a strechy material with a spring constant of 38 n/m is stretched 3.3 cm from its equilibrium length. what is the magnitude of the resulting spring force?
Answers
The magnitude of the resulting spring force is -1.254 N
The magnitude of the resulting spring force can be calculated using Hooke's Law, which states that the force exerted by a spring is proportional to the amount of stretch or compression.
The formula for Hooke's Law is F = -kx, where F is the force, k is the spring constant, and x is the amount of stretch or compression from the equilibrium length.
In this case, the spring constant is 38 N/m and the amount of stretch is 3.3 cm or 0.033 m. Therefore, the magnitude of the resulting spring force can be calculated as follows:
F = -kx
F = -(38 N/m)(0.033 m)
F = -1.254 N
Note that the negative sign indicates that the force is acting in the opposite direction of the stretch, which is towards the equilibrium length. Therefore, the magnitude of the resulting spring force is 1.254 N.
Learn more about The magnitude: brainly.com/question/24256733
#SPJ11
Related Questions
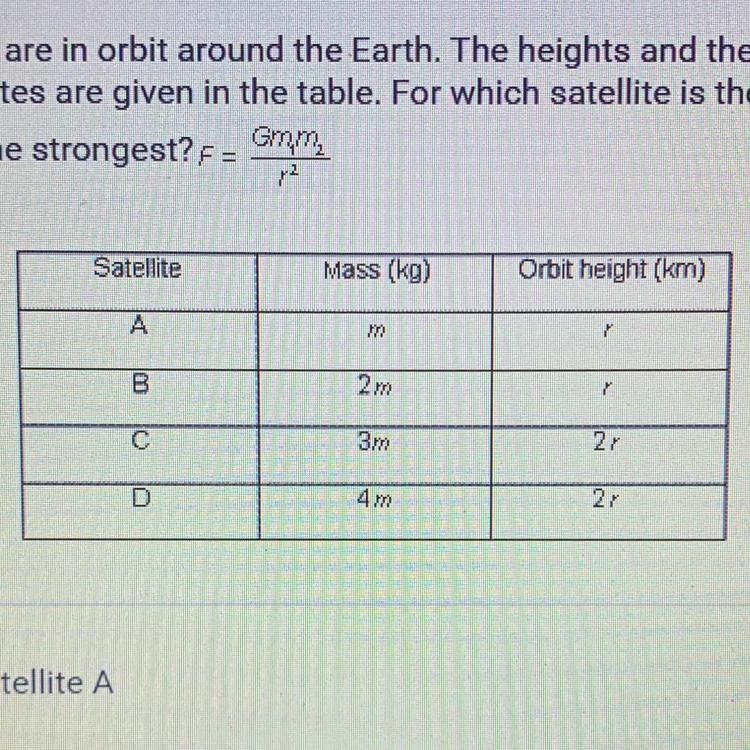
Four satellites are in orbit around the Earth. The heights and the masses of
the four satellites are given in the table. For which satellite is the gravitational
pull of Earth the strongest?F= Gm1m2/r^2
A. Satellite A
B. Satellite B
C. Satellite C
D. Satellite D
Answers
Answer:
satellite B
Explanation:
A .F= G (mM)/r²
B .F= G (2mM)/r² = 2G (Mm)r²
C .F= G (3mM)/(2r)² = ¾G (mM)/r²
D .F= G (4mM)/(2r)² = G (mM)/r²
how can I make a square fit in a triangle hole
Answers
cut the square and make it a triangle
10 a body, with a constant resistance to motion of 20 n, has a mass of 18 kg. a . force which decreases at a uniform rate from 60 n to 35 n during 25 s, is applied on the body. calculate the change in velocity of the body during the first 20 s
Answers
The change in velocity with a constant resistance of the body during the first 20 s = -10/9 ms⁻¹
The change in velocity of the body during the first 20 s = 10/9
Mass = 18 kg.
Resistance to motion = 20 N
Decreases at a uniform rate from 60 N to 35 N
time = 25 s,
Force which decreases at a uniform rate = (60 - 35)/25 = 25/25
= 1 NS⁻¹
Initial velocity,
F = p/t
= mv/t = 18*v/t
V = (60 - 20) /18 = 20/9
Final velocity,
Decreases at a uniform rate = = 1 NS⁻¹
at 20 s = 20 N decrease
total force applied at 20 s without resistance = 60 -20-20 = 20.
V final = 20/18 = 10/9
Change in velocity = V final - v initial
= 10/9 - 20/9
= -10/9
Resistance is described as a refusal to provide in or to something that slows down or prevents some thing. An instance of resistance is a toddler combating against her kidnapper. An instance of resistance is wind against the wings of a aircraft.
The unit of the electrical resistance, measured with direct present day, is the ohm (Ω), named after the German physicist and mathematician Georg Simon Ohm. in step with ohm's regulation, the resistance R is the ratio of the voltage U across a conductor and the modern R = U / I.
Learn more about resistance here:-https://brainly.com/question/17563681
#SPJ4
A sled mass of 40 kg is pulled along a snow covered surface. The coefficient of static friction is 0.40 and the coefficient of sliding friction is 0.25.
a) What force is needed to start the sled moving?
b) What force is needed to start to keep the sled moving at a constant speed?
c) Once moving, what total force must be applied to the sled to accelerate it at 3.0 m/s2
Answers
(a) The force needed to start the sled moving is 156.8 N.
(b) The force needed to keep the sled moving at a constant speed is 98.0 N.
(c) The total force needed to accelerate the sled at 3.0 m/s^2 is 236.8 N.
(a) The force needed to start the sled moving is equal to the force of static friction, which is Fs = μs * mg = 0.40 * 40 kg * 9.81 m/s^2 = 156.8 N.
(b) Once the sled is in motion, the force needed to keep it moving at a constant speed is equal to the force of kinetic friction, which is F(kinetic) = μk * mg = 0.25 * 40 kg * 9.81 m/s^2 = 98.0 N.
(c) To accelerate the sled at 3.0 m/s^2, we need to use the equation F = ma, where F is the net force applied to the sled, m is the mass of the sled, and a is the acceleration. Rearranging the equation, we get F = m * a = 40 kg * 3.0 m/s^2 = 120 N. However, we also need to overcome the force of kinetic friction, which is 98.0 N. Therefore, the total force needed to accelerate the sled at 3.0 m/s^2 is F = 120 N + 98.0 N = 236.8 N.
To learn more about force, here
https://brainly.com/question/13191643
#SPJ4
The law of Conservation of energy best describes which of the following:
Group of answer choices
That disregarding non-conservative forces, a bouncy ball dropped from exactly 2m will bounce back up to exactly 2m.
All of the above are examples of the law of conservation of energy.
That when "Thermal loss" occurs, the energy 'lost' is actually just another form of kinetic energy on a much smaller scale, that can't be recaptured for usable work.
That the universe has the same amount of energy now as it did when it first began, and how much energy it will have in the distant future.
Answers
Answer:
All the above
Explanation:
14.27 If you carry heavy weights in your hands, how will this affect the natural frequency at which your arms swing back and forth/
A frequency will increase
B The frequency will stay the same
C The fluency will decrease
Answers
The natural frequency at which your arms swing back and forth will change if you are holding heavy objects in your palms. The frequency will rise if the right response (option A).
Your arms move in a manner akin to a pendulum as you swing them. The length and bulk of your arms dictate the natural frequency at which they swing back and forth.
Your arms gain bulk as a result of adding weight to your hands, increasing the natural frequency of your arm swing.
Your arm swing may feel more unnatural due to this increased frequency.
Maintaining your arm swing can be harder and could wear more quickly.
Learn more about natural frequency here:
https://brainly.com/question/10464574
#SPJ4
Physics - Standing wave modes on a string - assignment

Answers
a)
When a standing wave propagates through a string, the length of the string is a multiple of half the wavelength:
\(L=n\cdot\frac{\lambda_n}{2}\)The factor n corresponds to the number of the harmonic. Then, the first harmonic is given by the condition n=1:
\(\begin{gathered} L=\frac{\lambda_1}{2} \\ \Rightarrow\lambda_1=2L \end{gathered}\)As we can see, the wavelength of the first harmonic is two times the length of the string.
Then, the wavelength of the first harmonic can be found by replacing the length L=63cm:
\(\lambda_1=2\times63cm=126cm\)b)
The product of the wavelength and the frequency is the speed of the wave:
\(v=\lambda f\)Replace λ=126cm=1.26m and f=330Hz to find the speed of the wave on the E-string:
\(v=(1.26m)(330Hz)=415.8\frac{m}{s}\approx416\frac{m}{s}\)c)
The frequency of the n-th harmonic is given by:
\(f_n=\frac{v}{\lambda_n}\)On the other hand:
\(\lambda_n=\frac{2L}{n}\)Then:
\(f_n=\frac{v}{2L}\times n\)Notice that v/2L is the frequency of the first harmonic (fundamental frequency). Then:
\(f_n=f_1\times n\)Replace the fundamental frequency of 330Hz and n=2,3,4 to find the second, third and fourth harmonic frequencies:
\(\begin{gathered} f_2=330Hz\times2=660Hz \\ f_3=330Hz\times3=990Hz \\ f_4=330Hz\times4=1320Hz \end{gathered}\)d)
Replace n=3 into the expression for the wavelength of the n-th harmonic to find the wavelength of the third harmonic:
\(\lambda_n=\frac{2L}{n}=\frac{2\times63cm}{3}=\frac{126cm}{3}=42cm\)Therefore, the answers are:
a) 126cm
b) 416m/s
c) 660Hz, 990Hz, 1320Hz
d) 42cm
In the diagram below, the solid line represents a wave generated in a rope. oB °C As the wave moves to the right, point P on the rope is moving towards which position? (1) A (2) B (3) C(4) D
Answers
As the wave moves to the right, point P on the rope is moving towards position (4) D.
Based on the given diagram, the solid line represents a wave generated in a rope. The wave is moving towards the right direction. To determine the direction of motion for point P, we need to observe the neighboring positions on the rope.
Looking at the diagram, we can see that the particles to the left of point P (towards position A) are moving downward, while the particles to the right of point P (towards position D) are moving upward.
Since the wave is propagating towards the right, point P, located between the downward-moving and upward-moving particles, will be moving towards position D.
As the wave moves to the right, point P on the rope is moving towards position D.
To know more about wave, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/15663649
#SPJ11
What is true about an object that is used as a reference point for determining motion?
It is stationary.
It is stationary.
It is accelerating.
It is accelerating.
It is decelerating.
It is decelerating.
It is changing direction.
It is changing direction.
Answers
The true statement about the reference point for determining motion is that "it is stationary"
WHAT IS A REFERENCE POINT:
A reference point refers to a position or substance used to ascertain whether or not an object is moving. A reference point is used in such a way that the distance moved by the tested object is compared with the stationary position of the reference point. This means that the reference point must always be stationary i.e. not moving from a fixed position. The change in an object in relationship with the reference point is the distance moved by the tested object. Therefore, the true statement about the reference point for determining motion is that "it is stationary".Learn more: https://brainly.com/question/13463561?referrer=searchResults
What happens to length of the mercury column if a small amount of water vapor is in the vacuum part?
Answers
Answer:
I hope it helped you...please mark as brainliest.....thanks!!!!!!!
Explanation:
Inches of mercury is ideal for vacuum lifting with vacuum cups, as the amount of vacuum required is rarely high. Typical vacuum handling utilizes anything between 15″Hg and 25″Hg. Therefore, “Hg is suitable as a measurement of system performance in this type of operation
The column of mercury employed in a mercury barometer, the height of which (inches of mercury) is used as a measure of atmospheric pressure.
At some point, all water vapour that is found in a vacuum system came from the atmosphere. Consider that air at 25° C and 50% relative humidity contains 12 torrs of water vapour. ... Additionally, any surface will adsorb a certain number of monolayers of water molecules.
Credits:
Vacuum Measurement: A Basic Guide - Fluid Power Journal
Sources of Water Vapor in Vacuum Systems | Normandale ...
Parents and teachers should strive to have children engage in activities within the child's zone of proximal growth, meaning that the activities are:
A. easily accomplished on the first try, so that the child does not become discouraged
B. not so easy that the child can accomplish them right off the bat, nor so difficult that even with help, they cannot be accomplished
C. difficult to accomplish, so that the child always seeks assistance in order to actively engage in social interactions
D. easily accomplished, so that child does not become dependent on adult assistance
Answers
Parents and teachers should strive to have children engage in the activities within child's zone of proximal growth, meaning that the activities are : B.)not so easy that the child accomplish them right off the bat and nor so difficult that even with help, they cannot be accomplished.
What are the activities that parents and teachers should strive to have children engage in?Activities in a child's zone of proximal development are those that parents and teachers should try to get kids involved in. ZPD is the range of activities that are not too easy for the child to accomplish on their own, but also not too difficult that they cannot be accomplished with some guidance or assistance from adults or more capable peers.
To know more about ZPD, refer
https://brainly.com/question/1433194
#SPJ1
The question is how do the impulses applied to the two balls compare?

Answers
Given data:
* The force applied on the ball is F = 900 N.
* The time of contact between Bob and the ball is t_1 = 0.3 s.
* The time of contact between Jill and the ball is t_2 = 0.6 s.
Solution:
The impulse applied by the bob is,
\(\begin{gathered} J_1=Ft_1 \\ J_1=900\times0.3 \\ J_1=270\text{ kgm/s} \end{gathered}\)The impulse applied by Jill is,
\(\begin{gathered} J_2=Ft_2 \\ J_2=900\times0.6 \\ J_2=540\text{ kgm/s} \end{gathered}\)Thus, the impulse applied by Jill is more than the impulse applied by Bob.
Hence, 4th option is the correct answer.
A 0.50-kilogram frog is at rest on a rock next to a pond. The frog leaps pushing off of the rock with an acceleration of 5.0 m/s2. What is the magnitude of the net force exerted on the frog as it leaps? a)2.5 N b)1.5 N c)1.0 N d)2.0 N
Answers
Given that,
Mass of a frog, m = 0.5 kg
The frog leaps pushing off of the rock with an acceleration of 5.0 m/s².
To find,
The magnitude of the net force exerted on the frog as it leaps.
Solution,
Let the net force exerted on the frog is given by the formula as follows :
F = ma
Putting the values of m and a to find F as follows :
F = 0.5 kg × 5 m/s²
F = 2.5 N
So, the magnitude of net force is 2.5 N.
The magnitude of the net force exerted on the frog as it leaps is 2.5 Newtons.
Hence, Option a) 2.5N is the correct answer.
Given the data in the question;
Mass of frog; \(m = 0.5kg\)Acceleration; \(a = 5.0m/s^2\)Force Exerted; \(F = ?\)
To determine the magnitude of the net force exerted on the frog as it leaps, we the expression from the Newton's Second law of motion:
\(F = m * a\)
Where m is mass and a is acceleration
We substitute our given values into the equation
\(F = 0.5kg * 5.0m/s^2\\\\F = 2.5kgm/s^2\\\\F= 2.5N\)
The magnitude of the net force exerted on the frog as it leaps is 2.5 Newtons.
Hence, Option a) 2.5N is the correct answer.
Learn more on Newton's Second law of motion here: https://brainly.com/question/19473547
a heater 60w evaporates 6×10–3kg of boiling water in 60s.what is the specific latent heat of vaporisation of water in jkg–1
Answers
Your question doesn't look right, so lemme assume you meant this.
A heater marked 60w evaporate 6x 10^-³kg of boiling water in 60 seconds. What is the specific latent heat of vaporization of water in jkg?
so you can understand it better..
Latent heat of evaporation is the heat required required to change water to vapor at the same temperature.(100°C)
eg. water boils at 100°C and in presence of more heat it turns to vapor at that Same temperature.
This heat is know as latent heat of Vaporization.
it's give by H=mL
where L is the specific latent heat of vaporization.
The specific latent heat of vaporization of water is 6×10⁵ Joule/kg.
What is latent heat?The heat or energy that is absorbed or released during a substance's phase change is known as latent heat. It might go from a solid to a liquid or from a liquid to a gas, or vice versa. Enthalpy, a characteristic of heat, is connected to latent heat.
Given parameters:
Mass of the water = 6 × 10⁻³ kg.
Power of the heater = 60 watts.
Time taken = 60 second.
Hence, total heat absorbed by the water = 60×60 joule = 3600 joule.
Hence, specific latent heat of vaporization of water =
total heat absorbed /mass of the water
= 3600/6 × 10⁻³ J/kg
= 6×10⁵ Joule/kg.
Learn more about latent heat here:
https://brainly.com/question/28044951
#SPJ2
To maintain a higher temperature (in a thermotat), which way hould the control knob be moved?-to the right o that it move toward the contact, or to the left?
Explain why?
Answers
Turn the dial either clockwise to make the unit colder or anticlockwise to make the unit warmer to set the thermostat to any temperature.
A thermostat is a part of a regulating mechanism that senses the temperature of a physical system and takes action to keep it close to a desired setpoint.
Any system or gadget that heats or cools to a setpoint temperature uses a thermostat. Examples include central heating systems for buildings, air conditioners, HVAC systems, water heaters, kitchen appliances like refrigerators and ovens, and incubators for use in science and medicine.
To know more about the thermostat, here
brainly.com/question/22598217
#SPJ4
What is an example of a series circuit
Answers
Answer:
Explanation
The most famous and common example is Christmas tree lights. You can't tell easily by looking at them whether they are in series or parallel. But you sure know the difference when one of them burns out. When that happens, the whole string goes dead. No matter what you do (other than find out which bulb burned out) will not fix the problem.
Another example is anything that is temperature controlled. For example a furnace is controlled by a thermostat. When the room temperature reaches a certain point, the thermostat is constructed in a certain way so that it forms an open circuit and no current can flow through it. The furnace motor turns off and the furnace stops pumping hot air into a room.
What are three different types of electromagnetic radiation that you use in your everyday life? Be sure to identify the source of the radiation as well as the type of electromagnetic radiation that is used.
Answers
Explanation:
Some Uses of Electromagnetic waves :
(A) Microwaves
Satellite CommunicationFor cooking food, etc(B) X - Rays (produced by slowing fast moving electrons)
Used in diagnosis of bones, etcluggage content search at airport, etc(C) Radio Waves
Radio and television broadcasting Navigational communication, etc2. Summarize how the force of gravity
factors into at least three processes in
the formation of stars. SC.8.E.5.4
Answers
what is the distance 9m) traveled by a butterfly with a speed of 0.97m/s and a flight time of 3400s?
Answers
We will have the following:
\(d=(0.97m/s)(3400s)\Rightarrow d=3298m\)So, the butterfly traveled 3298 meters.
From Example 5-38, the Moment Generating Function of a Poisson random variable, X, is given as Mx(t) = e¹(e¹-1) If Y = 2X, then the Moment Generating Function of Y is My(t) = e¹(e²¹-1) My(t) = e^(2e¹-1) My(t) = e22(e¹-1) My(t) = e¹(e¹-1)
Answers
In Example 5-38, the Moment Generating Function of a Poisson random variable, X, is given as Mx(t) = e¹(e¹-1). If Y = 2X, then the Moment Generating Function of Y is My(t) = e^(2e¹-1).Hence, the correct option is: My(t) = e^(2e¹-1).Explanation:
Given that, X follows a Poisson distribution with parameter λ and Moment Generating Function is,Mx(t) = E[e^(tX)] = Σ (e^(tx) * p(x))x = 0, 1, 2, 3, …..where p(x) is the probability mass function of Poisson distribution which is given by,p(x) = (e^(-λ) * λ^x) / x!Now, for Y = 2X, we can write Y as,Y = g(X) = 2XThen, using probability generating function (pgf), we can obtain the pgf of Y as,My(s) = E[s^Y] = E[s^(2X)] = E[(s^2)^X] = Mx(s^2) = e^(λ(s^2 - 1))Hence, the Moment Generating Function of Y is,My(t) = E[e^(tY)] = E[e^(2tX)] = Mx(2t) = e^(λ(2t-1)) = e^(2e¹-1)Hence, the correct option is: My(t) = e^(2e¹-1).
to know more about Moment intake pls visit:
https://brainly.com/question/31978876
#SPJ11
A green ball has a mass of 0.525 kg and a blue ball has a mass of 0.482 kg. A croquet player strikes the green ball and it gains an initial velocity of 2.26 m/s. It then strikes the blue ball, which is initially at rest. After the collision, the green ball has a velocity of 1.14 m/s in the same direction. If the balls roll on a frictionless surface and the collision is head-on, what is the final velocity of the blue ball? (Round your answer to the nearest hundredths place.)
Answers
Answer:
v' = 1.21 m/s
Explanation:
Mass of a green ball, m = 0.525 kg
Mass of a blue ball, m' = 0.482 kg
Initial velocity of green ball, u = 2.26 m/s
Initial velocity of blue ball, u' = 0 (at rest)
After the collision,
The final velocity of the green ball, v = 1.14 m/s
We need to find the final velocity of the blue ball after the collision if the collision is head on. Let v' is the final velcity of the blue ball. Using the conservation of momentum to find it :
\(mu+m'u'=mv+m'v'\\\\0.525 (2.26)+0=0.525 (1.14)+0.482v'\\\\0.588=0.482v'\\\\v'=\dfrac{0.588}{0.482}\\\\v'=1.21\ m/s\)
So, the final velocity of the blue ball is 1.21 m/s.
What is the main purpose of single celled organisms
Answers
Answer: These functions include metabolism, homeostasis and reproduction. Specifically, these single cells must transport materials, obtain and use energy, dispose of wastes, and continuously respond to their environment
Explanation:
Answer:
carries out all of the functions needed by the organism
Explanation:
Need help with # of protons

Answers
Answer:
2
Explanation:
helium has 2 protons and 2 neutrons
I HOPE IT WILL HELP YOU.
Thank you.
^ - ^

How electromagnet works in circuit breaker
Answers
Explanation:
A circuit breaker is an automatic switch that cut off current in a circuit when the current become too large. When the current in a circuit increases, the strength of the electromagnet will increase in accordance; this will pull the soft iron armature towards the electromagnet.
Excluding the noble gas group, how does the number of valence electrons in an element influence its chemical stability?
A. Elements with intermediate numbers of valence electrons are the last chemically stable.
B. Elements with the highest number of valence electrons are the most chemically stable.
C. Elements with intermediate number of valence electrons are the most chemically stable.
D. Elements wit the lowest number of valence electrons are the most chemically stable.
Answers
Answer:
C. Elements with intermediate number of valence electrons are the most chemically stable.
For a particular reaction, ΔH° is-13.9 kJ/mol and ΔS°is-41.6 J/(mol, K). Assuming these values change very little with temperature, over what temperature range is the reaction spontaneous in the forward direction?
The reaction is spontaneous for temperatures
O Greater than
O Less than
Answers
The reaction will be spontaneous in the forward direction at temperatures greater than 334 K (60.85°C) and non-spontaneous at temperatures less than 334 K.
The expression for the spontaneity of a reaction is given by ΔG = ΔH − TΔS
where ΔH and ΔS are the enthalpy and entropy changes of the reaction and T is the absolute temperature in kelvin (K).
The spontaneity of a reaction is given by the expression ΔG = ΔH − TΔS, where ΔH and ΔS are the enthalpy and entropy changes of the reaction and T is the absolute temperature in kelvin (K).
The temperature range over which a reaction is spontaneous in the forward direction is determined by the Gibbs free energy (ΔG).
For a reaction to be spontaneous, ΔG must be negative:
ΔG < 0ΔG = ΔH − TΔS= -13.9 kJ/mol - (T(K))(−41.6 J/(mol, K)/1000 J/kJ)= -13.9 + 0.0416T
If ΔG is negative for a particular temperature range, then the reaction is spontaneous in the forward direction for that temperature range.
If ΔG is positive, the reaction is non-spontaneous, and if ΔG = 0, the reaction is at equilibrium.
Therefore, to find the temperature range at which the reaction is spontaneous in the forward direction, we can set ΔG equal to zero and solve for T:
ΔG = -13.9 + 0.0416T= 0
T = 334.13 K (to 3 significant figures)
Learn more about chemical reaction at
https://brainly.com/question/14277568
#SPJ11
Using Newton's method three times find the value of x, correct to 2 decimal places, for which the function f(x)=
lnx
x+1
has a stationary point. You are given that the value is near x=3.
Answers
To find the value of x, correct to 2 decimal places, for which the function f(x) = ln(x)/(x + 1) has a stationary point using Newton's method.
We need to iterate the following steps three times:
Start with an initial guess for x near x = 3.
Let's assume our initial guess is x₀ = 3.
Calculate the derivative of f(x).
f'(x) = (1 - ln(x))/(x^2 + x)
Use the Newton's method iteration formula:
xᵢ₊₁ = xᵢ - f(xᵢ)/f'(xᵢ)
For each iteration, we substitute the current value of x into the formula to find the next value.
x₁ = x₀ - f(x₀)/f'(x₀)
x₁ = 3 - (ln(3)/(3 + 1))/((1 - ln(3))/(3^2 + 3))
x₁ ≈ 2.83
x₂ = x₁ - f(x₁)/f'(x₁)
x₂ ≈ 2.82
x₃ = x₂ - f(x₂)/f'(x₂)
x₃ ≈ 2.82
After three iterations, the value of x, correct to 2 decimal places, for which the function f(x) = ln(x)/(x + 1) has a stationary point is approximately x ≈ 2.82.
Learn more about derivative here :
https://brainly.com/question/25324584
#SPJ11
Why does precipitation
occur when warm air rises?
Answers
Answer:
the warm air rises, cools and condenses to form clouds
PLEASE HELP IMMEDIATELY
Which is the equation for an object's potential energy? (1 point)
O PE = mg h
O PE=1/2mgh
0 PE = 2mgh
O PE = mgh
In a baseball game, Joseph hits a ball to the outfield. When does the ball have the most
potential energy? (1 point)
O when the ball is caught
O when the ball reaches its greatest velocity
O when the ball reaches its highest point
Owhen the bat hits the ball
The roof of an apartment building is 58 meters high. A water tank on the roof has a mass of
38,000 kilograms. What is the potential energy of the water tank? (1 point)
O 2,204,000 J
O 211,672,160 J
O10,799,600 J
O 21,599,200 J
Which statement best describes an object's potential energy? (1 point)
O The object's mass and height determine its potential energy.
O The object's mass and velocity determine its potential energy.
O The object's kinetic energy determines its potential energy.
O The object's mass, gravity, and height determine its potential energy.
Which scenario shows how to use collaborative learning to explore potential energy?
(1 point)
Members of a team work together to create a plan, and then members choose different tasks
Oto carry out the plan.
O One student directs a team, assigning tasks to individual members.
O Members of a team work together to create a plan, and then one student does the work.
A teacher divides a class into teams, outlines a plan, and tells the teams how to carry out the plan.
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
c
C
Answer:
1. PE = mgh
2. When the ball reaches its highest point
3. 21,599,200
4. The object's mass, gravity, and height determine its potential energy
5. Members of a team work together to create a plan, and then members choose different tasks to carry out the plan.
Explanation: Finished the quick check :)
Merry-Go-Round 1
Jack sits at the end of a circular Merry-Go-Round. It has a radius of 40 meters. The
center of the Merry-Go-Round is 50 meters from a straight wall, as shown in the
diagram below. The point labeled Start on the represents Jack's location when the
Merry-Go-Round starts. This view is from directly above the Merry-Go-Round.
50 m
Wall
40 m
Start
type your answer.....
Return
1 point
From the Start point, the Merry-Go-Round rotates counterclockwise 75⁰ to
point A. How far is Jack from the wall? Round your answer to the nearest
hundredth of a meter.
Answers
Jack is approximately 60.15 meters from the wall when he is at point A.
To find the distance between Jack and the wall when he is at point A, we need to follow these steps:
1. Determine the angle formed between the wall, the center of the Merry-Go-Round, and point A.
2. Use the Law of Cosines to find the distance between Jack and the wall.
Step 1:
Since the Merry-Go-Round rotates counterclockwise 75°, the angle between the wall, the center of the Merry-Go-Round, and point A will be 75°.
Step 2:
Using the Law of Cosines with the given angle and sides:
Let the distance between Jack and the wall be x.
x² = 50² + 40² - 2(50)(40)cos(75°)
x² = 2500 + 1600 - 4000cos(75°)
x² ≈ 3617.83
Now find the square root of x² to get the distance x:
x ≈ √3617.83
x ≈ 60.15
for more such questions on counterclockwise
https://brainly.com/question/29765641
#SPJ11