Answers
Answer:
9.461 × 10^12 Km s
..............................
Related Questions
Research Galileo’s work on falling bodies. What did he want to demonstrate? What opinions or theories was he trying to refute? What arguments did he use to persuade others that he was right? Did he depend on experiments, logic, findings of other scientists, or other approaches?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Galileo's famous argument against the Aristotle's theory of falling bodies goes like this. "Let's say heavy objects do fall faster than light ones. Then it seems the heavier weight will fall with the lighter weight acting, as it were, a bit like a parachute. In that case, the two balls will together fall more slowly than the heavy weight would on its own. On the other hand, once the two weights are tied together and held out over the parapet, they have effectively combined their weights, becoming one greater weight... they must therefore fall even faster than the heavy weight would on its own." Contradiction. Hence weight has no effect on falling rates.
Some philosophers are very fond of this argument. Gendler uses it as a prototypical example of how "reasoning about particular entities within the context of an imaginary scenario can lead to rationally justified conclusions". Snooks goes further saying "it is striking that one leaves the falling balls example with something approaching certainty for its outcome". And Brown goes all the way and claims that Aristotle's theory is "self-contradictory", and we gain a priori knowledge here. The argument does give off that flavor of "synthetic a priori" reasoning, as in geometry but without images. But is it a proof or a fallacy? Even Gendler admits that some "obvious" premises are missing, and Atkinson even calls it a "non-sequitur" for similar reasons. But Galileo's logic is not questioned it seems. Shouldn't it be?
Galileo proved force causes acceleration. Galileo concluded from the law of parabolic fall that bodies fall on Earth at a constant acceleration and that gravity, which pulls all bodies down, is constant.
What is Galileo's law of falling bodies?According to Galileo's law of free fall, in the absence of any resistance from the air, all bodies fall with the same acceleration, regardless of their mass. This law was developed by Galileo. The application of Newtonian mechanics demonstrates that this law is only a close approximation.
A water clock was utilized in the process of timekeeping. Galileo demonstrated that motion on an inclined plane had a constant acceleration, and that this acceleration was only dependent on the angle of the plane and not the mass of the rolling body. This demonstrated that the acceleration of free falling bodies is the same.
Galileo proposed that in the absence of air, all bodies, regardless of how much matter they contain, would fall at the same rate in relation to the earth. It appears that Aristotle considered all media to be viscous, and he argued that heavier bodies fall at a faster rate.
Learn more about Galileo’s experiment, here:
https://brainly.com/question/3920616
#SPJ2
A copper atom has an atomic number of 29 and an atomic mass of 64. What
is the structure of this atom?
OA. It has a central nucleus composed of 29 protons and 64 neutrons,
surrounded by an electron cloud containing 29 electrons.
B. It has a central nucleus composed of 29 protons and 35 neutrons,
surrounded by an electron cloud containing 29 electrons.
OC. It has a central nucleus composed of 29 protons and 29 neutrons,
surrounded by an electron cloud containing 35 electrons.
D. It has a central nucleus composed of 35 protons and 29 neutrons,
surrounded by an electron cloud containing 29 electrons.
Answers
Answer:
It has a central nucleus composed of 29 protons and 35 neutrons, surrounded by an electron cloud containing 29 electrons
Explanation:
Atoms Composition:
A atom is mainly composed of a centrally-placed nucleus. A nucleus consists of protons and neutrons with a cloud of electrons surrounding the outside. A proton is a nuclear particle having a positive charge equal to that of an electron and a mass more than 1800 times the electron. A neutron is a nuclear particle having a mass almost identical to that of an electron, but no electric charge.Calculation:
Mass number = Proton + Neutron64 = 29 + NeutronCollect like termsNeutron = 64 – 29Neutron = 35Which graph shows the change in velocity of an object in free fall?

Answers
Answer:
The graph of the velocity of an object in free fall would look like a straight line sloping downward. As the object falls, its velocity increases at a constant rate, so the graph of its velocity versus time will be a straight line with a negative slope. This is because acceleration due to gravity is a constant -9.8 meters per second squared, so the velocity of a free-falling object will increase by 9.8 meters per second every second.
Therefore, the graph that shows the change in velocity of an object in free fall is a straight line with a negative slope. Here is an example of such a graph:
Free Fall Velocity Graph
Weather hazards and natural disasters such as tsunamis, earthquakes, and flooding are considered which type of migration factor?
A. Pull factor
B. Both push and pull factors
C. Neither push or pull factor
D. Push factor
Answers
Push factors lead people to leave their current location
Pull factors lead people to come to a specific location
[brainliest appreciated]
Answer:
D. Push Factor
Explanation:
Pull factors are known as positive aspects of a place that make people want to stay/remain in that area.Push factors are known as negative aspects of a place that make people want to leave/depart from that area.Weather hazards and natural disasters are horrendously negative things that people actively seek to avoid; they make people want to leave or depart from an area in order to escape them. As such, they are considered push factors.
(Weather hazards and natural disasters are not pull factors because when discussing push vs pull we are specifically describing the mentioned factor. This aspect is not considered both because the migration factor mentioned in this question actively makes people want to move to any area that avoids their issue. Remember that pull factors make people want to move to a specific place for a unique advantage, while push factors make people want to move to any general place for a common advantage.)
A candle is placed in front of a concave mirror as it is shown . State the image characteristics (SALT)
Answers
As a result, the picture behind the mirror is virtual, upright, and enlarged.
What does SALT in concave mirrors stand for?You will find that the properties of an image (SALT) created in a concave mirror depend on the object's position. A) if the item is larger than C. Size, attitude, and location are all important considerations.
The image will be true, but reversed and much reduced. To obtain a crisp flame image, move the burning candle towards the mirror while moving the screen away from it. The size of the inverted picture grows.
Concave mirrors may create both physical and virtual images. A virtual and enlarged picture is produced when the item gets closer to the mirror. When the item is placed further away from the mirror,.
learn more about Concave mirrors
https://brainly.com/question/27841226
#SPJ1
1.) A roller coaster travels on a frictionless track as shown in the illustration.
a.) If the speed of the car at Pt A is 5.0 m/s, what is the speed at Pt B
(More in the photo provided)

Answers
For the roller coaster on a frictionless track:
a. The speed at Point A is 5.0 m/s, the speed at Point B will also be 5.0 m/s.b. The height between Points A and B where kinetic energy equals potential energy is 5.0 m.c. For the car to reach Point C, the height at Point B must be greater than or equal to 8.0 m.d. For the car to reach Point C, the height at Point A must be greater than or equal to 8.0 m.How to solve speed and height?a. The speed of the car at Point B can be determined using the principle of conservation of energy. The total mechanical energy (sum of kinetic energy and potential energy) remains constant in the absence of external forces like friction. Therefore, if there is no energy loss, the kinetic energy at Point A is equal to the kinetic energy at Point B.
Given that the speed at Point A is 5.0 m/s, the speed at Point B will also be 5.0 m/s.
Answer: A. 5.0 m/s
b. To find the height at which kinetic energy equals potential energy, we can set the equations for kinetic energy and potential energy equal to each other.
At Point A, the roller coaster has both kinetic energy and potential energy. The total mechanical energy is the sum of these two:
Initial mechanical energy at Point A = Kinetic energy at Point A + Potential energy at Point A
At Point B, the roller coaster will have kinetic energy and potential energy, but we want to find the height at which kinetic energy equals potential energy. Let's call this height "h."
Mechanical energy at Point B = Kinetic energy at Point B + Potential energy at Point B
Since the speed at Point B is the same as the speed at Point A (5.0 m/s), the kinetic energy at both points is the same.
Equating the mechanical energy at Point A to the mechanical energy at Point B:
Initial mechanical energy at Point A = Mechanical energy at Point B
Kinetic energy at Point A + Potential energy at Point A = Kinetic energy at Point B + Potential energy at Point B
Since the kinetic energy is the same at both points, simplify the equation:
Potential energy at Point A = Potential energy at Point B
The potential energy at any point is given by the formula mgh, where m is the mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height.
Therefore, at the height h between Points A and B, the potential energy equals the potential energy at Point A:
mgh = mghA
Since the mass and acceleration due to gravity are the same, cancel them out:
h = hA
This means that the height where kinetic energy equals potential energy is the same as the height at Point A.
Answer: The height between Points A and B where kinetic energy equals potential energy is 5.0 m.
c. To determine if the car will reach Point C, compare the potential energy at Point B with the potential energy at Point C. If the potential energy at Point B is greater than or equal to the potential energy at Point C, the car will reach Point C.
Potential energy at Point B = mghB
Potential energy at Point C = mghC
Given that the height at Point C is 8.0 m, compare the potential energies:
Potential energy at Point B ≥ Potential energy at Point C
mghB ≥ mghC
Since the mass (m) and acceleration due to gravity (g) are constant, cancel them out:
hB ≥ hC
Therefore, for the car to reach Point C, the height at Point B must be greater than or equal to 8.0 m.
d. The minimum speed needed at Point A for the car to reach Point C can be determined by comparing the potential energy at Point A with the potential energy at Point C. If the potential energy at Point A is greater than or equal to the potential energy at Point C, the car will have enough energy to reach Point C.
Potential energy at Point A = mghA
Potential energy at Point C = mghC
Given that the height at Point A is 5.0 m, compare the potential energies:
Potential energy at Point A ≥ Potential energy at Point C
mghA ≥ mghC
Since the mass (m) and acceleration due to gravity (g) are constant, cancel them out:
hA ≥ hC
Therefore, for the car to reach Point C, the height at Point A must be greater than or equal to 8.0 m.
To summarize, for the car to reach Point C, the height at Point B must be greater than or equal to 8.0 m, and the height at Point A must also be greater than or equal to 8.0 m.
Find out more on speed and height here: https://brainly.com/question/31252698
#SPJ1
Write 3 – 4 sentences evaluating the use of nuclear fission to generate electric energy. Provide at least one point in favor of and two points against using fission.
Answers
Answer:
One point in favor of using nuclear fission to generate electric energy is that it is a relatively low-carbon option, producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions than fossil fuels. However, there are several points against using fission as an energy source. One is that it produces radioactive waste that can be difficult and costly to dispose of safely. Another is that there is the risk of accidents or leaks, which can have serious consequences for both people and the environment. Additionally, the construction of nuclear power plants is expensive and time-consuming, and the plants themselves have a limited lifespan.
what is a everyday activities examples of newtons 1 law of motion
Answers
Answer:
bouncing a baskletball
Explanation:
Answer:someone kicking a soccer ball.
Explanation:
Because the ball isn’t in motion until acted on by another object (the foot)
How is thermal energy being transferred when steam rises from a beaker of boiling water?
O A. Conduction
• B. Radiation
O c. Translation O D. Convection
Answers
Answer:
d. convention
Explanation:
hope this helped
The average wavelength in a series of ocean waves is 15.0 m. A wave arrives on average every
10 s, so the frequency is 0.1 Hz. What is the average speed of the waves?
Answers
The average speed of the waves is 1.5 m/s
From the question,
We are to determine the average speed of the waves.
Using the formula
v = fλ
Where
v is the speed
f is the frequency
and λ is the wavelength
From the given information
f = 0.1 Hz
λ = 15.0 m
∴ Speed of the wave = 0.1 × 15.0
Speed of the wave = 1.5 m/s
Hence, the average speed of the waves is 1.5 m/s
Learn more here: https://brainly.com/question/16689934
Consider the circuit in Figure 5 with e(t) = 12sin(120pit) V. When S1 and S2 are
open, i leads e by 30°. When SI is closed and S2 is open, i lags e by 30°. When S1 and S2 are closed, i has an amplitude 0.5A. What are R, L, and C?

Answers
Based on the information, it should be noted that the resistance R is 0.5 Ω.
How to calculate the resistanceWhen S1 and S2 are open, i leads e by 30°. In this case, the circuit consists of only the inductor (L) and the capacitor (C) in series. Therefore, the impedance of the circuit can be written as:
Z = jωL - 1/(jωC)
Since i leads e by 30°, we can express the phasor relationship as:
I = k * e^(j(ωt + θ))
Z = jωL - 1/(jωC) = j(120π)L - 1/(j(120π)C)
Re(Z) = 0
By equating the real parts, we get:
0 = 0 - 1/(120πC)
Let's assume that there is a resistance (R) in series with the inductor and capacitor. The impedance equation becomes:
Z = R + jωL - 1/(jωC)
Z = R + jωL
Im(Z) = ωL > 0
Substituting the angular frequency and rearranging the inequality, we have:
120πL > 0
L > 0
This condition implies that the inductance L must be greater than zero.
When S1 and S2 are closed, i has an amplitude of 0.5 A. In this case, the impedance is:
Z = R + jωL - 1/(jωC)
Since the amplitude of i is given as 0.5 A, we can express the phasor relationship as:
I = 0.5 * e^(j(ωt + θ))
By substituting this phasor relationship into the impedance equation, we can determine the value of R. The real part of the impedance must be equal to R:
Re(Z) = R
Since the amplitude of i is 0.5 A, the real part of the impedance must be equal to 0.5 A: 0.5 = R
Therefore, the resistance R is 0.5 Ω.
Learn more about resistance on
https://brainly.com/question/17563681
#SPJ1
A man is standing away from the School
Building at a distance of
300m . He claps his hands and hears an echo calculate the time interval of him hearing his echo
Answers
The time interval between the man clapping and hearing his echo is approximately 1.75 seconds.
What do you mean by echo?An echo is a repetition or reflection of a sound or signal. It can be caused by sound waves bouncing off a surface, signal interference, or the repetition of a message in communication.
The speed of sound in air at room temperature is approximately 343 meters per second. When a person claps, the sound waves propagate outward in all directions and reach the school building, where they bounce off and return to the person as an echo. The time it takes for the sound to travel the distance to the building and back to the person is the time interval between the clap and the echo.
To calculate the time interval, we can use the following formula:
time = distance / speed
where distance is the total distance traveled by the sound (twice the distance from the person to the school building), and speed is the speed of sound in air.
distance = 2 x 300m = 600m
speed = 343 m/s
time = 600m / 343 m/s = 1.75 seconds (rounded to two decimal places)
Therefore, the time interval between the man clapping and hearing his echo is approximately 1.75 seconds.
Learn more about echo here:
https://brainly.com/question/9527413
#SPJ9
A trebuchet launches a pumpkin at an angle of 63 degrees at an initial velocity of 51 m/ s from the ground. What is the range of the pumpkin?
Answers
Answer:
214.72m
Explanation:
The range (R) of a projectile can be calculated using the formula:
R = u²sin2θ/g
Where R = Horizontal range
u = initial velocity
θ = angle of initial velocity
g = acceleration due to gravity (9.8m/s²)
According to the provided information in this question, R= ?, u= 51m/s, θ = 63°, g = 9.8m/s².
Hence, R = u²sin2θ/g
R = 51² × sin 2×63/ 9.8
R = 2601 × sin 126/9.8
R = 2601 × 0.809/9.8
R = 2104.25/9.8
R = 214.72m
An ideal gas, initially at a volume of 6 L and
pressure of 8 kPa, undergoes isothermal expansion until its volume is 8 L and its pressure
is 6 kPa.
1): Calculate the work done by the gas during
this process.
Answer in units of J.
2): Find the heat added to the gas during this
process.
Answer in units of J.
Answers
(1) The work done by the gas during this process is -13.71 J.
(2) The heat added to the gas during this process 13.71 J.
What is the work done by the gas?The work done by the gas is calculated as follows;
W = -nRT ln(V₂/V)
Where;
V₁ is the initial volume of the gasV₂ is the final volume of the gasn is the number of molesR is the ideal gas constantThe number of moles of gas is calculated as follows;
n = PV/RT
n = (8 kPa x 6 L) / (8.314 J/mol.K x 273 K)
n = 0.021 mol
The work done by the gas is calculated as follows;
W = -nRT ln(V₂/V)
W = -(0.021 x 8.314 x 273) ln(8/6)
W = -13.71 J
For isothermal process, the change in internal energy is zero.
So, the heat added to the gas is equal to the work done on the gas.
Q = -W = 13.71 J
Learn more about work done by gas here: https://brainly.com/question/11982158
#SPJ1
Usually, we do a
when a population is hard to study, for some reason.
Answers
Usually, we use sampling when a population is hard to study, for some reason.
Sampling is a technique commonly employed in research and statistics when it is impractical or impossible to study an entire population directly. It involves selecting a subset, or sample, from the population and using the information gathered from the sample to make inferences about the entire population. This is done with the assumption that the sample is representative of the population and that the findings from the sample can be generalized to the larger population.
There are several reasons why a population might be difficult to study comprehensively. One reason is the size of the population. For example, if the population of interest is the entire world or a country, it would be practically impossible to study each individual in the population due to logistical constraints and limited resources. In such cases, sampling allows researchers to gather information from a smaller, manageable subset of the population.
Another reason for using sampling is when the population is dispersed or geographically scattered. If the population is spread out across a wide area, it can be challenging and costly to reach and collect data from every individual. Sampling allows researchers to select representative individuals or clusters from different regions, making data collection more feasible.
Additionally, there are cases where the population is inaccessible or hard to reach due to privacy concerns or ethical considerations. For example, if the population consists of individuals with certain medical conditions or sensitive personal information, it may be challenging to obtain consent or access to the entire population. In such cases, researchers can use sampling methods to obtain data from a subset of individuals who are willing to participate and meet the necessary criteria.
In summary, sampling is a valuable tool when studying populations that are hard to access, too large, or dispersed. It allows researchers to gather relevant data from a representative subset of the population and make valid inferences about the larger population, despite the challenges posed by studying the population as a whole.
For more such information on: sampling
https://brainly.com/question/13219833
#SPJ8
The question probable may be:
Usually, we use when a population is hard to study, for some reason.
An alternative to CFL bulbs and incandescent bulbs are light-emitting diode (LED) bulbs. A 60 W incandescent bulb can be replaced by a 12 W LED bulb. Both produce 800 lumens of light. Assuming the cost of electricity is $0.29 per kilowatt-hour, how much does it cost (in dollars) to run the LED bulb for one year if it runs for four hours a day?
Answers
Answer:
C = $5.08
it costs $5.08 to run the LED bulb for one year if it runs for four hours a day
Explanation:
Given;
Power of Led bulb P = 12 W
Rate r = $0.29 per kilowatt-hour
Time = 4 hours per day
The number of hours used in a year is;
time t = 4 hours per day × 365 days per year
t = 1460 hours
The energy consumption of Led bulb in a year is;
E = Pt
E = 12 W × 1460 hours
E = 17520 watts hour
E = 17.52 kilowatt-hour
The cost of the energy consumption is;
C = E × rate = Er
C = 17.52 × $0.29
C = $5.08
it costs $5.08 to run the LED bulb for one year if it runs for four hours a day
Hank, whose mass is 55 kg, runs at a rate of 4.5 m/s. What kind of energy does he have? *
Answers
Answer:
Mass = 55kg
Velocity = 4.5 m/s
K.E(kinetic energy) = ?
Now,
K.E = 1/2*M*V^2
= 1/2*55*4.5*4.5
= 1113.75/2
= 556.87 joule
How much time will it take for a bug to travel 2 meters across the floor if it is traveling at 0.5 m/s?
Answers
Find the change in EPE (ΔU) as a charge of (a) 2.2 x 10⁻⁶ c and (b) -1.1 x 10⁻⁶c moves from A⇒B given that the change in EP (ΔU) between the points is 24V
Answers
The change in EPE (ΔU) as a charge of (a) 2.2 x 10⁻⁶ c and (b) -1.1 x 10⁻⁶c moving from A⇒B given that the change in EP (ΔU) between the points is 24V are 5.28 x 10⁻⁵ J and 2.64 x 10⁻⁵ J respectively.
How can we calculate the change in electric energy using the given equations?The change in electric potential energy (ΔU) can be calculated using the equation ΔU = qΔV, where q is the charge and ΔV is the change in electric potential between the two points.
For a charge of 2.2 x 10⁻⁶ c moving from A to B:
ΔU = (2.2 x 10⁻⁶ c)(24 V) = 5.28 x 10⁻⁵ J
For a charge of -1.1 x 10⁻⁶ c moving from A to B:
ΔU = (-1.1 x 10⁻⁶ c)(24 V) = -2.64 x 10⁻⁵ J
The negative sign on the second case indicates that the work done would be done against the direction of the electric field and thus the energy would be absorbed from the field.
Therefore, the correct answers are as given above.
learn more about change in electric energy: https://brainly.com/question/12995630
#SPJ1
two car moving in the same direction have speed of 100km/h-1 and 130km/h.what is the resultant of velocity .shoe carnival in the same direction having speed of 100 km per hour - 1 and 130 km per hour to kilometre-per-hour - 1
Answers
Answer:
jjjjjjhshahshhddhdhh
34. [8 Marks] A spring is compressed with a 5.0 kg mass by 20.0 cm from its equilibrium position. When the spring is released, the 5.0 kg mass travels along a smooth horizontal surface and then up a frictionless plane at 30° to the horizontal. Calculate the distance it would travel up the inclined plane before coming back down again.
Answers
Answer and Explaination:
To solve this problem, we can analyze the forces acting on the mass as it travels up the inclined plane. We'll consider the gravitational force and the force exerted by the spring.
1. Gravitational force:
The force due to gravity can be broken down into two components: one perpendicular to the inclined plane (mg * cosθ) and one parallel to the inclined plane (mg * sinθ), where m is the mass and θ is the angle of the inclined plane.
2. Force exerted by the spring:
The force exerted by the spring can be calculated using Hooke's Law, which states that the force exerted by a spring is directly proportional to the displacement from its equilibrium position. The force can be written as F = -kx, where F is the force exerted by the spring, k is the spring constant, and x is the displacement from the equilibrium position.
Given:
Mass (m) = 5.0 kg
Compression of the spring (x) = 20.0 cm = 0.20 m
Angle of the inclined plane (θ) = 30°
First, let's find the force exerted by the spring (F_spring):
F_spring = -kx
To find k, we need the spring constant. Let's assume that the spring is ideal and obeys Hooke's Law linearly.
Next, let's calculate the gravitational force components:
Gravitational force parallel to the inclined plane (F_parallel) = mg * sinθ
Gravitational force perpendicular to the inclined plane (F_perpendicular) = mg * cosθ
Since the inclined plane is frictionless, the force parallel to the inclined plane (F_parallel) will be canceled out by the force exerted by the spring (F_spring) when the mass reaches its highest point.
At the highest point, the gravitational force perpendicular to the inclined plane (F_perpendicular) will be equal to the force exerted by the spring (F_spring).
Therefore, we have:
F_perpendicular = F_spring
mg * cosθ = -kx
Now, let's substitute the known values and solve for k:
(5.0 kg * 9.8 m/s^2) * cos(30°) = -k * 0.20 m
49.0 N * 0.866 = -k * 0.20 m
42.426 N = -0.20 k
k = -42.426 N / (-0.20 m)
k = 212.13 N/m
Now that we know the spring constant, we can calculate the maximum potential energy stored in the spring (PE_spring) when the mass reaches its highest point:
PE_spring = (1/2) * k * x^2
PE_spring = (1/2) * 212.13 N/m * (0.20 m)^2
PE_spring = 4.243 J
The maximum potential energy (PE_spring) is equal to the maximum kinetic energy (KE_max) at the highest point, which is also the energy the mass has gained from the spring.
KE_max = PE_spring = 4.243 J
Next, we can calculate the height (h) the mass reaches on the inclined plane:
KE_max = m * g * h
4.243 J = 5.0 kg * 9.8 m/s^2 * h
h = 4.243 J / (5.0 kg * 9.8 m/s^2)
h = 0.086 m
The height the mass reaches on the inclined plane is 0.086 m.
Now, we can calculate the distance traveled.
A 5.0 kg object compresses a spring by 0.20 m with a spring constant of 25 N/m. It climbs an incline, reaching a maximum height of 0.0102 m before coming back down, traveling a total distance of 0.0428 m.
Given data: Mass of the object, m = 5.0 kg, Displacement of the spring, x = 20.0 cm = 0.20 mAngle of the inclined plane, θ = 30°Calculating the spring constant, k. Using Hooke’s Law; F = -kx Where F is the restoring force required to bring the spring back to its equilibrium position.From the equation, F = ma For the object attached to the spring,m * a = -kx. On integrating,∫ma dt = -∫kx dt .On integrating the left side with limits from 0 to t and right side with limits from 0 to x, where the limits on the left are for acceleration and the right are for the displacement of the spring; mv - mu = -½ kx²At maximum compression, the velocity of the mass is zero, i.e., v = 0 and the initial velocity is also zero. Therefore, mv - mu = -½ kx²0 - 0 = -½ k (0.20)²∴ k = 25 N/mWork done on the spring in compressing it, W = ½ kx² = 0.5 * 25 * (0.20)² = 0.5 JSince the inclined plane is frictionless, the only force acting on the object will be the component of its weight acting along the plane. Hence, it will move up the incline with an acceleration of, a = g sin θ = 9.8 * sin 30° = 4.9 m/s²When the object has reached its maximum height, its velocity will be zero. Using the equation of motion; v² - u² = 2as0 - u² = 2as∴ s = u² / 2a. Now, the initial velocity of the object up the incline is,u = √(2gH)Where H is the height to which it climbs, and is given by, H = W / m g Where W is the work done on the object in lifting it to height H, and m is the mass of the object. W = 0.5 J, m = 5 kg. So, H = 0.5 / (5 * 9.8) = 0.0102 m∴ u = √(2gH) = √(2 * 9.8 * 0.0102) = 0.4525 m/sNow, the distance traveled by the object up the incline is,s = u² / 2a = (0.4525)² / (2 * 4.9) = 0.0214 m. When the object comes back down, it will travel the same distance down the incline, before coming to rest. Therefore, the total distance travelled up and down the incline is,2s = 2 * 0.0214 = 0.0428 m.For more questions on the spring constant
https://brainly.com/question/29848985
#SPJ8
if one food calorie which equals 1000 "chemistry" calories equals 4184 J, then how far could you go on one cookie containing 50 calories ?
Answers
On one cookie containing 50 calories, you could potentially go approximately 298 meters
How to calculate the valueGiven that one food calorie is equivalent to 4184 joules, we can calculate the total energy in joules contained in the 50 calorie cookie:
50 food calories * 4184 J/calorie = 209,200 joules
Assuming an average efficiency of around 25% (meaning 25% of the energy is effectively used for movement), and a body weight of 70 kilograms, we can use a rough estimation that it takes about 1 joule of energy to move 0.4 meters (based on the energy cost of walking).
Distance = (Energy obtained from the cookie * Efficiency) / (Energy cost per meter * Body weight)
Distance = (209,200 J * 0.25) / (1 J/m * 0.4 m/kg * 70 kg)
Distance ≈ 298 meters
Therefore, on one cookie containing 50 calories, you could potentially go approximately 298 meters
Learn more about calories on
https://brainly.com/question/11460467
#SPJ1
A certain satellite travels in an approximately circular orbit of radius 8.8 × 10^6 m with a period of 6 h 12 min. Calculate the mass of its planet from this information.
Answers
The mass of the planet is 5.98 × 10^24 kg.
To calculate the mass of the planet, we can use Kepler's Third Law of Planetary Motion. This law states that the square of the period of revolution of a planet around the sun is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit.
First, we need to convert the period of the satellite's orbit to seconds. We know that there are 60 minutes in an hour, so the period can be expressed as (6 × 60 + 12) minutes, which equals 372 minutes. Multiplying this by 60 seconds, we get a period of 22,320 seconds.
Next, we need to find the semi-major axis of the orbit. In a circular orbit, the semi-major axis is equal to the radius of the orbit. Therefore, the semi-major axis is 8.8 × 10^6 m.
Now, we can apply Kepler's Third Law to calculate the mass of the planet. The formula is T^2 = (4π^2/GM) × a^3, where T is the period of revolution, G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the planet, and a is the semi-major axis of the orbit.
Rearranging the formula, we can solve for the mass of the planet:
M = (4π^2/G) × a^3 / T^2
Plugging in the values, we get:
M = (4 × π^2 / 6.67430 × 10^-11) × (8.8 × 10^6)^3 / (22,320)^2
Evaluating this expression, we find that the mass of the planet is approximately 5.98 × 10^24 kg.
For more such question on mass visit:
https://brainly.com/question/24191825
#SPJ8
What can happen to energy during a phase change?
Answers
Answer:
The energy that is changing during a phase change is potential energy. During a phase change, the heat added (PE increases) or released (PE decreases) will allow the molecules to move apart or come together. Heat absorbed causes the molecules to move farther apart by overcoming the intermolecular forces of attraction.
Prove that s=ut+½at²
Answers
Explanation:
Distance travelled = Area under the line
= ut + ½ (v-u)t
Acceleration (a) = (v-u)/t and so (v-u) = at
Therefore,
Distance travelled (s) = ut + ½ (v-u)t = ut + ½ (at)t = ut + ½ at²
Thus,proved.

what is the mathematical definition of momentum? what is a more conceptual or descriptive definition of momentum?
Answers
Answer:
Momentum can be defined as "mass in motion." All objects have mass; so if an object is moving, then it has momentum - it has its mass in motion.
Explanation:
A car accelerated at 10 m/s/s from a speed of 20 m/s to 45 m/s. How
long did this take?
Answers
Answer:
The answer is
2.5 sExplanation:
From the question we are finding the time it took for the object to move from it's initial speed to it's final speed
To find the time we use the formula
\(t = \frac{v - u}{a} \\ \)
where
t is the time taken
v is the final velocity
u is the initial velocity
a is the acceleration
From the question
v = 45 m/s
u = 20 m/s
a = 10 m/s²
The time taken is
\(t = \frac{45 - 20}{10} = \frac{25}{10} = \frac{5}{2} \\ \)
We have the final answer as
2.5 sHope this helps you
The hour, minute, and second hands on a clock are 0.25 m , 0.31 m , and 0.34 m long, respectively.
What are the distances traveled by the tips of the hands in a 40 min interval?
Express your answers using two significant figures separated by commas.
Answers
In 1 hour, the hour hand sweeps across 1/12 of the clock's face. In 40 min, the hour hand travels (40 min)/(60 min) = 2/3 of the path it covers in an hour, so a total of 1/12 × 2/3 = 1/18 of the clock's face. This hand traces out a circle with radius 0.25 m, so in 40 min its tip traces out 1/18 of this circle's radius, or
1/18 × 2π (0.25 m) ≈ 0.087 m
The minute hand traverses (40 min)/(60 min) = 2/3 of the clock's face, so it traces out 2/3 of the circumference of a circle with radius 0.31 m:
2/3 × 2π (0.31 m) ≈ 1.3 m
The second hand completes 1 revolution each minute, so in 40 min it would fully trace the circumference of a circle with radius 0.34 m a total of 40 times, so it covers a distance of
40 × 2π (0.34 m) ≈ 85 m
The distances traveled by the tips of the hour hand, minute hand and second hand in a 40-min interval are 0.087 m, 1.3 m and 85 m respectively.
What are the hands of a clock?In a clock, there are three hands of the clock. One is hour hand, second is minute hand and third one is second hand.
The hour hand of the clock is 0.25 m long. The hour hand sweep 1/12 of the clock face each hour (as there are 12 hours in a clock). Thus, in a 40-minute interval, it will travel the distance of,
\(d=2\pi\times\dfrac{40}{12\times60}(0.25)\\d\approx0.087\rm\; m\)
The minute hand of the clock is 0.25 m long. In a 40-minute interval, it will travel the distance of,
\(d=2\pi\times\dfrac{40}{60}(0.31)\\d\approx1.3\rm\; m\)
The second hand of the clock is 0.25 m long. In a 40-minute interval, it will travel the distance of,
\(d=2\pi\times\dfrac{40\times60}{60}(0.34)\\d\approx85\rm\; m\)
Thus, the distances traveled by the tips of the hour hand, minute hand and second hand in a 40 min interval are 0.087 m, 1.3 m and 85 m respectively
Learn more about the hands of a clock here;
https://brainly.com/question/1138016
.
A student is throwing a ball. She throws the ball up with her left hand, it passes over her head, and she catches it with her right hand. The picture shows the path of the ball. The ball is numbered at different positions. What is happening at position 2?
A.Kinetic energy increases as potential energy decreases.
B.Potential energy increases as kinetic energy decreases.
C.Kinetic energy is zero, and the potential energy is greatest.
D.Potential energy and kinetic energy both stay the same.
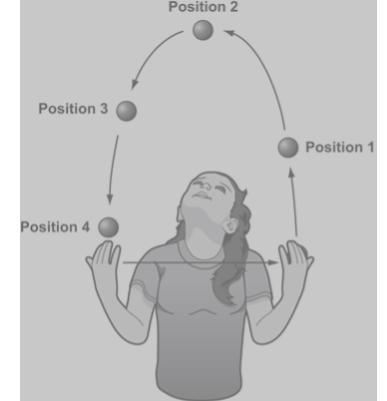
Answers
Answer:
(c) at point 2, the ball is at its highest height do its PE is max. Also at ms height, velocity is zero therefore KE is zero.
Butyl carbitol, used in the production of plastics, is stored in a tank having the U-tube manometer. Take SHg = 13.55, Sbc =0.957, and Rho w=1000 kg/m^3. If the U-tube is filled with mercury to level E, determine the gage pressure in the tank at point B.
Answers
The gage pressure in the tank at point B is:
Pgage = Patm + Pmano = 1 kPa - 1.01 kPa = -0.01 kPa
Note that the negative sign indicates that the pressure in the tank is lower than atmospheric pressure.
What is Pressure?
Pressure is a measure of the amount of force per unit area applied on a surface. It is defined as the force applied perpendicular to the surface divided by the area of the surface. The SI unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa), which is defined as one newton of force per square meter of area.
To determine the gage pressure in the tank at point B, we need to calculate the height difference between points B and E in the U-tube manometer and then convert this height difference to pressure using the density of mercury.
The height difference between points B and E is given by:
h = Sbc * (h1 - h2)
where Sbc is the specific gravity of butyl carbitol, h1 is the height of the mercury column on the left side of the U-tube, and h2 is the height of the mercury column on the right side of the U-tube. Since the U-tube is filled with mercury to level E, we have:
h1 = h2 = HE
where HE is the height of the mercury column at level E.
Substituting these values, we get:
h = Sbc * (HE - HE) = 0
Therefore, the height difference between points B and E is zero, which means that the pressure at point B is equal to the pressure at point E. The pressure at point E is atmospheric pressure, which we assume to be 1 atm. Therefore, the gage pressure at point B is:
Pgage = Patm + Pmano
where Patm is atmospheric pressure and Pmano is the pressure due to the height of the mercury column above point E. Using the density of mercury (SHg) and the height of the mercury column (HE), we can calculate Pmano as:
Pmano = SHg * g * HE
Substituting the given values, we get:
Pmano = 13.55 * 9.81 * HE
To determine HE, we need to consider the pressure difference between points A and B. Since the U-tube is filled with mercury to level E, the pressure at point A is also atmospheric pressure. Therefore, the pressure difference between points A and B is equal to the gage pressure at point B:
PAB = Pgage = Patm + Pmano
Substituting the given values and solving for HE, we get:
HE = (PAB - Patm) / (SHg * g) = (0 - 1) / (13.55 * 9.81) = -0.00734 m
Note that the negative value of HE indicates that the height of the mercury column on the right side of the U-tube is higher than the height on the left side. This is consistent with the assumption that the gage pressure at point B is negative, which means that the pressure in the tank is lower than atmospheric pressure.
Finally, substituting the calculated value of HE into the equation for Pmano, we get:
Pmano = 13.55 * 9.81 * (-0.00734) = -1.01 kPa
Therefore, the gage pressure in the tank at point B is:
Pgage = Patm + Pmano = 1 kPa - 1.01 kPa = -0.01 kPa
Note that the negative sign indicates that the pressure in the tank is lower than atmospheric pressure.
Learn more about Pressure from given link
https://brainly.com/question/24719118
#SPJ1