A force acts on a 9.90 kg mobile object that moves from an initial position of to a final position of in 5.40 s. Find (a) the work done on the object by the force in the 5.40 s interval, (b) the average power due to the force during that interval, and (c) the angle between vectors and .
Answers
Given that,
Mass of object = 9.90 kg
Time =5.40 s
Suppose the force is (2.00i + 9.00j + 5.30k) N, initial position is (2.70i - 2.90j + 5.50k) m and final position is (-4.10i + 3.30j + 5.40k) m.
We need to calculate the displacement
Using formula of displacement
\(s=r_{2}-r_{1}\)
Where, \(r_{1}\) = initial position
\(r_{2}\) = final position
Put the value into the formula
\(s= (-4.10i + 3.30j + 5.40k)-(2.70i - 2.90j + 5.50k)\)
\(s= -6.80i+6.20j-0.1k\)
(a). We need to calculate the work done on the object
Using formula of work done
\(W=F\cdot s\)
Put the value into the formula
\(W=(2.00i + 9.00j + 5.30k)\cdot (-6.80i+6.20j-0.1k)\)
\(W=-13.6+55.8-0.53\)
\(W=41.67\ J\)
(b). We need to calculate the average power due to the force during that interval
Using formula of power
\(P=\dfrac{W}{t}\)
Where, P = power
W = work
t = time
Put the value into the formula
\(P=\dfrac{41.67}{5.40}\)
\(P=7.71\ Watt\)
(c). We need to calculate the angle between vectors
Using formula of angle
\(\theta=\cos^{-1}(\dfrac{r_{1}r_{2}}{|r_{1}||r_{2}|})\)
Put the value into the formula
\(\theta=\cos^{-1}\dfrac{(-4.10i + 3.30j + 5.40k)\cdot(2.70i - 2.90j + 5.50k)}{7.54\times6.778})\)
\(\theta=79.7^{\circ}\)
Hence, (a). The work done on the object by the force in the 5.40 s interval is 41.67 J.
(b). The average power due to the force during that interval is 7.71 Watt.
(c). The angle between vectors is 79.7°
Related Questions
A golfer hits a shot to a green that is elevated 2.80 m above the point where the ball is struck. The ball leaves the club at a speed of 18.7 m/s at an angle of 49.0˚ above the horizontal. It rises to its maximum height and then falls down to the green. Ignoring air resistance, find the speed of the ball just before it lands.
Answers
Answer:
32.812m/s
Explanation:
Now the time of the projectile motion is given by;
t = usinA/ g
Where A is angle =49°
u is initial velocity,u = 18.7m/s
Hence t = 18.7 ×sin49°/ 9.8 = 1.44s
The final velocity from Newton's law V = U + gt
= 18.7 + (9.8 ×1.44)= 32.812m/s
Use the graph to answer the following questions.

Answers
Answer:
8a = 20. 8b=4
Explanation:
Distance is total amount the object moved. It went from 10, to -2 which is 12 meters away, then to 6 which is 8, adding 8 and 12 is 20 so that is the distance. Displacement is how far it is relative to the starting position, so 10 and 6 are 4 meters away, therefore displacement is 4.
Hope I helped : )
13.
14. Why does a person feel weightlessness during freefall?
Answers
Answer:
When in free fall, the only force acting upon your body is the force of gravity - a non-contact force. Since the force of gravity cannot be felt without any other opposing forces, you would have no sensation of it. You would feel weightless when in a state of free fall.
1.1. Nitrogen gas is an example of al an... A. element B. compound C. heterogeneous mixture D. homogeneous mixture
Answers
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The answer to this is B because nitrogen gas is N2 and they are chemically bonded not simply mixed.
You attach a speaker to an air track cart and then attach the cart to one end of the air track by means of a spring and start the system oscillating by stretching the spring 0.797 m from its equilibrium position and then releasing it. The force constant for the spring is k = 49.8 N/m, the total mass of the speaker and air track cart are 4.00 kg, and the speaker emits sound with a frequency of 405 Hz. If your lab partner Hal stands at the end of the air track, determine the highest and lowest frequencies he hears. The speed of sound in air is 343 m/s. (Enter answers to at least the nearest Hz.)
Lowest Frequency =
Highest Freqency =
Answers
The lowest possible frequency at which a string could vibrate to form a standing wave pattern is known as the fundamental frequency or the first harmonic. The second lowest frequency at which a string could vibrate is known as the second harmonic; the third lowest frequency is known as the third harmonic; and so on.
“HIGHEST FREQUENCY”Gamma rays have the highest energies, the shortest wavelengths, and the highest frequencies. Radio waves, on the other hand, have the lowest energies, longest wavelengths, and lowest frequencies of any type of EM radiation.
Fern life begins as _____.
a spore
a sperm
an egg
Answers
Which best explains a difference between Einstein’s general theory of relativity and his special theory of relativity?
His general theory includes uniform and accelerated motion, but his special theory applies only to uniform motion.
His general theory includes uniform and accelerated motion, but his special theory applies only to accelerated motion.
His general theory applies only to accelerated motion, but his special theory includes uniform and accelerated motion.
His general theory applies only to uniform motion, but his special theory includes uniform and accelerated motion.
Answers
Answer:
His general theory includes uniform and accelerated motion, but his special theory applies only to uniform motion.
Explanation:
According to Einstein's 1915 general theory of relativity, the force of gravity arises from the curvature of space and time.
According to theory of special relativity:
1. The laws of physics are the same for all non-accelerating observers
2. The speed of light in a vacuum was independent of the motion of all observers.
His general theory includes uniform and accelerated motion, but his special theory applies only to uniform motion.
Answer:
for those who dont like to read
the answer is A.
hope i helped
Explanation:
The first law of thermodynamics leads us to conclude that
A. disorder in the universe is increasing with the passage of time.
B. the total energy in the universe is decreasing with time.
C. it is theoretically impossible to convert work into heat with 100% efficiency
D. the total energy of the universe is constant.
E. the total energy in the universe is increasing with time.
Answers
Answer:
D
Explanation:
D - The total energy in the universe is constant
The first law of thermodynamics states that heat is also another form of energy, and that thermodynamic processes are as a result, subjected to the principle of conservation of energy. The principle of conservation of energy is another way of boldly saying that heat energy cannot be created and neither can heat energy be destroyed.
I hope that's clear enough
Calculate the solar angle for the day at 10am and 2pm individually for the location of 21.23 south latitude on the 18th march 1993 (Assume it is non leap year)
Answers
Based on the latitude and time of the place, the solar angle for the day at 10am and 2pm is 51.6° and 73.0°.
What is the solar hour angle?The solar hour angle of a point on the earth’s surface is the angle through which the earth would turn to bring the meridian of the point directly under the sun.
The rotation of the earth on its axis is 15° per hour where before noon is negative and after noon is positive. For example, at 10:00 a.m. local apparent time the hour angle is −30°.
Therefore, based on the latitude and time, the solar angle for the day at 10am and 2pm is 51.6° and 73.0°.
Learn more about solar angle at: https://brainly.com/question/6336054
What is the velocity of a dropped object after it has fallen for 12 s?
Answers
Hellow!
For this use the next formula:
Vf = Vo + gt
Initial velocity is zero, so the formula simplificate:
Vf = gt
Data:
Vf = Final velocity = ?
g = Gravity = 9.8 m/s²
t = Time = 12 s
Replacing according our data:
Vf = 9.8 m/s² * 12 s
Vf = 117.8 m/s
The final velocity will be 117.8 meters per second.
What type of circuit is in the diagram?
b
O series circuit
O parallel circuit
PLEASE HELPPP

Answers
a 2kg aluminum block and a6kg copper block are connected by alight string over a frictionless pulley and fixed steel block of angle 30 degree .if the coefficient of friction on the surface is 0.2,find the acceleration of the two block and the tension in the string?
Answers
(a) The acceleration of the two block is determined as 0.93 m/s².
(b) The tension in the string is 5.78 N.
Net force on the aluminum block
The net force on the aluminum block is calculated as follows;
\(T - \mu_a m_a g = m_a a \ --- \ (1)\)
Net force on the copper blockThe net force on the copper block is calculated as follows;
\(m_cg sin(30) - T -\mu _cm_c gcos(30) = m_c a --- (2)\)
where;
T is tension in the stringma is mass of aluminummc is mass of copperg is acceleration due to gravitySolve for T using (1) and (2)
\(a = g(\frac{m_c sin30\ - \ \mu _c m_c cos30 \ - \mu_ a m_a}{ma_a + m_c} )\\\\a = 9.8(\frac{6 sin30\ - \ 0.2 (6) cos30 \ - 0.2 (6)}{2 +6} )\\\\a = 0.93 \ m/s^2\)
Tension in the stringFrom equation (1);
T = μm_ag + m_aa
T = 0.2(2)(9.8) + 2(0.93)
T = 5.78 N
Learn more about tension here: https://brainly.com/question/918617
#SPJ1
In the lab, you learned how the ocular reticle is calibrated: you compare one scale against another one. For example: for 4 ocular spaces, there were 10 stage spaces. Now, let's apply the same concept to comparing two other scales: Celsius and Fahrenheit. Water freezes at 0C = 32F, and it boils at 100C = 212F. Therefore, in one scale, there is a variation of 100 points, while in the other, the variation is 180 points. Use this information to calculate: how many degrees Fahrenheit increase if the temperature increased from 20C to 21C?
Answers
The temperature would rise by 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit if it went from 20 to 21 degrees Celsius.
What is the rise in temperature, expressed in Fahrenheit?Since 1880, the Earth's temperature has increased by an average of 0.14° F (0.08° C) per decade, or nearly 2° F overall. Since 1981, the pace of warming has increased more than double, to 0.32° F (0.18° C) every decade.
When up, does Fahrenheit grow colder?To assist us remember that as we move up the scale, we go from colder to hotter, let's label our thermometer. In other terms, a higher number of Fahrenheit degrees is hotter than a lower number of Fahrenheit degrees.
To know more about Fahrenheit visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/30285159
#SPJ4
A horse slows from a velocity of 9.5 m/s to 5.5 m/s over a distance of 32 m. Find time.
Answers
Answer:
8
Explanation:
Finding time= t=change in velocity or distance/acceleration
so 32/9.5-5.5
32/4
8
(d) Suppose you use a spring to launch a payload horizontally from the asteroid so that the payload ends up far from the asteroid, travelling at a speed of 3 m/s. The payload has a mass of 29 kg. If the spring is to be compressed initially an amount of 1.4 m, what stiffness ks must the spring be designed to have
Answers
Answer:
ks= 133.2 N/m
Explanation:
Assuming that we can neglect the gravitational potential energy of the mass, and that no other forces acting on the payload, total mechanical energy must be conserved.This energy, at any time, is part elastic potential energy (stored in the spring) and part kinetic energy.When the spring is initially compressed, the payload is at rest, so all energy is elastic potential.Once the spring has returned to its natural state, all this elastic potential energy must have been turned into kinetic energy.If the payload is launched horizontally, and no gravity is present,this means that its final speed will be horizontal only also, according to Newton's First Law.So, we can write the following equation:\(\Delta U + \Delta K = 0 (1)\)
where ΔU = -1/2*k*(Δx)² (2)and ΔK = 1/2*m*v² (3)Replacing in (2) and (3) by the givens, and simplifying, we can find the stiffness ks as follows:\(k_{s} =\frac{m*v^{2}}{\Delta x^{2}} = \frac{29 kg*(3m/s)^{2}}{(1.4m)^{2}} = 133.2 N/M (4)\)
In the figure, a small spherical insulator of mass 6.00 x 10^-2 kg and charge +0.400 uC is hung by a thin wire of negligible mass. A charge of -0.220 uC is held 0.290 m away from the sphere and directly to the right of it, so the wire makes an angle with the vertical, as shown. What is the angle?

Answers
This angle is negative, which means that the wire is bent to the left instead of to the right, as shown in the diagram.
StepsThe electrostatic force on the charged insulator is given by Coulomb's law as:
F_electric = k * (q1 * q2) / r²
where k is the Coulomb constant (9 x 10⁹ N*m²/C²), q1 and q2 are the charges of the two objects, and r is the distance between them.
In this case, q1 = 0.400 uC and q2 = -0.220 uC. The distance between them is given as 0.290 m.
F_electric = (9 x 10⁹) * (0.400 x 10⁻⁶) * (-0.220 x 10⁻⁶) / (0.290)²
F_electric = -1.19 x 10⁻⁵ N
Since the insulator is in equilibrium, the electrostatic force must be balanced by the tension in the wire.
Let T be the tension in the wire, and θ be the angle that the wire makes with the vertical.
The horizontal component of the tension in the wire is given by T * sin(θ), and the vertical component is given by T * cos(θ).
Since the insulator is in equilibrium, the sum of the forces in the vertical direction must be zero:
T * cos(θ) - m * g = 0
where m is the mass of the insulator (6.00 x 10⁻² kg), and g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s²).
Solving for T, we get:
T = m * g / cos(θ)
The sum of the forces in the horizontal direction must also be zero:
T * sin(θ) = F_electric
Substituting T and F_electric from the above equations, we get:
(m * g / cos(θ)) * sin(θ) = -1.19 x 10⁻⁵
Simplifying, we get:
tan(θ) = -1.19 x 10⁻⁵ / (m * g)
Substituting the given values, we get:
tan(θ) = -1.19 x 10⁻⁵ / (6.00 x 10⁻² kg * 9.8 m/s²)
tan(θ) = -2.06 x 10⁻⁵
Taking the inverse tangent, we get:
θ = -0.00118 degrees
However, this angle is negative, which means that the wire is bent to the left instead of to the right, as shown in the diagram.
learn more about mass here
https://brainly.com/question/19385703
#SPJ1
3. What is the acceleration of a 50 g object pushed with a force of 0.5 N
Answers
The acceleration of a 50 g object pushed with a force of 0.5 N is 10 m/s².
To find the acceleration of the object, we can use Newton's second law of motion, which states that the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration:
F = m * a
Given:
Force (F) = 0.5 N
Mass (m) = 50 g = 0.05 kg
Substituting the given values into the equation, we have:
0.5 N = 0.05 kg * a
To find the acceleration (a), we rearrange the equation:
a = F / m
a = 0.5 N / 0.05 kg
a = 10 N/kg
Since acceleration is measured in meters per second squared (m/s²), we convert the unit of N/kg to m/s²:
1 N/kg = 1 m/s²
Therefore, the acceleration of the 50 g object pushed with a force of 0.5 N is 10 m/s².
For more such questions on acceleration, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/30595126
#SPJ8
A car is uniformly accelerated at a rate of 2 m/sec2 for 12 sec. If the original speed of the car is 36 m/sec, what is its final speed?
Answers
Answer:
60m/s
Explanation:
v=u+at
v=36+(2×12)
v=36+24
v=60m/s
How much impulse is imparted on a 0.14 kg baseball initially traveling at 32 m/s when it is struck by a baseball bat and begins to travel in the opposite direction at 49 m/s
Answers
ANSWER AND EXPLAINATION:
To calculate the impulse imparted on the baseball, we can use the impulse-momentum principle, which states that the impulse experienced by an object is equal to the change in momentum of the object. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
Impulse = Change in momentum
The momentum of an object is given by the product of its mass and velocity:
Momentum = mass × velocity
In this case, the baseball has an initial mass of 0.14 kg and an initial velocity of 32 m/s. After being struck by the bat, it travels in the opposite direction at a velocity of 49 m/s.
Therefore, the change in momentum is given by:
Change in momentum = (mass × final velocity) - (mass × initial velocity)
Change in momentum = mass × (final velocity - initial velocity)
Change in momentum = 0.14 kg × (49 m/s - (-32 m/s))
Change in momentum = 0.14 kg × (49 m/s + 32 m/s)
Change in momentum = 0.14 kg × 81 m/s
Change in momentum = 11.34 kg·m/s
So, the impulse imparted on the baseball is 11.34 kg·m/s.
A cyclist and his bicycle have a combined mass of 88 kg and a combined
weight of 862.4 N. The cyclist accelerates at 1.2 m/s2. After 2 seconds he
reaches a speed of 2.4 m/s. What is his momentum at this point?
A. 36.7 kg m/s
B. 359.3 kg:m/s
C. 105.6 kg-m/s
D. 211.2 kg:m/s
Answers
The cyclist accelerates at 1.2 m / s² after 2 seconds he reaches a speed of 2.4 m / s, then the momentum at this point would be 211.2 kg-m/s, therefore the correct answer is option D.
What is momentum?It can be defined as the product of the mass and the speed of the particle, it represents the combined effect of mass and the speed of any particle, and the momentum of any particle is expressed in Kg m/s unit.
As given in the problem a cyclist and his bicycle has a combined mass of 88 kg and a combined weight of 862.4 N. The cyclist accelerates at 1.2 m/s2. After 2 seconds he reaches a speed of 2.4 m/s.
The momentum of the cyclist = 88 × 2.4
= 211.0 kgm/s
Thus, the momentum of the cyclist would be 211.0 kgm/s.
To learn more about momentum from here, refer to the link given below;
brainly.com/question/17662202
#SPJ2
Shawn and his bike have a total mass of 40.6 kg. Shawn rides his bike 2 km in 14.5 min at a constant velocity. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s^2.
What is Shawn’s kinetic energy?
Answer in units of J.
Answers
Shawn’s kinetic energy is 147.73 J if Shawn rides his bike 2 km in 14.5 min at a constant velocity.
What are some examples of kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy, which can be seen in the movement of an object, particle, or cluster of particles, is the energy of motion. Any moving object uses kinetic energy.
where m is the object's mass ( total mass of bike and Shawn in this case)
v = the object's velocity
First, let's calculate Shawn's speed in SI units.
Speed is calculated as distance traveled divided by time.
Displacement is equal to 2.1 km, 2.1 1000 m, or 2100 m.
Time = 13.9 minutes = 13.9 x 60 seconds = 834 seconds
2100 m/834 s x 2.52 m/s is the velocity.
Therefore, Kinetic Energy in motion 147.73 J.
Learn more about kinetic energy from the given link.
https://brainly.com/question/26472013
#SPJ1
How are volume and decibels related
Answers
Answer:
The more energy a sound has the louder we perceive it
Explanation:
To measure volume we use the unit of decibels – abbreviated to dB. The lowest perceivable volume, meaning the quietest sound humans can hear, is 0 decibels. ... Thus, 60 dB are perceived as twice as loud as 50 dB
Answer:
To measure volume we use the unit of decibels – abbreviated to dB.
Explanation:
We measure volume in sound pressure level. The unit of measurement is called decibels. ... The more energy a sound has the louder it seems to be.
A motorcycle stoop is at a traffic light, when the light turns green, the motorcycle accelerates to a speed of 78 km/h over a distance of 50 m. What is the average acceleration of the motorcycle over this distance?
Answers
The average acceleration of the motorcycle over the given distance is approximately 9.39 m/s².
To calculate the average acceleration of the motorcycle, we can use the formula:
Average acceleration = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time
First, let's convert the final velocity from km/h to m/s since the distance is given in meters. We know that 1 km/h is equal to 0.2778 m/s.
Converting the final velocity:
Final velocity = 78 km/h * 0.2778 m/s = 21.67 m/s
Since the motorcycle starts from rest (initial velocity is zero), the formula becomes:
Average acceleration = (21.67 m/s - 0 m/s) / time
To find the time taken to reach this velocity, we need to use the formula for average speed:
Average speed = total distance/time
Rearranging the formula:
time = total distance / average speed
Plugging in the values:
time = 50 m / 21.67 m/s ≈ 2.31 seconds
Now we can calculate the average acceleration:
Average acceleration = (21.67 m/s - 0 m/s) / 2.31 s ≈ 9.39 m/s²
To learn more about acceleration
https://brainly.com/question/2303856
#SPJ8
is power and voltage the same thing yes or no
Answers
PLS HELP!! I’LL GIVE 25 POINTS TO WHOEVER ANSWERS
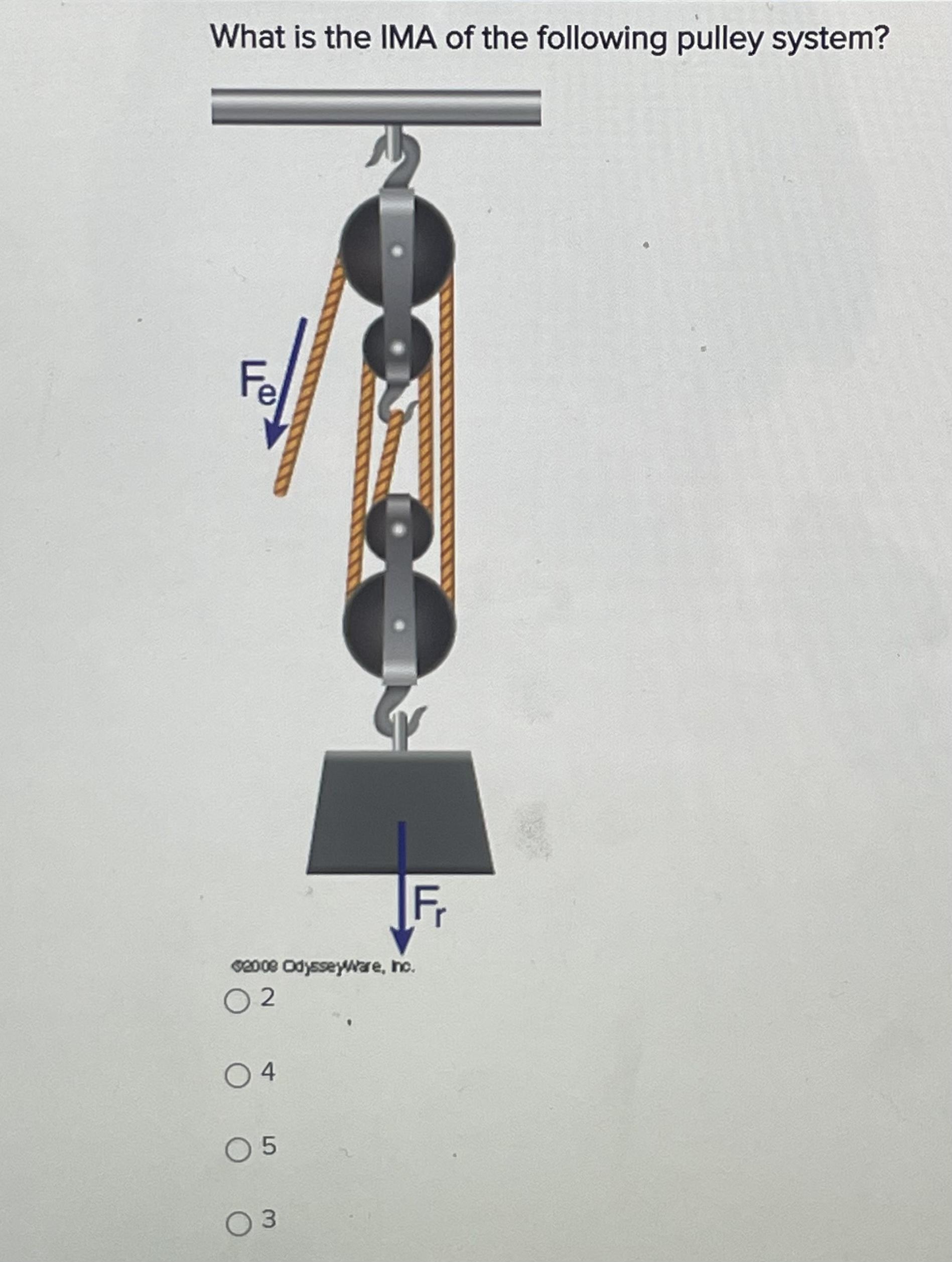
Answers
IMA of the pulley system is 3.
The length of the effort arm of a lever divided by the length of the resistance arm represents the ideal mechanical advantage, IMA.
IMA = Resistance force/Effort force
IMA = Fr/Fe
Calculating IMA involves measuring the number of ropes present in the pulley system.
Therefore, IMA = 3
To learn more about IMA, click:
https://brainly.com/question/14745827
#SPJ1
If I tell you that you have a right triangle with one leg having length a and another leg having length b , if we
call the hypotenuse c, express the length of c in terms of legs a and b.
Answers
C is found using the Pythagorean theorem:
C = sqrt(a^2 + b^2)
Okay, so I was searching the Internet and I happened to come across that keeping bird feathers are illegal. (fyi I took feathers a lot of times when I was younger especially eagle feathers) . why
Answers
A machine has a velocity ratio of 5 and the efficiency is 80% what effort would be needed to lift a load of 200N
Answers
Explanation:
To determine the effort needed to lift a load of 200N, given a velocity ratio of 5 and an efficiency of 80%, we can use the formula:
Efficiency = (Output Work / Input Work) * 100
Efficiency can also be calculated as the ratio of the output force to the input force. In this case, the output force is the load being lifted (200N), and the input force is the effort required.
Given that the velocity ratio is 5, it means that for every 5 units of distance the effort moves, the load moves 1 unit of distance. This implies that the effort is exerted over a greater distance than the load.
Let's denote the effort force as "E" and the distance moved by the effort as "dE." Similarly, the load force is "L," and the distance moved by the load is "dL."
Using the velocity ratio, we have the following relationship:
dE / dL = 5
Now, we can calculate the input work (Wi) and the output work (Wo):
Input Work (Wi) = Effort (E) * Distance moved by the effort (dE)
Output Work (Wo) = Load (L) * Distance moved by the load (dL)
Given that the efficiency is 80%, we can rewrite the formula for efficiency as:
0.80 = (Wo / Wi) * 100
Now, let's solve for the effort (E) using the given values:
Load (L) = 200N
Efficiency = 0.80
Velocity Ratio = 5
First, calculate the output work (Wo):
Wo = Load (L) * Distance moved by the load (dL)
Since the velocity ratio is 5, the distance moved by the load (dL) will be 1/5 of the distance moved by the effort (dE):
dL = (1/5) * dE
Wo = L * (1/5) * dE
Wo = 200N * (1/5) * dE
Wo = 40N * dE
Next, calculate the input work (Wi):
Wi = Effort (E) * Distance moved by the effort (dE)
Wi = E * dE
Now, substitute the values into the efficiency formula:
0.80 = (Wo / Wi) * 100
0.80 = (40N * dE) / (E * dE) * 100
0.80 = 40 / E * 100
0.80 * E = 40
E = 40 / 0.80
E = 50N
Therefore, the effort needed to lift a load of 200N with a velocity ratio of 5 and an efficiency of 80% is 50N.
Which of the following is not an example of velocity?
O 12.5 m/s up
O 13 m/s to the left
O 0 m/s north
O50 m/s
Answers
Answer:
answer is 50m/s because velocity requires a quantity and a direction (vector quantity)
What happens to plankton during the spring bloom?Which organisms are consumers? (Select all that apply.) coyote, snail ,green algae, or bacteria
Answers
Answer:
See explanation
Explanation:
Plankton refers to the small and microscopic organisms drifting or floating in the sea or fresh water, consisting chiefly of diatoms, protozoans, small crustaceans, and the eggs and larval stages of larger animals(Oxford dictionary).
The spring bloom is a sudden growth or increase in plankton abundance. It begins around the early spring and continues until late in the spring or sometimes even early in the summer.
One organism that is a consumer of plankton are the snails. One of the commonest snails that eat plankton are the Nerite Snails.