And, final velocity = 0
v = u - at
here
V = 0 = final velocity
u = 2 m/s
so,
0 = 2 - 1.962 × t
t = 1.02 s

11. A metallic block of mass sokg exerts o pressure of ION/m² on the surface. Determine the area of contact between the block and the surface.
Answers
The area of contact between the block and the surface is 50 m².
What is mass?A body's mass is an inherent quality. Before the discovery of the atom and particle, it was widely considered to be tied to the amount of matter in a physical body.
The measure of matter in a particles or object is represented by the dimensionless quantity mass (symbolised m). The kilogramme is the International System's (SI) preferred unit of mass (kg).
What is pressure?Pressure is defined as force applied on a body per unit area. Pressure is the force perpendicularly applied to an object's surface per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure is the pressure in relation to the outside pressure. There are many different units used to express pressure.
Equation :Given,
mass(m) = 50kg
pressure (p) = 10N/m²
Taking,
g= 10 m/s²
p= mg/A⇒ 10= 50 × 10/A∴
A= 500/10 = 50 m²
To know more about pressure, visit :
brainly.com/question/28012687
#SPJ1
Given sin ti + cos ti + tk
Answers
Answer:
I don't understand the question that up added
Explanation:
what do you mean by ti and tk
The mass of Jupiter is 1.9 x 10 kg and that of the sun is 2 x 10 kg. If the distance between them is 78 x 10 km, find the gravitational force between them.
Answers
Using the formula F = G * (m1 * m2) / r^2, where G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects, and r is the distance between them, we can calculate the gravitational force between Jupiter and the sun.
Plugging in the values, we get:
F = (6.674 x 10^-11 N * (m^2 / kg^2)) * ((1.9 x 10^27 kg) * (2 x 10^30 kg)) / (78 x 10^6 m)^2
Simplifying this, we get:
F = 1.98 x 10^27 N
Therefore, the gravitational force between Jupiter and the sun is approximately 1.98 x 10^27 Newtons.
The gravitational force between Jupiter and the sun, calculated using Newton's law of gravitation with their masses and distance, is \(1.95 * 10^{22} N.\)
The gravitational force between Jupiter and the sun is determined using Newton's law of gravitation, which states that two masses attract each other with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their distance apart. Given that the mass of Jupiter is \(1.9 * 10^{27} kg\) and that of the sun is \(2 * 10^{30} kg\), and the distance between them is \(78 * 10^6 km (which is 78 * 10^9 m)\), we can use the formula: Gravitational force = G(m1m2)/r^2where G is the universal gravitational constant, m1, and m2 are the masses of the two bodies, and r is the distance between them. Substituting the values gives Gravitational force \(= (6.67 * 10^{-11} Nm^2/kg^2) * (1.9 * 10^{27} kg) * (2 x 10^{30} kg) / (78 * 10^9 m)^2= 1.95 * 10^{22} N\)Thus, the gravitational force between Jupiter and the sun is \(1.95 * 10^{22} N.\)Summary: The gravitational force between Jupiter and the sun is found using Newton's law of gravitation, which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their distance apart. Given the mass of Jupiter, the mass of the sun, and the distance between them, we can calculate the gravitational force using the formula. The gravitational force between Jupiter and the sun is \(1.95 * 10^{22} N.\)For more questions on gravitational force
https://brainly.com/question/27943482
#SPJ8
Hey there, I have a physics question that sadly I can't figure out since the pearson e book keeps crashing. Also I am blind and CAN'T SEE PICTURES OR GRAPHS!! So for the question: Let θ be the angle that the vector A⃗ makes with the +x-axis, measured counterclockwise from that axis. Find the angle θ for a vector that has the following components.Part AAx= 4.20 m, Ay= -2.10 mExpress your answer in degrees.
Answers
ANSWER:
333.4°
STEP-BY-STEP EXPLANATION:
To find angle for a vector:
\(\theta=\tan ^{-1}\mleft(\frac{A_y}{A_x}\mright)\)We substitute the values of this case and the angle would then be:
\(\begin{gathered} \theta=\tan ^{-1}\mleft(\frac{-2.10}{4.20}\mright) \\ \theta=\tan ^{-1}(-0.5) \\ \theta=-26.56\cong-26.6 \\ \theta=360-26.6 \\ \theta=333.4\text{\degree} \end{gathered}\)The angle is 333.4°
Two boxes with masses 20 kg and 5 kg are attached to an ideal rope and pulley system, as shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the 20 kg box and the surface is 0.14.
What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the 20 kg box as it moves to the right?
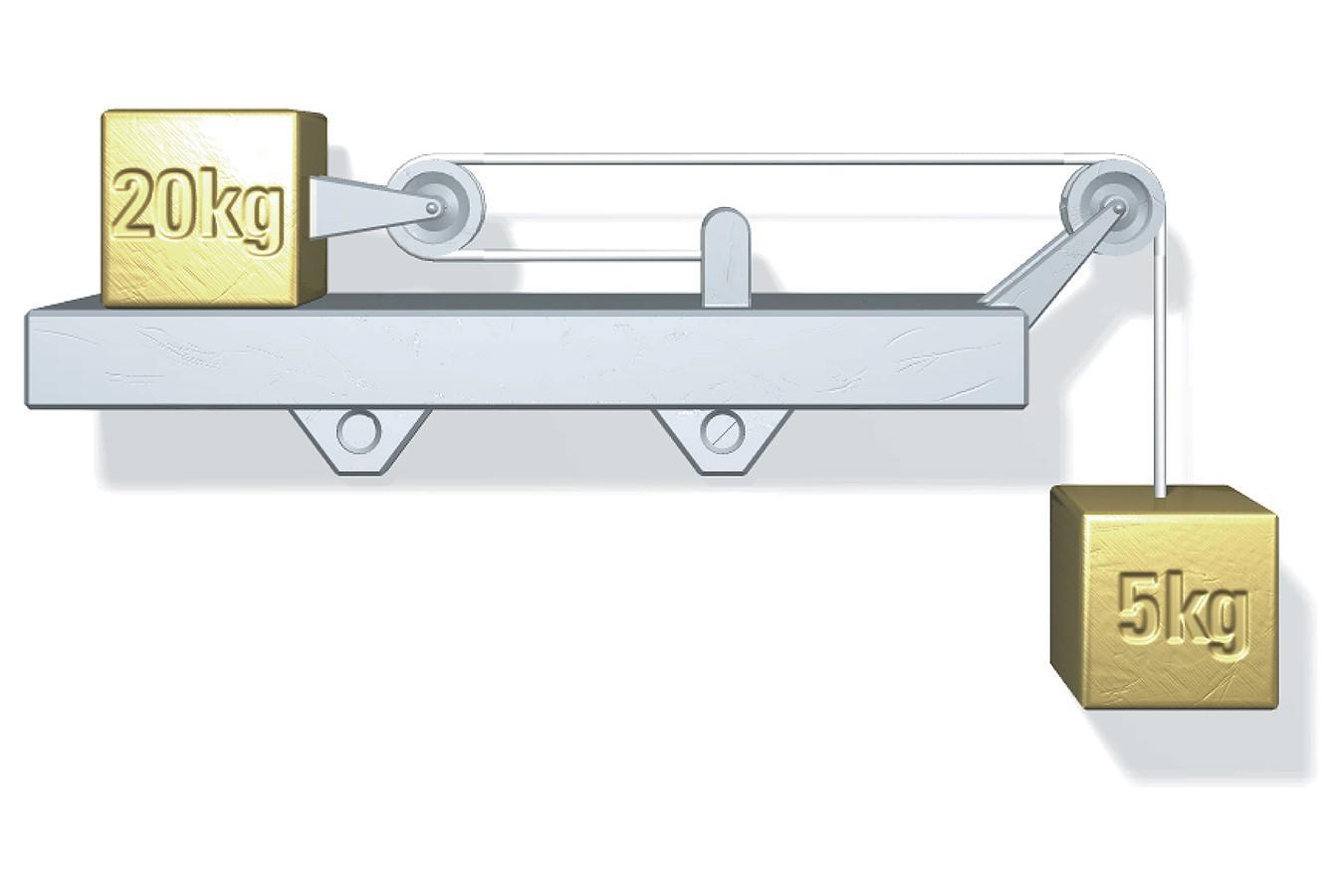
Answers
Answer:
22/25 m/s^
Explanation:

The magnitude of the acceleration of the 20 kg box as it moves to the right is 7.84 m/s².
How to calculate the acceleration?In this system, the force of gravity acts on both boxes, but the tension in the rope is the same on both sides of the pulley, so it cancels out. The frictional force acts only on the 20 kg box, opposing its motion to the right.
To find the acceleration of the 20 kg box, we need to use Newton's second law of motion, which states that the net force acting on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration:
Net force = mass x acceleration
The net force on the 20 kg box is the force of gravity pulling it down minus the force of friction opposing its motion to the right:
net force = (20 kg)(9.8 m/s²) - (0.14)(20 kg)(9.8 m/s²) = 156.8 N
The net force on the 5 kg box is the force of gravity pulling it down plus the tension in the rope pulling it up:
Net force = (5 kg)(9.8 m/s²) + T
Since the tension is the same on both sides of the pulley, we can set these two equations equal to each other and solve for the tension:
T = (20 kg)(9.8 m/s²) - (0.14)(20 kg)(9.8 m/s²) - (5 kg)(9.8 m/s²) = 93.68 N
Now we can use the net force on the 20 kg box to find its acceleration:
Net force = (20 kg) x acceleration
156.8 N = (20 kg) x acceleration
Acceleration = 7.84 m/s²
Therefore, the magnitude of the acceleration of the 20 kg box as it moves to the right is 7.84 m/s².
To know more about acceleration follow
https://brainly.com/question/11221641
#SPJ1
A ball is projected at an angle of 53°. If the initial velocity is 48 meters/second, what is the vertical component of the velocity with which it was launched?
A.) 31 meters/second
B.) 38 meters/second
C.) 44 meters/second
D.) 55 meters/second
Answers
Answer:
The vertical component of the velocity can be found using the formula:
V₀y = V₀ * sin(θ)
where V₀ is the initial velocity, θ is the angle of projection, and V₀y is the vertical component of the velocity.
Substituting the given values, we have:
V₀y = 48 * sin(53°)
Using a calculator, we can evaluate sin(53°) to be approximately 0.799:
V₀y = 48 * 0.799
V₀y ≈ 38.352
Therefore, the vertical component of the velocity with which the ball was launched is approximately 38 meters/second, which corresponds to option B.
Answer:
B.) 38 meters/second
Explanation:

. A 5cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal
length 10 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position
and size of the image. Also find its magnification
Answers
The nature of the image formed by the convex lens is virtual, the position of the image is 30 cm away from the lens on the same side as the object, and the size of the image is twice the size of the object. The magnification is 2, meaning the image is magnified.
Given:
Object height (h) = 5 cm
Focal length of the convex lens (f) = 10 cm
Object distance (u) = 15 cm (positive since it's on the same side as the incident light)
To determine the nature, position, and size of the image, we can use the lens formula:
1/f = 1/v - 1/u
Substituting the given values:
1/10 = 1/v - 1/15
To simplify the equation, we find the common denominator:
3v - 2v = 2v/3
Simplifying further:
v = 30 cm
The image distance (v) is 30 cm. Since the image distance is positive, the image is formed on the opposite side of the lens from the object.
To find the magnification (M), we use the formula:
M = -v/u
Substituting the values:
M = -30 / 15 = -2
The magnification is -2, indicating that the image is inverted and twice the size of the object.
For more such information on: convex lens
https://brainly.com/question/30010355
#SPJ8
Please see the photo below:

Answers
explain what is wrong with diagram. label the arrow correctly on the second diagram .

Answers
Vessel Mass Acting Downward (mg)
Bayonet Force Acting Above Vessel (Fb)
This force is called buoyancy. Buoyancy pushes objects up. Gravity exerts a downward force on an object determined by the object's mass. Therefore, if the downward force exerted by gravity on an object is less than the buoyant force the object floats.
Since the buoyant force on the body and the weight of the body are equal and opposite, the net force on the body is zero, giving the body a net force to levitate. The wind force acting on a sail moving a boat is an example of Newton's third law of motion. That is, every action has an equal and opposite reaction. But the relationship between force and motion is not as simple as the wind blowing just behind the sails propels the ship forward.
Learn more about The buoyant force here:- https://brainly.com/question/3228409
#SPJ9
Mark weighs 375 N and is carrying a full-sized cello as he climbs the stairs to a height of 4 m. It takes him 3 seconds to do this.
How does the amount of work he does change if he were to climb the same flight of stairs again in the same amount of time, but this time without the cello?
A) It depends on the weight of the cello.
B) It remains the same.
C) It increases
D) It decreases.
Answers
Mark's work decreases when he climbs the same flight of stairs again in the same amount of time without the cello.
The correct answer is option D.
The amount of work Mark does depends on the weight of the cello, as well as the distance he climbs and the time it takes. Work is calculated using the formula :
Work = Force × Distance.
In the given scenario, Mark is carrying a full-sized cello while climbing the stairs. The weight of the cello adds to the force he exerts. So, the total force Mark exerts is the weight of the cello plus his own weight (375 N).
When Mark climbs the stairs with the cello, he is doing work against the force of gravity.
The work done is equal to the force exerted multiplied by the distance climbed (375 N + weight of cello) × 4 m.
Now, if Mark were to climb the same flight of stairs again in the same amount of time (3 seconds), but this time without the cello, the amount of work he does would decrease. This is because without the cello, the force exerted would only be Mark's weight (375 N), which is less than the total force exerted with the cello.
Therefore, mark's work decreases.
For more such questions on work visit:
https://brainly.com/question/28356414
#SPJ8
A metallic circular plate with radius r is fixed to a tabletop. An identical circular plate supported from above by a cable is fixed in place a distance d above the first plate. Assume that dd is much smaller than r. The two plates are attached by wires to a battery that supplies voltage V.
A)What is the tension in the cable? Neglect the weight of the plate.
Express your answer in terms of the variables d, r, V, and constants ϵ0, π.
B)The upper plate is slowly raised to a new height 2d. Determine the work done by the cable by integrating ∫(from d to 2d) F(z)dz, where F(z) is the cable tension when the plates are separated by a distance z.
Express your answer in terms of the variables d, r, V, and constants ϵ0, π.
C)Compute the energy stored in the electric field before the top plate was raised.
Express your answer in terms of the variables d, r, V, and constants ϵ0, π.
D)Compute the energy stored in the electric field after the top plate was raised.
Express your answer in terms of the variables d, r, V, and constants ϵ0, π.
E)Is the work done by the cable equal to the change in the stored electrical energy? If not, why not?
a)The work done in separating the plates is equal to energy change in the plates.
b)The work done in separating the plates is equal to the magnitude of the energy change in the plates. This does not mean that the work done is equal to the change in the energy stored in the plates. The work done on the plates is positive but the plates lose energy. The plates are connected to the battery, so the potential difference across them remains constant as they are separated. Therefore charge is forced off of the plates through the battery, which does work on the battery.
Answers
Answer:
the tension in the cable is \(\mathbf{F = \frac{\pi E_o v^2r^2}{2d^2}}\)
the work done by the cable is \(\mathbf{W= \frac{\pi E_ov^2r^2}{4d}}\)
Explanation:
A)
If we have two circular plate supported by a cable at a fixed distance, then the electric field formed between the two plate of the capacitor can be represented by the equation.
\(\mathbf{E = \frac{voltage \ \ V}{distance \ \ d}}\)
However; the net electric field i.e the sum of the electric filed produced is represented as:
\(\mathbf{E' = \frac{E}{2}} \\ \\ \mathbf{E' = \frac{V}{2d}}\)
So, if we assume that the lower plate and the upper plate possess the charge +q and -q respectively. Then, the tension of the cable which is the same as Force F can be written as:
\(\mathbf{F = q* E'}\)
\(\mathbf{F = \frac{q*v}{2d}}\) ----- equation (1)
Also ; we know that
\(\mathbf{C = \frac{q}{v}= \frac{E_oA}{d}}\)
\(\mathbf{\frac{q}{v}= \frac{E_o \pi r^2}{d}} \ \ \ \ \ \mathbf{since \ A = \pi r^2}\)
\(\mathbf{{q}= \frac{\pi E_o {v} r^2}{d}}\) ----- equation (2)
Replacing equation 3 into equation (2); we have:
\(\mathbf{F = \frac{\pi E_o vr^2}{d}* \frac{v}{2d}}\)
\(\mathbf{F = \frac{\pi E_o v^2r^2}{2d^2}}\)
Therefore, the tension in the cable is \(\mathbf{F = \frac{\pi E_o v^2r^2}{2d^2}}\)
B)
Assume that the upper plate is displaced by dz in an upward direction ; Then we can express the workdone by the tension as :
\(\mathbf{dW = T *dz} \\ \\ \mathbf{dW = F*dz} \\ \\ \mathbf{dW = \frac{\pi E_o v^2r^2}{2z^2}dz }\)
The net workdone to raise the plate from separation d to 2d is:
\(\mathbf{W = \int\limits^{2d}_{2zd} {dw} = \frac{\pi E_ov^2r^2}{2} \int\limits^{2d}_d \frac{dz}{z^2} }\)
\(\mathbf{W= \frac{\pi E_ov^2r^2}{2} [-\frac{1}{z}]^{2d}_d }\)
\(\mathbf{W= - \frac{\pi E_ov^2r^2}{2} [\frac{1}{2d}-\frac{1}{d}]}\)
\(\mathbf{W= - \frac{\pi E_ov^2r^2}{2} [\frac{-1}{2d}]}\)
\(\mathbf{W= \frac{\pi E_ov^2r^2}{4d}}\)
the work done by the cable is \(\mathbf{W= \frac{\pi E_ov^2r^2}{4d}}\)
C) To calculate the energy stored in the Electrical energy Capacitor before the top plate is raised ; we have:
\(\mathbf{U_i = \frac{1}{2}Cv^2} \\ \\ \mathbf{U_i = \frac{1}{2}(\frac{E_oA}{d})v^2} \\ \\ \mathbf{U_i = \frac{1}{2}(\frac{E_o \pi r^2}{d})v^2} \\ \\ \mathbf{U_i = \frac{E_o \pi r^2 v^2}{2d}} }\)
D) The energy stored in the plate after the the top plate was raised is as follows:
\(\mathbf{U_f = \frac{1}{2}C'v^2} \\ \\ \mathbf{U_f = \frac{1}{2}(\frac{E_oA}{2d})v^2} \\ \\ \mathbf{U_f = \frac{1}{2}(\frac{E_o \pi r^2}{2d})v^2} \\ \\ \mathbf{U_f = \frac{E_o \pi r^2 v^2}{4d}} }\)
E) Yes, work done by the cable equal to the change in the stored electrical energy. The Difference in energy stored before and after the top plate is raised:
\(\mathbf{U_i-U_f} = \mathbf{\frac{E_o \pi r^2 v^2}{2d}} }} - \mathbf {\frac{E_o \pi r^2 v^2}{4d}} }}\)
\(\mathbf{U_i-U_f}= \mathbf {\frac{E_o \pi r^2 v^2}{4d}} }}\)
Thus;
b)The work done in separating the plates is equal to the magnitude of the energy change in the plates. This does not mean that the work done is equal to the change in the energy stored in the plates.
Object A is 71 degrees and object B is 75 degrees how will thermal energy flow
Answers
Given :
Object A is 71 degrees and object B is 75 degrees .
To Find :
How will thermal energy flow.
Solution :
We know, by law of thermodynamics thermal energy will flow from higher temperature to lower temperature.
So, in the given question energy will flow from object B from object A.
Hence, this is the required solution.
Gold forms a solid solution with silver. Since the densities of pure gold and silver are 19.32 g/cm³ and 10.49 g/cm³, respectively, calculate the number of gold atoms per cubic centimeter for a silver-gold alloy containing 10% Au and 90% Ag by weight.
Answers
There are 3.37 × \(10^{22}\) gold atoms per cubic centimeter in the silver-gold alloy.
The density of a binary alloy can be calculated using the following equation:
ρ = w1ρ1 + w2ρ2
where,
ρ = density of the alloy
w1 and w2 = weight fractions of the two components (in this case, gold and silver)
ρ1 and ρ2 = densities of the pure components.
We are given that the alloy contains 10% gold and 90% silver by weight, so we can calculate the weight fractions as:
\(w_{Au}\) = 0.10
\(w_{Ag}\) = 0.90
We are also given the densities of pure gold and silver as:
ρ_Au = 19.32 g/\(cm^{3}\)
ρ_Ag = 10.49 g/\(cm^{3}\)
Now we can substitute these values into the density equation to find the density of the alloy:
ρ = \(w_{Au}\)ρ_Au +\(w_{Ag}\)ρ_Ag
ρ = (0.10)(19.32 g/\(cm^{3}\)) + (0.90)(10.49 g/\(cm^{3}\))
ρ = 11.08 g/\(cm^{3}\)
Next, we need to calculate the number of gold atoms per cubic centimeter in the alloy.
To do this, we can use Avogadro's number and the atomic weights of gold and silver:
\(N_A\) = 6.022 × \(10^{23}\) atoms/mol
Aum = 196.97 g/mol
Agm = 107.87 g/mol
The number of gold atoms:
\(n_{Au}\) = (\(w_{Au}\)ρ/ Aum) × \(N_{A}\)
Substituting the values, we get:
\(n_{Au}\) = (0.10 × 11.08 g/\(cm^{3}\)/ 196.97 g/mol) × 6.022 × \(10^{23}\) atoms/mol
\(n_{Au}\) ≈ 3.37 × \(10^{22}\) atoms/\(cm^{3}\)
Therefore, there are approximately 3.37 × \(10^{22}\) gold atoms per cubic centimeter in the silver-gold alloy.
know more about weight fractions here:
https://brainly.com/question/29078616
#SPJ11
If you catch the ruler 4.9 cm from the lower end, what is your reaction time?
Answers
Answer:
0.10s
Explanation:
the fall time is
4.9/100=.5*9.81*t^2
solve for t
1. A male African elephant can grow up to 14 feet tall and have a mass as large as 7,000 kg. What would
be the weight in Newtons of a male African elephant on the moon?
Answers
The weight of a male African elephant on the moon would be approximately 11,470.2 Newtons.
To calculate the weight of a male African elephant on the moon, we need to use the formula:
Weight = mass × acceleration due to gravity
The mass of the elephant is given as 7,000 kg. However, the acceleration due to gravity on the moon is approximately 1/6th (0.1667) of the acceleration due to gravity on Earth, which is approximately 9.8 m/s².
Weight on the Moon = 7,000 kg × 0.1667 × 9.8 m/s²
Weight on the Moon = 7,000 kg × 1.6386 m/s²
Weight on the Moon ≈ 11,470.2 Newtons
Therefore, the weight of a male African elephant on the moon would be approximately 11,470.2 Newtons.
For more such questions on Weight
https://brainly.com/question/86444
#SPJ11
Two objects are placed 3 meters apart. If they were moved, at what distance would the NEW gravitational force be about 1/4 of the original value?
1.5 meters (1/2 the distance)
6 meters (twice the distance)
3/4 meters (1/4 the distance)
12 meters (4 times the distance)
Answers
Answer:
3/4
Explanation:
1. Four students investigated the effect of gravity on falling objects. The students all used the same three balls and dropped them from a height of 8 meters. They recorded the time it took for each ball to hit the ground. Which student most likely had an error in the results?
(1 point)
Ziva
Jade
Owen
Eduardo
2.A student designs an investigation to study the effect of gravity on objects on Earth. He will use the criteria shown. How can the student improve the investigation?
(1 point)
by dropping the balls from the same height
by using balls that are the same mass
by finding balls made from different materials
by measuring the circumference of the balls
Answers
Answer:
1.Owen
2.By dropping the balls from the same height
3.She dropped the balls from different heights
4. Perform a second trial
What are atoms? Explain in detail.
Answers
Answer:
An atom is a particle of matter that uniquely defines a chemical element. An atom consists of a central nucleus that is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. The nucleus is positively charged and contains one or more relatively heavy particles known as protons and neutrons.
Explanation:
What is the atomic mass of the atom in the diagram below?
3
6
9
1

Answers
Simply said, an atom's entire mass is its atomic mass, which is commonly given in atomic mass units, or amu.
Where is atomic number on chart?The periodic table is divided into blocks for each element. These blocks have identifying letters and numbers. The atomic number, which appears at the very top, indicates how many protons make up an element's single atom.In electron dot diagrams, the valence electrons of an atom are represented by dots that are positioned all around the symbol of the element.The letter "A" is used to symbolise it. An atom's atomic number is equal to the quantity of protons in its nucleus or the quantity of electrons in an electrically neutral atom. The periodic system, in which the elements are grouped in order, uses the letter "Z" to signify the number of a chemical element.To learn more about atomic refer to:
https://brainly.com/question/13201890
#SPJ1
Highschool Physics
1. The driver of a car traveling at 9.0m/s is honking their horn. The horn has a frequency of 625 Hz. If the car is moving toward a person waiting at the crosswalk, what frequency of the horn does the person hear?
2. As the same car from question#1 passes the person, what frequency of the horn does the person hear as the car moves away from them?
Answers
Using the formula for the Doppler effect:
f' = (v + vr) / (v + vs) * f
Given:
Source frequency (horn): f = 625 Hz
Speed of sound: v = 343 m/s (approximate value at room temperature)
The velocity of the receiver, vr, is zero because the person waiting at the crosswalk is stationary.
The velocity of the source, vs, is the speed of the car, which is given as 9.0 m/s.
Thus:
f' = (v + vr) / (v + vs) * f
= (343 m/s + 0) / (343 m/s + 9.0 m/s) * 625 Hz
= (343 m/s) / (352 m/s) * 625 Hz
≈ 609 Hz
Therefore, the person waiting at the crosswalk hears a frequency of approximately 609 Hz.
(2)Using the same Doppler effect formula:
f' = (v - vr) / (v - vs) * f
In this case, the velocity of the receiver, vr, is still zero because the person remains stationary.
The velocity of the source, vs, is now negative, indicating that the car is moving away from the person.
Thus:
f' = (v - vr) / (v - vs) * f
= (343 m/s + 0) / (343 m/s - (-9.0 m/s)) * 625 Hz
= (343 m/s) / (352 m/s) * 625 Hz
≈ 609 Hz
In other words, as the car moves away from the person, they would still hear a frequency of approximately 609 Hz.
More on Doppler effect can be found here: https://brainly.com/question/15318474
#SPJ1
PLEASEEE HELPPPPP does anyone know these answers?

Answers
Answer:
oof ok
Explanation:
Thank you :)
Which individual or group had perhaps the most profound effect on establishing social work as a specialized practice
Answers
Answer:
Which individual or group had perhaps the most profound effect on establishing social work as a specialized practice
Explanation: