a plane flies directly between two cities, a and b, which are separated by 2300 km. from a to b, the plane flies into a 65 km/hr headwind. on the return trip from b to a, the wind velocity is unchanged. the trip from b to a takes less than the trip from a to b. what is the airspeed of the plane, assuming it is the same in both directions?
Answers
The airspeed of the plane can be any positive value.
To solve this problem, let's assume the airspeed of the plane is denoted by V (in km/hr). We need to find the value of V.
When the plane flies from city A to city B, it is flying against a headwind. The effective ground speed of the plane is reduced by the speed of the headwind. Given that the headwind has a velocity of 65 km/hr, the ground speed of the plane from A to B is (V - 65) km/hr.
On the return trip from city B to city A, the wind velocity is unchanged. Since the plane is now flying with the wind, the effective ground speed of the plane is increased by the speed of the wind. Therefore, the ground speed of the plane from B to A is (V + 65) km/hr.
We are given that the trip from B to A takes less time than the trip from A to B. This means that the ground speed from B to A is greater than the ground speed from A to B. Mathematically, we can express this as:
(V + 65) > (V - 65)
Simplifying the inequality, we get:
V + 65 > V - 65
130 > 0
For more such questions on airspeed visit:
https://brainly.com/question/27093584
#SPJ8
Related Questions
The lower the ph value the larger the concentration of hydrogen ions
Answers
The lower the ph value the larger the concentration of hydrogen ions.
What is ph value?In chemistry, pH, historically denoting "potential of hydrogen", is a scale used to specify the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Acidic solutions are measured to have lower pH values than basic or alkaline solutions.
A pH of 7 is neutral. A decrease in pH below 7 shows an increase in acidity (hydrogen ions), while an increase in pH above 7 shows an increase in alkalinity (hydroxyl ions). Each pH unit represents a 10-fold change in concentration.
The lower the ph value the larger the concentration of hydrogen ions.
To learn more about ph value refer to the link:
brainly.com/question/28580519
#SPJ1
pls helppppppp me pls
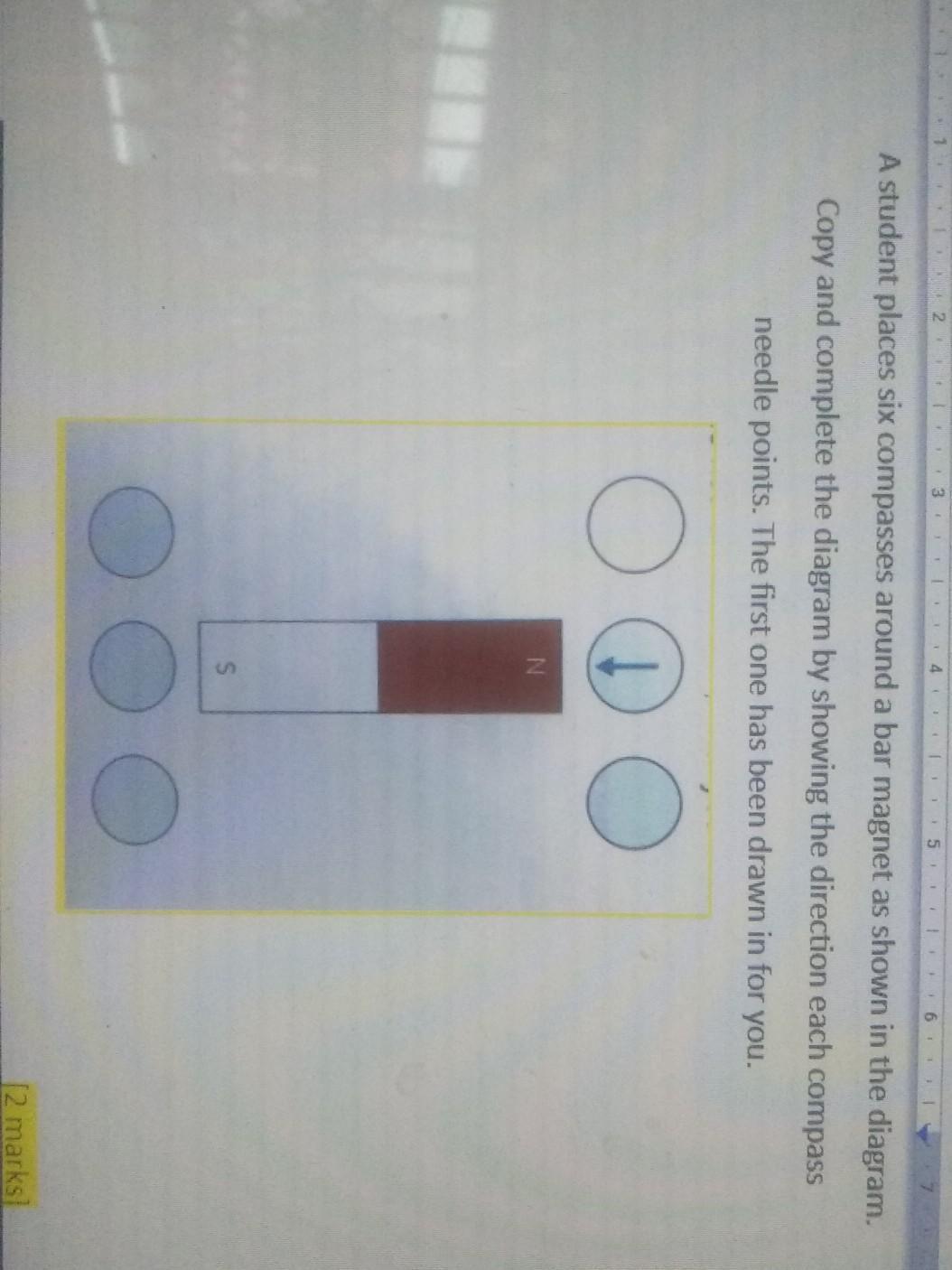
Answers
d ko pp alam sagot cencia n po
an inattentive driver is traveling 18.0m/s when he notices a red light ahead. his car is capable of decelerating at a rate of 3.65m/s2. if it takes him 0.200s to get the brakes on and he is 20.0m from the intersection when he sees the light, will he be able to stop in time?
Answers
The distance the automobile will travel while the driver is reacting, as well as the distance it will travel to stop once the brakes are applied there are 20.0 m between them and the intersection.
Where do you have to stop when the light is red?Before the stop line or crosswalk, motorists facing a flashing red traffic control light must stop. Drivers are required to stop before the intersection if there is no stop sign or crosswalk. Only when it is safe and after ceding the right-of-way, should drivers move forward.
The vehicle will continue to move for 0.200 s at its initial speed of 18.0 m/s, covering the following distance:
d1 = v0 × t + 1/2 × a × t²
= 18.0 m/s × 0.200 s + 1/2 × 0 m/s² × (0.200 s)²
= 1.80 m
The car will decelerate after using the brakes at a speed of 3.65 m/s2 until it comes to a stop. To determine the length of time it will take to halt, we can apply the kinematic equation shown below:
d2 = (v_f² - v_0²) / (2× a)
= (0 m/s - 18.0 m/s)² / (2 × -3.65 m/s²)
= 22.63 m
The distance that the car will travel overall before coming to a stop is as follows:
d_total = d1 + d2
= 1.80 m + 22.63 m
= 24.43 m
The driver will be unable to stop in time and will run the red light because there are 20.0 m between them and the intersection.
To know more about distance visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/29769926
#SPJ4
Rank the water levels of a mixed-tide system according to height. Put the highest water level on top.
higher high water
lower high water
higher low water
lower low water
Answers
Higher high water
Lower high water
Higher low water
Lower low water
In a mixed-tide system, the water levels exhibit two high tides and two low tides within a tidal cycle. The ranking of the water levels according to height is as follows:
Higher high water: This is the highest water level observed during the tidal cycle. It occurs when the gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun align to produce a stronger tidal bulge. It typically happens around the time of a new moon or a full moon.
Lower high water: This is the second-highest water level observed during the tidal cycle. It occurs when the gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun are not aligned, resulting in a weaker tidal bulge. It typically happens around the time of the first quarter and third quarter moon phases.
Higher low water: This is the higher of the two low water levels observed during the tidal cycle. It occurs when the gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun produce a weaker tidal trough. It typically happens between the two high tides.
Lower low water: This is the lowest water level observed during the tidal cycle. It occurs when the gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun are not aligned, resulting in a stronger tidal trough. It typically happens between the higher low water and the next high tide.
The ranking of water levels in a mixed-tide system, from highest to lowest, is: higher high water, lower high water, higher low water, lower low water
To know more about mixed-tide ,visit:
https://brainly.com/question/30932016
#SPJ11
An airplane flies from Houston to New York City, which is a distance of 2280 kilometers. The trip takes 3.5 hours. What was the plane's average speed? Round to the nearest whole number.
a)603 km/hr
b)651 km/hr
c)760 km/hr
d)813 km/hr
Answers
Answer:
a)603 km/hr
Explanation:
The rate at which the temperature increases with depth is called the geothermal gradient. What is the geothermal gradient in a tectonically stable region where the temperature is 119° C at a depth of 5.0 km?
(Assume a surface rock temperature of 14° C.)
Answers
The geothermal gradient in the tectonically stable region is approximately 21°C/km, indicating that the temperature increases by an average of 21 degrees Celsius per kilometer of depth.
To calculate the geothermal gradient, we need to find the rate at which the temperature increases with depth.
Temperature at the surface (T₁) = 14°C
Temperature at a depth of 5.0 km (T₂) = 119°C
Temperature difference = T₂ - T₁ = 119°C - 14°C = 105°C
Depth difference = 5.0 km - 0 km = 5.0 km
Geothermal gradient = Temperature difference / Depth difference
Geothermal gradient = 105°C / 5.0 km
Calculating this expression, we find:
Geothermal gradient ≈ 21°C/km
learn more about geothermal gradient here:
https://brainly.com/question/27975108
#SPJ11
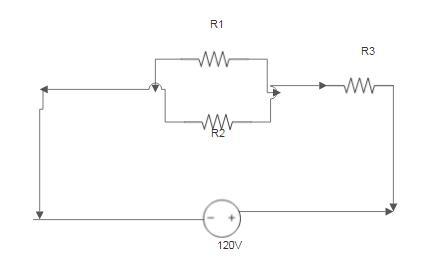
The crew will plug portable equipment into a UOP (Utility Outlet Port). Each UOP has two connections that can be used for 120-volt power. One portal is used to power a complex circuit of total resistance of 10 Ω. The complex circuit consists of 3 different resistors of which two are in parallel and the third is in series. One of the resistors that is in parallel has a resistance of 4 Ω. The product of the other two resistors is 28.25. Determine the possible resistances. Draw a model of the circuit.
Answers
We have that for the Question the possible resistances are and the diagram displaying the model of the circuit is attached below
R2=3,469ohmsR3=8.142ohmsFrom the question we are told
The crew will plug portable equipment into a UOP (Utility Outlet Port). Each UOP has two connections that can be used for 120-volt power. One portal is used to power a complex circuit of total resistance of 10 Ω. The complex circuit consists of 3 different resistors of which two are in parallel and the third is in series. One of the resistors that is in parallel has a resistance of 4 Ω. The product of the other two resistors is 28.25. Determine the possible resistances. DResistancesFrom the description we have
R_2R_3=28.25
Generally the equation for the Total R is mathematically given as
\(R_t=R_3+\frac{R1+R_2}{R_1+R_2}\\\\Therefore\\\\10=R_3+\frac{R1+R_2}{R_1+R_2}\\\\2R3-3R2=5.875 \\\\\)
Hence
From the two distinct equations
\(R2=\frac{28.35}{R3}\)
R2=3,469ohmsR3=8.142ohmsFor more information on Resistances visit
https://brainly.com/question/4289257?referrer=searchResults
Estimate how long a 3000 w electric kettle would take to
boil away 100g of water. the specific latent heat of
vapourisation of water is 2.25 mjkg.
Answers
For a 3000 w electric kettle to boil away 100g of water It would take approximately 0.075 seconds where the specific latent heat of vapourization of water is 2.25 mjkg.
The estimated time it would take a 3000 W electric kettle to boil away 100 g of water can be calculated using the equation: Time = (Amount of energy required to boil the water/Power of the electric kettle) .Since amount of energy required to boil the water = specific latent heat of vapourization of water x Mass of water
Specific latent heat of vapourization of water = 2.25 MJ/kg Mass of water = 100 g, Therefore, the amount of energy required to boil the water is 225 J. Power of the electric kettle = 3000 W ,Time = (225 J/3000 W) ,Time = 0.075 s . It would take approximately 0.075 seconds for a 3000 W electric kettle to boil away 100 g of water.
To know more about Specific latent heat refer to the link brainly.com/question/3682999
#SPJ4
four resistors having resistances of 20 ω, 40 ω, 60 ω, and 80 ω are connected in series across an ideal dc voltage source. if the current through this circuit is 0.50 a, what is the voltage of the voltage source?
Answers
The voltage of the ideal DC voltage source is 100 volts.
To find the voltage of the ideal DC voltage source, we need to apply Ohm's Law, which states that the voltage across a resistor is equal to the current flowing through it multiplied by its resistance.
In a series circuit, the total resistance (R_total) is the sum of the individual resistances:
R_total = R1 + R2 + R3 + R4
Given resistances:
R1 = 20 Ω
R2 = 40 Ω
R3 = 60 Ω
R4 = 80 Ω
R_total = 20 Ω + 40 Ω + 60 Ω + 80 Ω
R_total = 200 Ω
Now, using Ohm's Law:
V_source = I_total * R_total
Given current (I_total) = 0.50 A
R_total = 200 Ω
V_source = 0.50 A * 200 Ω
V_source = 100 V
Therefore, the voltage of the ideal DC voltage source is 100 volts.
learn more about voltage source on
https://brainly.com/question/19678649
#SPJ11
A 50,000 kg plane is flying at a constant velocity of 130 m/s. Is the plane in a state of equilibrium
Answers
Answer:
yes
Explanation:
Equilibrium means that all the forces acting upon the object are balanced. A cruising airplane has all four forces balanced, with no external forces acting on it. As a result it will remain in its motion at a constant velocity until an external force acts upon it
What conversion takes place in a motor?
O A. An electric current into a magnetic field
B. A lower voltage into a higher voltage
O C. Mechanical energy into electric energy
O D. Electric energy into mechanical energy
Answers
Answer:
D. Electric energy into mechanical energy
Explanation:
hope it helps
#CarryOnLearning
The process of charging a conductor by bringing it near another charged object and then grounding the conductor is called
a) Charging by contact
b) Charging by polarization
c) Induction
d) Neutralization
Answers
The process of charging a conductor by bringing it near another charged object and then grounding the conductor is called Induction. The correct option is C.
The process described, in which a conductor is charged by bringing it near another charged object and then grounding the conductor, is known as induction. Induction involves the redistribution of charges within the conductor without direct contact between the two objects.
Here's how the process works: When a charged object is brought close to the conductor, the charges in the conductor are rearranged.
This occurs due to the electric field of the charged object influencing the distribution of charges within the conductor. However, the conductor itself remains electrically neutral overall.
If the conductor is then grounded, allowing it to make contact with the Earth or a large reservoir of charge, any excess charges in the conductor are neutralized or redistributed, resulting in the conductor becoming charged with the opposite polarity to that of the inducing object.
Therefore, the correct term for this process is c, induction.
To know more about Induction, refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/32650288#
#SPJ11
.Strictly speaking, the light that meets and passes through a pane of window glass _________.
*is not the same light that emerges
*gains energy
*is largely converted to heat in the glass
*is the same light that emerges
Answers
Strictly speaking, the light that meets and passes through a pane of window glass is not the same light that emerges. When light interacts with a pane of window glass, it undergoes several processes that result in its transformation.
As light enters the glass, it encounters the atoms or molecules within the material. These particles absorb and re-emit the incoming light through a process called scattering. This scattering causes a delay and a change in the direction of the light waves, effectively slowing them down.
Additionally, window glass is not perfectly transparent, and it absorbs a small fraction of the light passing through it. This absorption results in a conversion of some of the light's energy into thermal energy, which manifests as heat within the glass.
Due to these interactions, the light that eventually emerges from the other side of the glass is not exactly the same as the incident light. It has experienced scattering, a slight delay, and a partial conversion to heat energy.
However, the emerging light maintains the same general properties, such as its wavelength, color, and intensity. Hence, while it is not precisely the same light, it is a modified version of the original light that entered the glass.
To know more about Glass Transmits same Light refer here
https://brainly.com/question/14348977#
#SPJ11
What will be the atomic radius of copper, if the distance between two adjacent copper atoms in metallic copper is 256 pm?
Answers
The atomic radius of copper is approximately 128 picometers (pm).
The atomic radius of an element is defined as half the distance between the nuclei of two identical adjacent atoms in a molecule. In the case of metallic copper, the copper atoms are arranged in a crystal lattice, and the distance between two adjacent copper atoms in the lattice is known as the interatomic distance or lattice parameter.
We are given that the distance between two adjacent copper atoms in metallic copper is 256 pm. Since this is the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms, the sum of the atomic radii of the two copper atoms is equal to 256 pm.
Therefore, the atomic radius of copper can be calculated as follows:
Atomic radius of Cu = (interatomic distance between adjacent Cu atoms) / 2
Atomic radius of Cu = 256 pm / 2
Atomic radius of Cu = 128 pm
Hence, the atomic radius of copper is approximately 128 picometers (pm).
To learn more about picometers visit:
https://brainly.com/question/14272356
#SPJ11
one type of supersonic wind tunnel is a blow-down tunnel, where air is stored in a high-pressure reservoir, and then, upon the opening of a valve, exhausted through the tunnel into a vacuum tank or simply into the open atmosphere at the downstream end of the tunnel. for this example, we consider just the high-pressure reservoir as a storage tank that is being charged with air by a high-pressure pump. as air is being pumped into the constant-volume reservoir, the air pressure inside the reservoir increases. the pump continues to charge the reservoir until the desired pressure is achieved. consider a reservoir with an internal volume of 30 m3. as air is pumped into the reservoir, the air pressure inside the reservoir continually increases with time. consider the instant during the charging process when the reservoir pressure is 10 atm. assume the air temperature inside the reservoir is held constant at 300 k by means of a heat exchanger. air is pumped into the reservoir at the rate of 1 kg/s. calculate the time rate of increase of pressure in the reservoir at this instant.
Answers
The time rate of increase of pressure in the reservoir at this instant is approximately 9.56 Pa/s.
To calculate the time rate of increase of pressure in the reservoir, we can use the Ideal Gas Law:
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature. We can rearrange this equation to find n:
n = PV / RT
Since air is being pumped into the reservoir at a rate of 1 kg/s, we can convert this mass flow rate to a molar flow rate using the molar mass of air (M_air = 28.97 g/mol or 0.02897 kg/mol):
Molar flow rate = mass flow rate / molar mass
Molar flow rate = 1 kg/s / 0.02897 kg/mol
Molar flow rate ≈ 34.51 mol/s
Now, we can find the time rate of increase of moles in the reservoir:
dn/dt = 34.51 mol/s
Next, let's differentiate the Ideal Gas Law with respect to time:
d(PV)/dt = R * d(nT)/dt
Since V and T are constants, we get:
dP/dt = R * dn/dt / V
Substituting the values:
dP/dt = (8.314 J/mol*K) * (34.51 mol/s) / (30 m³)
dP/dt ≈ 9.56 Pa/s
At this instant, the time rate of increase of pressure in the reservoir is approximately 9.56 Pa/s.
For more such questions on pressure, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/29321317
#SPJ11
Based on the nasa institute for space studies climate model, observed temperature increases are best represented when it includes the influences of?.
Answers
Observed temperature increases are best represented when it includes the influences of increases in greenhouse gases.
What are greenhouse gases ?
Greenhouse gases are gases in the atmosphere that affect the earth's energy balance. They cause the so-called greenhouse effect. Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, and nitrous oxide, the best-known greenhouse gases, occur naturally in the atmosphere at low concentrations. However, since the beginning of the last century, its proportion has increased significantly due to various anthropogenic causes.
Besides these trace gases, which occur only in very low concentrations in the atmosphere, water vapor is probably the most important greenhouse gas. However, its ability to absorb water vapor from the air is directly related to temperature, so it only plays a major role with respect to the natural greenhouse effect. Therefore, water vapor contributes little to man-made climate change.
To learn more about greenhouse gases , click the given link ;
https://brainly.com/question/21106299
#SPJ4
__ which is a acidic mass of pratially decomped organic matter
Answers
Answer: partially decomposed
Explanation:
Whose atomic theory explains how atoms emit (release) and absorb light?
Bohr’s
Dalton’s
Rutherford’s
Thomson’s
Answers
Answer:
Bohr’s
Explanation:
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A gas at 8.4 atm has a volume of 1.9 L. What volume would the gas have at 8.3 atm?
Answers
Answer:
the final volume of the gas is 1.923 L.
Explanation:
Given;
initial pressure, P₁ = 8.4 atm
initial volume of the gas, V₁ = 1.9 L
final pressure of the gas, P₂ = 8.3 atm
The final volume of the gas is calculated by applying Boyle's law as follows;
P₁V₁ = P₂V₂
V₂ = P₁V₁ / P₂
V₂ = (8.4 x 1.9) / 8.3
V₂ = 1.923 L
Therefore, the final volume of the gas is 1.923 L.
why is there a lower mass limit of 0.08 solar masses for main-sequence stars?
Answers
The lower mass limit of 0.08 solar masses for main-sequence stars is due to the conditions required for nuclear fusion to occur. Nuclear fusion is the process in which hydrogen atoms combine to form helium, releasing energy in the process.
Main-sequence stars generate energy through the fusion of hydrogen into helium in their cores. This process, known as hydrogen burning, occurs when the temperature and pressure in the core are high enough to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between hydrogen nuclei.
Objects with a mass below 0.08 solar masses, known as brown dwarfs, do not have sufficient mass to create the necessary core conditions for hydrogen fusion. The gravitational pressure in the core of such an object is not strong enough to raise the temperature to the required level for fusion to begin. Consequently, these low-mass objects do not shine like main-sequence stars and are considered substellar.
In contrast, main-sequence stars with masses above 0.08 solar masses have enough gravitational pressure in their cores to sustain hydrogen fusion, which produces the energy that makes them visible as stars. This lower mass limit is essential in distinguishing main-sequence stars from substellar objects and understanding the different mechanisms by which these celestial bodies generate energy.
Learn more about Nuclear fusion here :
https://brainly.com/question/16556922
#SPJ11
HELPPP PLEASE QUICk :(
What performance is Evaluate skill performance against a scale
A) Coaches
B) SMART goal setting
C) Self‒reflection
D) Rubrics
Answers
Evaluate skill performance against a scale is known as Rubrics; option D
What is performance evaluation?Performance evaluation is the systematic process of assessing the performance of an individual in a certain task, skill or job.
Performance evaluation is done against a set of standard measurements or a rating scale known as Rubrics.
Rubrics use a set of specific criteria to evaluate an individual student or a group of students performance in a certain task assigned to them.
Rubrics use a rating system where points or scores are awarded depending on the skillset level or ability demonstrated.
In conclusion, rubrics are used to evaluate performance.
Learn more about rubrics at: https://brainly.com/question/3651747
#SPJ1
20.In case the conductor is a heating appliance, then this energy(w) is converted into heat(H) i.e
A. w=H C. w=I2Rt
B. w=VIt D. all of above
Answers
Answer:
not sure just need points
Explanation:
a+b+c
In young's double silt experiment if the distance between the silts is 0.5 and the distance between the silts and screen is 2 times.Then what will be the width of bands
Answers
Answer: The width of bands will be 2λ
Explanation: Please see the attachments below

a dog lifts a 0.75 kg bone straight up through a distance of 0.11 m. How much work was done by the dog ?
Answers
The work done by the dog is 0.81J.
What is work done?Work done is a measure of energy expended in moving an object; most commonly calculated by multiplying the force by the distance.
It is said that no work is done if the object does not move.
The work done on an object is the amount of energy transferred to an object through work.
According to this question, a dog lifts a 0.75 kg bone straight up through a distance of 0.11 m. The force applied to break the bone must be calculated first as follows:
Force = mass × acceleration
Force = 0.75kg × 9.8m/s²
Force = 7.35N
Work done = 7.35N × 0.11m = 0.81J
Therefore, 0.81J is the work done by the dog.
Learn more about work done at: https://brainly.com/question/2750803
#SPJ1
"nets which are used on the ocean bottom or suspended from the surface by floats which cause fish to become intangled in the net as they try to swim through it are called"
Answers
The nets are referring to are called "gillnets". Gillnets are fishing nets that are used to catch fish by entangling them in the netting.
Gillnets are a type of fishing net that is widely used in both commercial and recreational fishing. They are typically made of monofilament or multifilament nylon or similar materials and are designed to hang vertically in the water with the top of the net held at the surface and the bottom weighted down.
Fish swimming into the net become entangled in the mesh, which is sized to allow the head of the fish to pass through but not the body, effectively trapping the fish. Gillnets are highly effective for catching a wide variety of fish species, including salmon, tuna, cod, and many others.
These nets can be set on the ocean bottom or suspended from the surface by floats. The mesh size of the netting is designed to allow the head of the fish to pass through, but not the rest of the body, which becomes entangled in the netting. Gillnets are commonly used in commercial and artisanal fishing operations and can be very effective in catching fish, but they can also have unintended consequences, such as bycatch of non-target species and damage to marine habitats.
To know more about nets.
https://brainly.com/question/16024427
#SPJ4
rank in order, from largest to smallest, the angular velocities ω1, ω2, and ω3 of these points.
Answers
ω₁ = ω₂ = ω₃ Every particle rotates about the axis of rotation with a constant angular velocity (ω). The rank for velocity is v₃ > v₂ = v₁ because = r and r₁ = r₂<r₃.
A pseudovector used to express how quickly the angular location or orientation of an item changes over time is called an angular velocity or rotational velocity ( or ). (i.e. how quickly an object rotates or revolves relative to a point or axis). The pseudovector's direction is normal to the instantaneous plane of rotation or angular displacement, and its magnitude corresponds to the object's angular speed, or the rate at which it rotates or revolves. The right-hand rule is typically used to specify the direction of angular motion.
The angular velocity comes in two flavors.
Orbital angular velocity, also known as the temporal rate of change of an object's angular location with respect to an origin, is the rate at which a point object revolves about a fixed origin.In contrast to orbital angular velocity, spin angular velocity describes how quickly a rigid body rotates with regard to its center of rotation and is independent of the choice of origin.To know more about angular velocity
https://brainly.com/question/6969770
#SPJ4
What is the mass of a 50kg object in space with no gravity?
Answers
Answer:
The answer would be 0kg.
Your welcome.
ACTIVITY 4
Applying the equation learned, answer the following problems:
1. A bowling ball whose mass is 4.0 kg is rolling at a rate of 2.5 m/s. What is its momentum? p = m/s. What Is Its Momentum?
Given:
Find:
Formula:
Solution:
2. A skateboard is rolling at a velocity of 3.0 m/s with a momentum of 6.0 kg-m/s. What is its mass?
Given:
Find:
Formula:
Solution:
3. A pitcher throws a baseball with a mass of 0.5 kg and a momentum of 10 kg-m/s. What is its velocity?
Given:
Find:
Formula:
Solution:
Subject Is Science
Good Perfect Complete=Brainlist
Copy Wrong Incomplete=Report
Good Luck Answer Brainly Users:-)

Answers
Answer:
1) 10 kg-m/s
2) 2 kg
3) 20 m/s
Explanation:
The momentum of an object can be calculated using the equation:
\(\large\boxed{p=mv}\)
where:
p is momentum (measured in kilogram meters per second).m is mass (measured in kilograms).v is the velocity (measured in meters per second).\(\hrulefill\)
Question 1For this question we need to find the momentum of a bowling ball whose mass is 4.0 kg is rolling at a rate of 2.5 m/s.
Given values:
m = 4.0 kgv = 2.5 m/sSubstitute the given values into the momentum formula and solve for p:
\(p=4.0\;\text{kg} \cdot 2.5\;\text{m/s}\)
\(p=10\;\text{kg m/s}\)
Therefore, the momentum of the bowling ball is 10 kg-m/s.
\(\hrulefill\)
Question 2For this question we need to find the mass of a skateboard rolling at a velocity of 3.0 m/s with a momentum of 6.0 kg-m/s.
Given values:
p = 6.0 kg-m/sv = 3.0 m/sAs we want to find mass, rearrange the momentum formula to isolate m:
\(\large\boxed{m=\dfrac{p}{v}}\)
Substitute the given values into the formula and solve for m:
\(m=\dfrac{6.0\; \text{kg m/s}}{3.0\; \text{m/s}}\)
\(m=2\;\text{kg}\)
Therefore, the mass of the skateboard is 2 kg.
\(\hrulefill\)
Question 3For this question we need to find the velocity of a baseball with a mass of 0.5 kg and a momentum of 10 kg-m/s.
Given values:
p = 10 kg-m/sm = 0.5 kgAs we want to find velocity, rearrange the momentum formula to isolate v:
\(\large\boxed{v=\dfrac{p}{m}}\)
Substitute the given values into the formula and solve for v:
\(v=\dfrac{10\; \text{kg m/s}}{0.5\; \text{kg}}\)
\(v=20\;\text{m/s}\)
Therefore, the velocity of the baseball is 20 m/s.
Potential energy due to an object's comparison or extension is called what potential energy
Answers
Answer:
Elastic potential energy
3) A block with an unknown mass rests on a rough table. Attached to the mass is a
string which is attached to a 12 kg mass that hangs over the edge of the table via a
pulley. The coefficient of friction is 0.35. When released from rest, the system
reaches a speed of 8 m/s after traveling a distance of 6 m.
a. Calculate the acceleration of the system.
b. What equation can you use to represent the force of friction acting on the
unknown mass.
c. Write out Newton's Second Law and solve for the unknown mass.

Answers
a. The acceleration of the system is 0.21 m/s^{2}
b. The equation of the force of friction is -
tension force - force of friction = unknown mass x its acceleration and force of friction is equal to product of coefficient of friction and normal force acting on unknown mass .
c. Newton's second law of motion applies when there are unbalanced forces acting on an object. According to the second law, the mass and the net force acting on the object both affect how quickly an object is accelerating . An object's acceleration is directly proportional to the net force applied and inversely proportional to the object's mass. An object's acceleration increases as the amount of force exerted on it does. A decreasing acceleration is caused by an increase in an object's mass.
The unknown mass is nearly equal to 30 kg .
What is acceleration ?
the rate at which the speed and direction of a moving object vary over time is termed as acceleration . An object going straight ahead when it accelerates or decelerates, is said accelerated. Even if the speed is constant, motion on a circle accelerates because the direction is always shifting. Both effects contribute to the acceleration for all other motions.
To know more about acceleration, click the given link ;
https://brainly.com/question/460763
#SPJ13