A pile driver with mass 10,000 kg strikes a pile with a speed of 10.0 m/s. If the pile was driven 20.0 cm into the ground, what force is applied to the pile by the driver as it strikes the pile? A) 325 kN B) 500 kN C) 2.5 X10^6 N D) 98,000 N
Answers
The force applied to the pile by the driver as it strikes the pile is 2,500,000 N, which is also written as \(2.5 * 10^6\) N. Thus, the correct answer is option C) \(2.5 * 10^6\) N.
The force applied to the pile by the driver as it strikes the pile can be calculated using the work-energy theorem. The work-energy theorem states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. In this case, we have: Work = Change in kinetic energy = 0.5 * mass * (\(final velocity^2 - initial velocity^2\))
Since the pile comes to a stop after being driven into the ground, the final velocity is 0 m/s. We are given the mass (10,000 kg) and the initial velocity (10.0 m/s). So we can find the work done:
Work = 0.5 * 10,000 kg * (\(0^2 - 10.0 m/s^2\)) = \(- 0.5 * 10,000 kg * 100 m^2/s^2\) = - 500,000 J
Now, we can relate the work done to the force applied and the distance the pile was driven into the ground. The work done is equal to the force multiplied by the distance: Work = Force * Distance
We are given the distance (20.0 cm = 0.2 m). We can rearrange the equation to solve for the force: Force = Work / Distance = -500,000 J / 0.2 m = -2,500,000 N
The force is negative because it is acting in the opposite direction of the initial velocity. However, we are interested in the magnitude of the force, so we take the absolute value: Force = 2,500,000 N
Therefore, the force applied to the pile by the driver as it strikes the pile is 2.5 x 10^6 N (Option C).
To know more about force , refer here
https://brainly.com/question/13191643#
#SPJ11
Related Questions
What is the maximum speed when the conditions are mass =450 kg, initial height= 30 m, and the roller coaster is initially at rest?
A. 30 m/s
B. 24.2 m/s
C. 93.9 m/s
D. 132, 300 m/s
Answers
Answer:
B. 24.2 m/s
Explanation:
Given;
mass of the roller coaster, m = 450 kg
height of the roller coaster, h = 30 m
The maximum potential energy of the roller coaster due to its height is given by;
\(P.E_{max} = mgh\\\\PE_{max} = 450 *9.8*30\\\\PE_{max} = 132,300 \ J\)
\(P.E_{max} = K.E_{max} \ (law \ of \ conservation\ of \ energy)\)
\(K.E_{max} = \frac{1}{2}mv_{max}^2\\\\ v_{max}^2 = \frac{2K.E_{max}}{m}\\\\ v_{max}^2 = \frac{2*132300}{450}\\\\ v_{max}^2 =588\\\\v_{max} = \sqrt{588}\\\\ v_{max} = 24.2 \ m/s\)
Therefore, the maximum speed of the roller coaster is 24.2 m/s.
Answer:
1. 24.2 m/s
2. 20.4 m
3. 22.5 m/s
4. 109,375 J
5. It is easy to calculate new scenarios.
Explanation:
5/5 on the Maximum Energy Quick Check
PLS help confused. Will mark brainiest to the right answer.

Answers
The larger force causes more acceleration than the smaller. The correct option is A
Determining the relationship between two forces and accelerationFrom the question, we are to determine the relationship between the two forces.
From Newton's second law of motion, we have that
F = ma
Where F is the force
m is the mass
and a is the acceleration
Then, we can write that
F ∝ a
That is,
Force varies directly as acceleration
In order words, the larger the force, the more the acceleration; and the smaller the force, the less the acceleration.
Hence can conclude that the larger force causes more acceleration
Learn more on Determining the relationship between two forces here: https://brainly.com/question/13370981
#SPJ1
A meteorite is DIFFERENT from a comet mainly because it
A) has a tail of ice and dust.
B) enters the Earth’s atmosphere.
C) has a nucleus made of snow and rock.
Eliminate
D) is found in orbit between Mars and Jupiter.
Answers
A boy pulls a bag of baseball bats across a ball field toward the parking lot. The bag of bats has a mass of 6. 80 kg, and the boy exerts a horizontal force of 24. 0 n on the bag. As a result, the bag accelerates from rest to a speed of 1. 12 m>s in a distance of 5. 25 m. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bag and the ground?
Answers
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the bag and the ground is found to be 0.0251. It represents the ratio of the frictional force to the normal force acting between them.
In this question, a boy pulls a bag of baseball bats across a ball field toward the parking lot. The bag of bats has a mass of 6.80 kg, and the boy exerts a horizontal force of 24.0 N on the bag. As a result, the bag accelerates from rest to a speed of 1.12 m/s at a distance of 5.25 m. We have to find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bag and the ground.The formula used to find the coefficient of kinetic friction is given as,μk= (a/g) + μs (1 - a/g), Where, μk = coefficient of kinetic friction, a = acceleration of the body, g = acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s2), μs = coefficient of static frictionGiven, Mass of the bag (m) = 6.80 kg, Force applied (F) = 24.0 N, Initial velocity (u) = 0 m/s, Final velocity (v) = 1.12 m/s, Distance covered (s) = 5.25 m, Acceleration (a) = (v2 - u2) / 2s. Substituting the given values, a = (1.12² - 0²) / (2 * 5.25)m/s²a = 0.247m/s². Now, we will use the formula of the coefficient of kinetic friction. μk= (a/g) + μs (1 - a/g)Let's assume the value of μs to be zero.μk= (a/g) + 0 (1 - a/g) = μk= (a/g) + 0 (1 - a/g) = μk = (a/g) = μk = (0.247m/s²) / (9.8m/s²) = μk= 0.0251. Therefore, the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bag and the ground is 0.0251. In order to move the bag, the boy had to overcome friction. From the given values, we calculated the acceleration of the bag, which was found to be 0.247 m/s². Using this acceleration, we can find the coefficient of kinetic friction, which came out to be 0.0251. This value represents the ratio of the frictional force to the normal force acting between the bag and the ground.For more questions on kinetic friction
https://brainly.com/question/30130573
#SPJ8
PLEASE ASAP! I SENT A PHOTO CHECK AND TELL!

Answers
Answer:
Answer B is the correct answer: "Motion of one projectile as seen from the other is a straight line."
Explanation:
Let's write the equations of motion for each projectile, using that projectile \(a\) is launched with velocity \(a\) which has components associated with the angle of launching, given in x and y coordinates as: \(a_x\,\,and\,\,a_y\).
Similarly, assume that projectile b is launched with velocity \(b\) with components due to the launching angle = \(b_x\,\,and \,\,b_y\)
then the equations of motion for the two projectiles launched at the same time (t) from the same spot (position that we assume to be at the origin of coordinates to simplify formulas) are:
\(x_a=a_x\,t\\y_a= a_y\,t-\frac{1}{2} g\,t^2\\and\\x_b=b_x\,t\\y_b= b_y\,t-\frac{1}{2} g\,t^2\)
therefore, from the frame of reference of projectile "b", the x and y position of projectile "\(a\)" would be:
\(x_{a\,b}= x_a-x_b= a_x\,t-b_x\,t=(a_x-b_x)\,t\) which is linear in "t"
\(y_{a\,\,b}=y_a-y_b= a_y\,t-\frac{1}{2} g\,t^2-\left[ b_y\,t-\frac{1}{2} g\,t^2\right]=(a_y-b_y)\,t\) which is also linear in t.
Therefore the motion of one projectile with reference to the other is a straight line (answer B)
Notice as well that this two projectiles cannot collide because they have been launched together, and supposedly at different speeds and angles. The only way that they can share the same x-coordinate and the same y-coordinate at the same time "t" is if their velocity components are equal, which is not what we are told.
\(x_a=x_b\\a_x\,t= b_x\,t\\and\\y_a= y_b\\a_y\,t-\frac{1}{2} g\,t^2= b_y\,t-\frac{1}{2} g\,t^2\\a_y\,t=b_y\,t\\a_y=b_y\)
gaya adalah...?? [tolong yaaa..]
Answers
I can try to help if you speak English
what two factors affect the amount of friction in a system?
Answers
Answer: Weight of the objects and Coefficient of friction
Explanation: The factors that affect the friction between two surfaces are the weight of the object and the coefficient of friction of the surface.
A 5. 0kg box is at rest on a table. The static friction coefficient μs between the box and table is 0. 50, and the kinetic friction coefficient μk is 0. 30. Then, a 30N horizontal force is applied to the box. What is the best estimate of the magnitude of the box's acceleration?
Answers
The acceleration of the box is best calculated to be equal to 3.06m/s²
How can I calculate the acceleration of the box?We would first compute the magnitude of the kinetic frictional force in order to determine the size of the acceleration of this box.
The following equation can be used to determine the kinetic frictional force acting on a physical body mathematically:
F = μkN = μk(mg)
F = 0.30 × 5.0 × 9.81
F = 14.7Newton.
Newton's second law of motion is used to calculate the net force, which is as follows:
∑Fx = Applied force - kinetic frictional force = ma
Acceleration, a = [Applied force - kinetic frictional force]/m
Acceleration, a = [30 - 14.7]/5
Acceleration, a = 15.3/5
Acceleration, a = 3.06m/s²
To know more about acceleration visit:
https://brainly.com/question/20382454
#SPJ4
1 point
Q8. Complete this sentence.If I leave the coffee in the same place then
after a long time it will be at the same temperature as the surroundings.
The coffee and the surroundings are now in................
(1 mark) *
Your answer (please answer quick)
Answers
Answer:
Thermal equilibrium
Explanation:
Two systems are said to be in thermal equilibrium when there is no further exchange of thermal energy between them. At thermal equilibrium, these systems possess equal temperature.
Thermal energy is transferred between objects of varying temperatures or between a system and the surrounding. The thermal energy is transferred from the object with higher temperature (hotter) to the one with lower temperature (colder) until a state of equilibrium is attained.
In the case of the coffee and the environment, if the coffee is at higher temperature than the surrounding, it loses heat energy to the surrounding until both of them are now at the same temperature. Conversely, if the coffee has a lower temperature than the surrounding, it gains thermal energy from the surrounding until thermal equilibrium is achieved.
What type of approval must you have before working with energy traveling through space in the form of waves or particles?.
Answers
employing radiation You need some sort of authorization before you can operate with energy that is being sent through space as waves or particles.
The emission or transmission of energy as waves or particles across a material medium or across space is referred to as radiation. This includes electromagnetic radiation from sources like radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma radiation (particle radiation). In physics and allied fields, a wave is a dynamic disturbance that propagates and causes one or more quantities to depart from equilibrium. When a wave is periodic, its component portions oscillate at a specific frequency frequently in the vicinity of an equilibrium (resting) value.
Learn more about radiation here
https://brainly.com/question/28202771
#SPJ4
Answer with full steps please!

Answers
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Because B/5
if i'm wrong sorry but i hope it's help^^
a .5 kg steel ball is suspended from teh ceiling by a 2.5 m long string. the ball is pulled to the side until it is 1 m above its lowest point and then released from rest. the tension in the string when the ball passes through its lowest position is
Answers
The tension in the string when the ball passes through its lowest position is 5N (rounded).
The pulling force transmitted axially by the means of a string, a rope, chain, or similar object, or by each end of a rod, truss member, or similar three-dimensional object; tension might also be described as the action-reaction pair of forces acting at each end of said elements.
How to calculate the tension in the string when the ball passes through its lowest position?
Tension = m*g
T = 0.5 * 9.8
= 4.9N
Approximately the tension would be equal to 5N (rounded)
Learn more about tension https://brainly.com/question/26178075
#SPJ4
Sorry if it’s a bit blurry. But thanks for answering if you do!

Answers
I don’t know too much about the earths core but I’m pretty sure it’s energy
1. A man pulls a crate with a rope. The crate slides along the floor in the horizontal direction (x direction). The man exerts a force of 50 N on the rope, and the rope is at an angle . Describe how the force components change as the angle increases from 0° to 90° and use your graph to explain your answer. Give a detailed explanation of the forces at . Show a sample calculation at one angle for both components.
Answers
The variation of the components of the force with the angle of inclination of the direction of the applied force, as shown in the graph indicates that the Fₓ has a maximum, while \(F_y\) has a minimum value given by Fₓ = 50 N × cos(0°) = 50 N, and \(F_y\) = 50 N × sin(0°) at θ = 0°, while at 45°, Fₓ = \(F_y\), with \(F_y\) having a maximum value of 50 N, and Fₓ = 0 at 90°.
What is a component of a force?The component of a force are the mutually perpendicular forces to which a force acting at an angle, relative the coordinate axis can be resolved into.
The component of the force applied by the man to the force required to move the box in the horizontal direction, Fₓ, increases as the angle approaches zero, and decreases as the angle approaches, 90°, given that the horizontal component of the force is found from the equation, \(F_x = F \times cos(\theta)\), where, \(\theta\) is the angle the line of action of the force makes with the horizontal, and F, is the force the man applies' such that we have at θ = 0°, Fₓ = 50 N × cos(0°) = 50 N
When the angle is θ = 45°, Fₓ = 50 N × cos(45°) = 25·√2 N
When the angle θ = 90°, Fₓ = 50 N × cos(90°) = 0
The vertical component of the force applied \(F_y\), however, increases as the angle made by the line of force with the horizontal, increases to 90°, as shown in the graph, and decreases to 0 as the inclination angle of the force decreases, such that the have:
When the angle made with the horizontal, θ = 0°, \(F_y\) = 50 N × sin(0°) = 0
When the angle made with the horizontal, θ = 45°, \(F_y\) = 50 N × sin(45°) = 25·√2 N
At θ = 90°, \(F_y\) = 50 N × sin(90°) = 50 N
The graph of both components starts at 50 N and 0 N when θ = 0°, and both intersect when θ = 45°, while the values of the horizontal and vertical component changes, such that at 90°, the vertical force component is the largest.
Please see the attached graph.
Learn more about the components of a force here:
https://brainly.com/question/3370950
#SPJ1

Which of the following determine the chemical properties of an element?
A)Its protons
B)Its inner shell electrons
C)The size of its nucleus
D)Its valence electrons
Answers
Answer:
D, valence electrons.
Explanation:
Since the number of shells are dependent on the number of valence electrons, which determines the period of the element. Because each shell of an element holds a total of 8 valence electrons, there is a chemical association that is being made between the outer electrons and the atom.
Answer:
The correct answer is D. Its valence electrons.
Explanation:
The valence electrons are those that participate in reactions with other elements. The fewer valence electrons that an element has, the less stable it becomes; an element with a full valence electron shell does not frequently interact with other elements. In this way, the valence electrons determine the chemical properties of an element.
Hope this helps!
A 15 kg wagon with frictionless wheels carrying a 5 kg mass is moving at a speed of 3.75 m/s when it reaches another frictionless wagon of mas 15 kg. This wagon is attached to a spring of negligible mass which has a spring constant of 250 N/m. The other end of the spring is fixed to the wall. Upon impact the two wagons stick together and compress the spring. Determine the distance the wagons travel until the spring is fully compressed.
Answers
The distance the wagons travel until the spring is fully compressed is 2 × xmax = 3.42 m. To solve this problem, we need to apply the principle of conservation of momentum and conservation of energy.
Initially, the momentum of the system is given by:
p1 = (15 kg + 5 kg) × 3.75 m/s = 75 kg m/s
After the collision, the two wagons stick together and move as one unit, with a combined mass of 30 kg. Let v be the common velocity of the two wagons after the collision. Then, the momentum of the system is given by:
p2 = 30 kg × v
According to the principle of conservation of momentum, p1 = p2. Therefore, we have:
75 kg m/s = 30 kg × v
which gives:
v = 2.5 m/s
Now, let's consider the energy of the system. Initially, the kinetic energy of the system is given by:
K1 = (1/2) × (15 kg + 5 kg) × (3.75 m/s)² = 421.875 J
After the collision, the energy of the system is stored in the compressed spring. The potential energy of a spring is given by:
U = (1/2) × k × x²
where k is the spring constant and x is the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position. At maximum compression, the displacement is xmax, and the potential energy is:
Umax = (1/2) × 250 N/m × xmax²
According to the principle of conservation of energy, the initial kinetic energy of the system is converted to potential energy of the spring at maximum compression. Therefore, we have:
K1 = Umax
which gives:
xmax = sqrt(2 × K1 / k) = 1.71 m
Therefore, the distance the wagons travel until the spring is fully compressed is 2 × xmax = 3.42 m.
To know more about conservation of momentum, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/3920210
#SPJ1
write the full hamiltonian for the h2- molecule with nuclei a and b and electrons 1,2 and 3. 2. (2.5 pts) show
Answers
The Hamiltonian for the H2 molecule with nuclei A and B and electrons 1, 2, and 3 can be written as:
H = T₁ + T₂ + T₃ + V₁A + V₂A + V₃A + V₁B + V₂B + V₃B + V₁₂ + V₁₃ + V₂₃ + VAB
where:
T₁, T₂, T₃ are the kinetic energy operators for electrons 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
V₁A, V₂A, V₃A are the electron-nucleus interaction potential energies for electrons 1, 2, and 3 with nucleus A, respectively.
V₁B, V₂B, V₃B are the electron-nucleus interaction potential energies for electrons 1, 2, and 3 with nucleus B, respectively.
V₁₂, V₁₃, V₂₃ are the electron-electron interaction potential energies between electrons 1 and 2, electrons 1 and 3, and electrons 2 and 3, respectively.
VAB is the nucleus-nucleus interaction potential energy between nucleus A and nucleus B.
The kinetic energy operator for each electron (Ti) is given by:
Ti = (-ħ²/2m) ∇i²
where ħ is the reduced Planck's constant and m is the mass of an electron.
The electron-nucleus interaction potential energy (ViA or ViB) between electron i and nucleus A or B is given by:
ViA or ViB = (-e²/4πε₀riA or riB)
where e is the elementary charge, ε₀ is the vacuum permittivity, and riA or riB is the distance between electron i and nucleus A or B.
The electron-electron interaction potential energy (Vij) between electron i and electron j is given by:
Vij = (e²/4πε₀rij)
where rij is the distance between electron i and electron j.
The nucleus-nucleus interaction potential energy (VAB) between nucleus A and nucleus B is given by:
VAB = (e²/4πε₀rAB)
where rAB is the distance between nucleus A and nucleus B.
Please note that this Hamiltonian represents the basic interactions between the particles in the H2 molecule. More complex terms, such as spin interactions and relativistic corrections, may be included depending on the level of approximation and accuracy required for the specific calculation.
To know more about Hamiltonian refer here
https://brainly.com/question/30881364#
#SPJ11
PLEASE HELPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPP

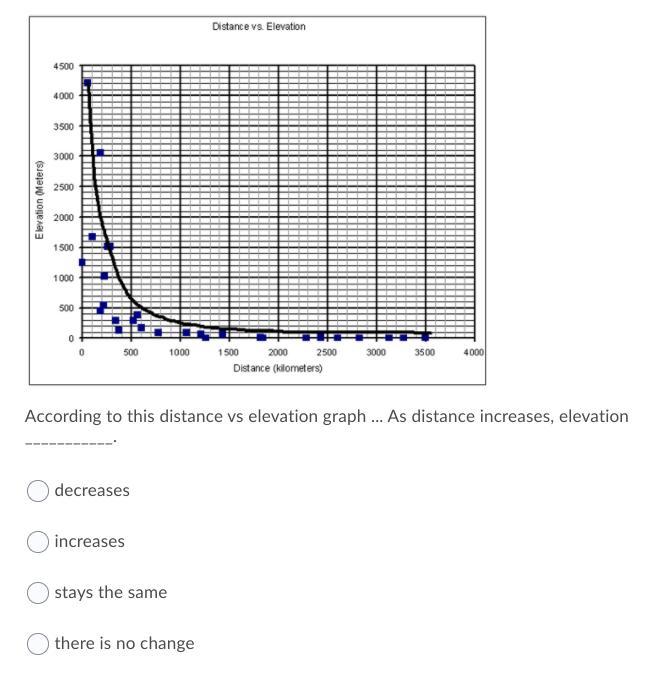

Answers
The first: 1,026m
The second: decreases
The third: 7.9 mya
hope i helped some :))
Two masses balance on opposite sides of a pivot on a balance beam. The mass on the left is 4. 3 cm away from the pivot. The mass on the right is 4. 2 cm away from the pivot. The mass on the left is 30. 4 grams. What is the mass on the right in grams? give your answer to one decimal place
Answers
The mass on the right is 28.9 grams.
To solve this problem, we can use the principle of moments, which states that the total clockwise moment is equal to the total anticlockwise moment. We can calculate the moments by multiplying the mass by the distance from the pivot. Let M1 be the mass on the left and M2 be the mass on the right. We can set up the equation:
M1 x 4.3 = M2 x 4.2
Substituting M1 = 30.4 grams, we can solve for M2:
M2 = (M1 x 4.3) / 4.2
M2 = (30.4 x 4.3) / 4.2
M2 = 31.12 grams
Therefore, the mass on the right is 31.12 grams. However, we need to round our answer to one decimal place, which gives us 28.9 grams as the final answer.
Learn more about Distance here.
brainly.com/question/29979670
#SPJ11
UVA and UVB rays can cause skin damage and skin cancer. True False
Answers
Answer:
true
Explanation:
they can cause skin damage
Is a chemical formula and chemical equation the same?
Answers
Answer: No
Explanation:
A chemical for formula is combined of atomic that is has a chemical compounds
Assume that the maximum aperture of the human eye, D
, is approximately 8mm
and the average wavelength of visible light, , is 5.5 x 10-4mm
.
a. Calculate the diffraction limit of the human eye in visible light.
b. How does the diffraction limit compare with the actual resolution of 1 to2 1 to 2 arcminutes ( 60 to
to 120
arcseconds)?
c. To what do you attribute the difference
Answers
a. The diffraction limit of the human eye in visible light is calculated using the formula θ = 1.22 × (λ / D).
b. The diffraction limit is compared to the actual resolution of 1 to 2 arcminutes (60 to 120 arcseconds).
c. The difference between the diffraction limit and actual resolution is attributed to optical imperfections, aberrations, and limitations of the visual system.
a. To calculate the diffraction limit of the human eye in visible light, we can use the formula:
θ = 1.22 × (λ / D)
Given:
λ = 5.5 × \(10^{(-4)\) mm
D = 8 mm
Substituting these values into the formula, we get:
θ = 1.22 × (5.5 x \(10^{(-4)\) mm / 8 mm)
Simplifying the expression, we find the diffraction limit of the human eye in visible light.
b. To compare the diffraction limit with the actual resolution of 1 to 2 arcminutes (60 to 120 arcseconds), we convert the diffraction limit calculated in part a to arcminutes or arcseconds and compare the values.
c. The difference between the diffraction limit and the actual resolution can be attributed to factors such as optical imperfections, aberrations, and limitations of the visual system, including the processing capabilities of the brain. These factors affect the actual resolution achievable by the human eye, leading to a difference from the diffraction limit.
Learn more about diffraction limits at
https://brainly.com/question/15081792
#SPJ4
a ball is thrown straight down from the top of a building with a speed greater than its terminal speed vt. which of the following graphs best represents the speed v of the ball as a function of time t while it falls to the ground?
Answers
The graph best represents the speed v of the ball as a function of time t while it falls to the ground is attached in the answer.
What is terminal velocity?
The speed that an object reaches when it freely falls through a gas or liquid is known as the terminal velocity. A parachutist who waits to open the chute will typically reach a terminal velocity of around 150 miles per hour (240 km/h).
A mist of minute oil droplets settles with an incredibly low terminal velocity, whereas raindrops fall at a considerably lower terminal velocity. An object compelled to go faster than its terminal velocity will slow down to this constant velocity upon release; an object dropped from rest will increase its speed until it achieves terminal velocity.
Learn more about terminal velocity here:
https://brainly.com/question/2654450
#SPJ1

what is physical properties of matter
Answers
Answer:
A quality of matter that is unrelated to a change in its chemical makeup is called a physical property.
Examples of physical properties of matter:
DensityColorHardnessMelting PointBoiling PointElectrical ConductivityPhysical properties are any qualities of matter that may be felt or seen without changing the sample's chemical composition.
Due to the wide range of features that make up physical attributes, they are further separated into intensive and extensive as well as isotropic and anisotropic categories.
Any characteristic that can be recognized and measured by sight, hearing, touch, smell, or other senses without evoking a chemical reaction is referred to as a physical property. Examples of physical traits are:
Color, Shape, Volume, Density, Calorific value, Boiling point, Viscosity, Pressure, Solubility, electrical current
Learn more about physical properties here:
https://brainly.com/question/12330204
3Three identical sheets of paper are taken, but arranged in different ways as shown. Which paper can support the most weight?
Answers
Answer:
The most thick paper can support maximum weight.
Explanation:
A paper is defined as a thin sheet of material that is prepared chemically or mechanically processing of the cellulose fibers which are derived from the grasses, wood, bamboos, trees or rags.
In the context, there are three different but identical sheets of paper that are arranged in different ways. Weights are placed over the papers. Now the most thick paper of the three provided will support most of the weight.
Paper thickness or paper weights are measured in GSM. GSM stands for grams per square meter. The thicker paper will have higher GSM.
What part of the plant takes in carbon dioxide?
1.Roots
2.Stomata
3.Minerals
4.Soil
Answers
The answer is number 2 stomata.
g in order to regain the orbit it had exactly one year earlier, the iss fires rockets that thrust parallel to its current velocity. as a result, the station's gravitational potential energy will:
Answers
In order for the International Space Station (ISS) to regain the orbit it had exactly one year earlier, it fires rockets that thrust parallel to its current velocity. The station's gravitational potential energy is not affected by the rocket's thrust.
The station's kinetic energy is, however, influenced by the rocket's thrust. The rocket's thrust is proportional to the mass of the propellant and the velocity of the exhaust gases in the opposite direction. Thrust is also influenced by the rate of propellant consumption. Since the station is already in a state of motion, the rocket's thrust serves to change the magnitude of the station's velocity, which affects its kinetic energy. When the station is in orbit, its kinetic energy is balanced by the gravitational potential energy of the earth. The ISS has a higher gravitational potential energy when it is in a higher orbit. When the station's velocity increases as a result of the rocket's thrust, its kinetic energy rises, and the station's potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. The higher kinetic energy causes the ISS to ascend to a higher orbit. When the velocity decreases, the station's kinetic energy decreases, and its potential energy increases. The station descends to a lower orbit as a result of this.
As a result, when the ISS is moving faster, its gravitational potential energy decreases, and when it is moving slower, its potential energy increases.
for such more questions on potential
https://brainly.com/question/24142403
#SPJ8
calculate the venturi and orifice coefficients using engineering judgment, comment on the comparison for agreement or lack of agreement.4. express the errors in f and re as a function of the precisions of manometer, graduate cylinder, and stop watch, in the pipe flow experiment. note that the pressure and flow rate are independently measured. 5. what are the advantages and disadvantages of flow-restriction meters such as the orifice plate and venturi? 6. why do we remove the air or air bubble in the manometer? if there is a 1.5 cm air length in the manometer pipe, estimate how much error will it cause in the experimental pressure?
Answers
The Venturi and orifice coefficients are given by the following formulas, respectively: Cv = Q / (CdA)Co = Q / (CdA), Where, Q is the flow rate, Cd is the discharge coefficient, and A is the cross-sectional area of the pipe. The value of Cd depends on the Reynolds number (Re) and the beta ratio (β), which is the ratio of the diameter of the flow-restricting device to the diameter of the pipe containing the fluid.
The values of Cd for Venturi and orifice are given below:Venturi: Cd = 0.98 - 0.04β + 0.4/βOrifice: Cd = 0.6 - 0.5/β2 + 0.85/β4For this problem, engineering judgment has to be used to estimate the values of Cd and β based on experimental data. A comparison of the calculated values of Cd and β for the Venturi and orifice can be made to check for agreement or lack of agreement.
Flow-restriction meters, such as the orifice plate and Venturi, are used to measure the flow rate of fluids in pipes. The advantages and disadvantages of these meters are given below:Advantages: Flow-restriction meters are simple and inexpensive to install. They can be used to measure the flow rate of a wide range of fluids. They are accurate for liquids and gases at high flow rates.
Disadvantages: Flow-restriction meters are sensitive to changes in viscosity, density, and temperature. They cause a pressure drop in the pipeline, which can affect the performance of pumps and compressors. They require regular maintenance to prevent clogging and fouling.
The manometer is used to measure the pressure drop across the flow-restricting device. The manometer works by balancing the pressure of the fluid with the weight of a liquid column in a tube. The air bubble in the manometer should be removed to ensure accurate measurements. If there is a 1.5 cm air length in the manometer pipe, it will cause an error in the experimental pressure due to the weight of the air. The error can be calculated as follows: Error = (ρair x g x h) / (ρfluid x g), Where ρair is the density of air, g is the acceleration due to gravity, h is the height of the air column, and ρfluid is the density of the fluid.
Learn more about viscosity here ;
https://brainly.com/question/30464801
#SPJ11
Question 3 (1 point)
You do Work by lifting a television up one meter. How much work would you do to lift it up two meters?
Answers
Answer:
twice as much work
Explanation:
How do you find average velocity during free fall?