2. What is the approximate wind speed in a tornado? Explain why tornado wind speeds are not considered in determining the design wind speed for a location.
Answers
The approximate wind speed in a tornado can reach up to 300 miles per hour (480 km/h). This wind speed is capable of causing serious damage to structures and properties in its path. This is the reason why tornadoes are considered to be one of the most dangerous weather phenomena on earth.
Tornadoes occur when warm and humid air meets with a cold front, creating instability in the atmosphere. This instability leads to the formation of a rotating column of air, which can then form a funnel-shaped cloud that descends towards the ground. As the cloud gets closer to the ground, it can cause destruction due to its high wind speed.
while tornado wind speeds can reach up to 300 miles per hour, they are not considered in determining the design wind speed for a location due to their rarity and unpredictability. Instead, designers use the design wind speed, which is based on more common weather conditions, to ensure that structures are built to withstand wind loads.
To know more about determining visit:
https://brainly.com/question/13485021
#SPJ11
Related Questions
i will give u brainliest!

Answers
Answer:
I think its false
Explanation:
It doesn't make sense that the doctor found it in her stool
BRAINLIEST! BRAINLIEST! BRAINLIEST! BRAINLIEST!
Please help me out with this!!
You and a friend are on a road trip with different friends traveling from El Paso to
San Antonio but going in different cars in order to fit all your friends. You are able
to travel 250 miles in 2.5 hours while your friend is barely able to get through 200
miles in the same time frame. Which car is going faster? (Response should be all
lower case letters: you or friend)
Answers
Answer:
the car you are in the cars have the same time frame and one covers more ground so on a possition time graph the slope will be greater
You want to have a subject exercise at 125 Watts with an RPM of
60 for 3 minutes. What resistance (in SI units) do you set the
cycle ergometer to (include your units
Answers
To determine the resistance in SI units that you need to set the cycle ergometer to, given that you want to have a subject exercise at 125 watts with an RPM of 60 for 3 minutes, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Determine the energy used in Joules during the 3 minutes at 125 watts.
P = W / tWhere:
P = power (125 watts)t = time (3 minutes converted to seconds
= 3 × 60 = 180 seconds)
W = energy used in Joules (to be determined)
Substituting the given values:
P = W / t125
= W / 180W
= 125 × 180W
= 22,500 Joules
Step 2: Determine the work done (in Joules) per revolution (360 degrees).
Work done per revolution = energy used in Joules / number of revolutions per minute / 60
Where:number of revolutions per minute = RPM / 60
Substituting the given values:
Work done per revolution = 22,500 / (60 / 60) / 360
Work done per revolution = 22,500 / 1 / 360
Work done per revolution = 22,500 × 360
Work done per revolution = 8,100,000 Joules
Step 3: Determine the torque needed to perform one revolution (360 degrees) of the pedals in SI units (N-m).Torque = work done per revolution / (2 × π)
Where:
2 × π = 6.2832
Substituting the given values:Torque = 8,100,000 / 6.2832
Torque = 1,288,684.08 N-m
Step 4:
Determine the resistance (force) needed at the pedals in Newtons (N) to produce the required torque.Resistance = Torque / pedal radius
Where:pedal radius = 0.175 m (average for a cycle ergometer)
Substituting the given values:
Resistance = 1,288,684.08 / 0.175
Resistance = 7,358,971.89 N (Newtons)
Therefore, you would need to set the resistance to 7,358,971.89 N (Newtons) on the cycle ergometer to achieve the desired subject exercise at 125 Watts with an RPM of 60 for 3 minutes.
To know more about ,resistance visit;
https://brainly.com/question/17563681
#SPJ11
What main factor determines the stages a star will follow after the main sequence?.
Answers
The main factor that determines the stages of a star after the main sequence is the star mass. Depending on the mass, stars will develop as average stars -low mass- or giant stars -high mass-.
How does the star evolution -star cycle- occur?
The star cycle is the sequence of changes that a star undergoes throughout its existence
Stars are born from the nebula, which is dust and gas particles condensation due to the gravity effect in the interstellar clouds.
These stellar clouds collapse and compose smaller regions, each of which later contracts and compose the stellar cores. This is a more advanced level of condensation.
Stelar cores are protostars that contract and increase their temperature until nuclear reactions occur. Hydrogen is converted into Helium and the new star gets born.
This new star is in its main sequence, which is the equilibrium point between gravity and nuclear fusion, which helps the star keeps stable as long as the fuel lasts.
Stars spend most of their lives in the main sequence until all hydrogen turns into helium and there is no more fuel left.
At this point, the star is a subgiant, and its core begins its contraction, increasing the star's temperature.
The star increases in size and luminosity, turning into a giant.
After the subgiant stage, the star enters a giant phase. The star can reach a size up to 100 times its current size.
When the core reaches a certain temperature, helium turns into carbon.
The following events depend on the star mass.
Star < 8 solar masses ⇒ the star turns into a white dwarf
When average-sized stars run out of fuel, the red giant begins to disintegrate, losing its outer layers and exposing its core, which will become a white dwarf.
Star > 8 solar masses ⇒ the star turns into a supernova/neutron star.
When fuel is over in the star, the gravitational collapse produces an explosion originating the supernova.
This neutron star is a celestial body that remains as a remnant after the explosion giving rise to a supernova.
In these cases, if the star core has a mass > 3 solar masses, the star collapses into a black hole.
In conclusion, the main factor that determines the stages a star follows after the main sequence is the star mass. Depending on the mass, stars will develop as average stars -low mass- or giant stars -high mass-.
You will learn more about stars cycle at
https://brainly.com/question/1511066
https://brainly.com/question/2386481
#SPJ1
show answer no attempt 50% part (b) how much energy is lost to friction if the motorcycle only gains an altitude of 21 m before coming to rest?
Answers
From the information provided, the energy lost to friction if the motorcycle only gains an altitude of 21 m before coming to rest is approximately 65,954.64 J.
To calculate the energy lost to friction, we need to first determine the initial total mechanical energy of the motorcycle and the final total mechanical energy of the motorcycle after it has climbed to a height of 21 meters and come to rest. The difference between the initial and final energies will give us the energy lost to friction.
The initial total mechanical energy of the motorcycle is given by:
Ei = (1/2)mv² + mgh + 2(1/2)Iw²
where m is the mass of the motorcycle, v is its initial speed, h is the height it climbs, g is the acceleration due to gravity, I is the moment of inertia of the wheels, and w is their initial angular velocity.
We need to calculate the moment of inertia of each wheel:
I = (1/2)mr²
where m is the mass of the wheel and r is its radius. Substituting the given values, we get:
I = (1/2)(12 kg)(0.33 m)² = 0.6534 kg m²
The initial angular velocity of each wheel is not given, so we can assume that it is initially at rest (i.e., w = 0).
Substituting the given values into the equation for E, we get:
Ei = (1/2)(180 kg)(25 m/s)² + (180 kg)(9.81 m/s²)(36 m) + 2(1/2)(0.6534 kg m²)(0)²
= 101,812.44 J
The final total mechanical energy of the motorcycle is given by:
Ef = mgh
where m, g, and h are as before, and the speed and rotational energy of the wheels are both zero.
Substituting the given values, we get:
Ef = (180 kg)(9.81 m/s²)(21 m) = 35,857.8 J
The energy lost to friction is the difference between the initial and final energies:
Energy lost = Ei - Ef = 101,812.44 J - 35,857.8 J = 65,954.64 J
Question - Suppose a 180 kg motorcycle is heading toward a hill at aspeed of 25 m/s. The two wheels weigh 12 kg each and are each annular rings with an inner radius of 0.280 m and an outer radius of 0.330 m. Randomized Variables m 180 kg ˇ-25 m/s h 36 m. how much energy is lost to friction if the motorcycle only gains an altitude of 21 m before coming to rest?
Learn more about energy here: brainly.com/question/25959744
#SPJ4
Suppose that you push on a heavy desk, but it does not move. What force opposes your push? How do you know that the opposing force balances the focus that you excerpt? (section 3 friction a force that opposes motion standard standards)
Answers
Answer:
friction doesn't let the desk move.
Explanation:
the law of motion states any object in motion should stay in motion.
What was the rate of reaction in trial 3? select the closest answer. A. 9. 55×10−6 m⋅s−1 b. 4. 86×10−6 m⋅s−1 c. 7. 33×10−6 m⋅s−1 d. 6. 58×10−6 m⋅s−1
Answers
Unfortunately, the information about trial 3 and the rate of reaction is missing in the given question. Without specific data or context,
The given question asks for the rate of reaction in trial 3 but does not provide the necessary information to calculate it. In order to determine the rate of reaction, specific data such as the change in concentration or the time taken for the reaction needs to be provided. Without this information, it is not possible to accurately determine the rate of reaction. The rate of reaction is a measure of how quickly reactants are converted into products and is influenced by factors such as temperature, concentration, and the presence of catalysts. Therefore, without the relevant data for trial 3, it is not possible to calculate or provide an answer regarding the rate of reaction in that specific trial.
Learn more about specific here;
https://brainly.com/question/5135413
#SPJ11
Consider the simple model of the zoom lens shown in Fig.34.43a in the textbook. The converging lens has focal length f1=12cm, and the diverging lens has focal length f2=−12cm. The lenses are separated by 4 cm as shown in Fig.34.43a. A)Now consider the model of the zoom lens shown in Fig.34.43b, in which the lenses are separated by 8 cm. For a distant object, where is the image of the converging lens shown in Fig.34.43b, in which the lenses are separated by 8 cm? B)The image of the converging lens serves as the object for the diverging lens. What is the object distance for the diverging lens? C)Where is the final image?
Answers
In the given setup, the image of the converging lens is formed 12 cm behind it, and the final image is formed 144/13 cm behind the diverging lens.
A) In the model shown in Fig.34.43b, where the lenses are separated by 8 cm, the image of the converging lens (f1=12 cm) is formed at a distance behind the converging lens. This distance can be determined using the lens formula:
1/f1 = 1/v1 - 1/u1,
where f1 is the focal length of the converging lens and u1 is the object distance.
Since the object is assumed to be at infinity (distant object), the object distance u1 is equal to infinity. Plugging these values into the lens formula, we get:
1/f1 = 1/v1 - 1/infinity.
As 1/infinity approaches zero, the equation simplifies to:
1/f1 = 1/v1.
Rearranging the equation, we find:
v1 = f1 = 12 cm.
Therefore, the image of the converging lens is formed at a distance of 12 cm behind the lens.
B) The image formed by the converging lens (v1 = 12 cm) serves as the object for the diverging lens. The object distance for the diverging lens (f2 = -12 cm) is equal to the image distance of the converging lens, which is 12 cm.
C) To determine the position of the final image, we can use the lens formula for the diverging lens:
1/f2 = 1/v2 - 1/u2,
where f2 is the focal length of the diverging lens and u2 is the object distance.
Substituting the given values, we have:
1/-12 = 1/v2 - 1/12.
Simplifying the equation, we find:
-1/12 = 1/v2 - 1/12.
Combining the fractions, we get:
-1/12 = (12 - v2) / (12v2).
Cross-multiplying and rearranging the equation, we find:
v2 = 144/13 cm.
Therefore, the final image is formed at a distance of 144/13 cm behind the diverging lens.
To learn more about converging lens from the given link
https://brainly.com/question/15123066
#SPJ4
A 90 kilogram diver jumped from a cliff. If it takes 2.26 seconds for the diver to hit the water, how high is the cliff?
Answers
Answer:
3.27 meters
Explanation:
mark brainliest please
The height of the cliff will be 25.05 m. The height of the cliff is obtained by the Newton equation of motion.
What is height?The vertical distance between the object's top and bottom is defined as height. It is measured in centimeters, inches, meters, and other units.
The given data in the problem is;
Mass of diver(m)=90 kilogram
Time period(t)=2.26 sec
Initial velocity (u)=0 m/sec
The height attained by the cliff is;
\(\rm H = ut + \frac{1}{2}gt^2 \\\\ H=\frac{1}{2}gt^2\\\\ H= \frac{1}{2}(9.81)(2.26)^2\\\\ H= \frac{1}{2} \times 9.81 \times 5.1076 \\\\ H=25.05 \ m\)
Hence, the height of the cliff will be 25.05 m.
To learn more about the height, refer to the link;
https://brainly.com/question/10726356
#SPJ2
A 19.7 kg sled is pulled with a 42.0 N force at a 43.0° angle, across ground where μ₁ = 0.130.
What is the normal force on the sled?
Answers
The following information is provided in the problem: A sled with a weight of 19.7 kg is pulled with a force of 42.0 N at an angle of 43.0° across ground where μ₁ = 0.130. We need to find out the normal force that is exerted on the sled.
Let us examine each of the forces acting on the sled.The weight of the sled is equal to its mass multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity. Therefore, the weight of the sled is:mg = 19.7 kg x 9.8 m/s² = 193.06 N.The force exerted on the sled can be divided into two components: one that is parallel to the ground and one that is perpendicular to the ground.The force parallel to the ground is:F₁ = 42.0 N x cos(43.0°) = 30.56 N.The force perpendicular to the ground is:F₂ = 42.0 N x sin(43.0°) = 28.30 N.The frictional force is equal to the coefficient of friction multiplied by the normal force. Therefore, we need to find the normal force on the sled in order to calculate the frictional force. Since the sled is not accelerating vertically, the normal force is equal to the weight of the sled plus the force perpendicular to the ground. Therefore, N = mg + F₂N = 193.06 N + 28.30 N = 221.36 N.The frictional force is:Fr = μ₁ x NFr = 0.130 x 221.36 N = 28.77 N.Thus, the normal force exerted on the sled is 221.36 N.For such more question on perpendicular
https://brainly.com/question/1202004
#SPJ8
A sound wave has a frequency of 1.5 Hz while traveling at a speed of 50 m/s. What is the wavelength?
Answers
Answer:
33.3m
Explanation:
Recall that for a regular wave, the relationship between, wavelength, frequency and velocity (speed) is given by :
v = fλ,
where:
v = velocity (speed) of the wave = 50m/s
f = frequency of the wave = 1.5 Hz
λ = wavelength (we are asked to find this)
simply substitute the given values into the equation:
v = fλ
50 = 1.5 λ,
λ = 50/1.5
λ = 33.3m
Which on the following subatomic particles can modify on an object
A: electrons
B: neutrons
C: protons
Answers
Answer:
electrons i think
Explanation:
20 points !!! An infrared wave traveling at the speed of light has a wavelength of 2x10^-5 m. Calculate the frequency of this wave.
Answers
Answer:
f=1.5MHz or f=1500Hz
Explanation:
f=v/λ
3×10⁸/2×10-⁵
f=1500Hz
f=1.5MHz
Which statement is true about a falling object? (Assume no
air resistance)
1. The kinetic energy of the object is conserved.
2.The difference between the kinetic and potential energy of the
object remains the same.
3.The potential energy of the object is conserved.
4.The sum of the kinetic and potential energy of the object remains
the same.
Answers
I would say the answer is 3 because by falling technically the ball would be kind of moving in the air. Plus potential energy is when for example a soccer ball isnt moving
Which is a physical property of matter that is always the same regardless of size or amount
Answers
Answer:
ntensive properties: A physical property that will be the same regardless of the amount of matter.
Explanation:
Can anyone answer my questions that I've asked?
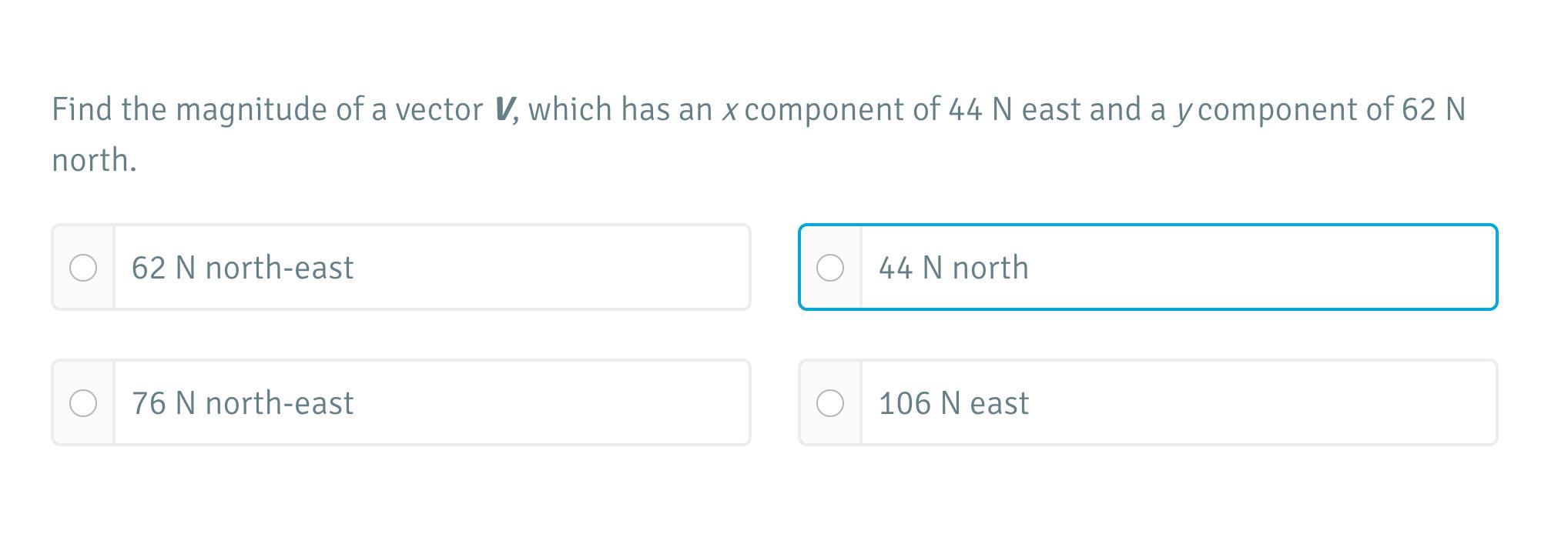
Answers
Answer:
76 N north-east
Explanation:
V = √(44²+62²) = 76 N
the lowest energy level of a certain quantum harmonic oscillator is 5.00 ev. what is the energy of the next higher level?
Answers
The lowest energy level of a certain quantum harmonic oscillator is 5.00 ev. The energy of the next higher level of the quantum harmonic oscillator is 10.00 ev.
The energy levels of a quantum harmonic oscillator are quantized, meaning that they can only exist at certain discrete energy values. The energy difference between these levels is given by the equation E = (n + 1/2)hν, where E is the energy of the level, n is the quantum number, h is Planck's constant, and ν is the frequency of the oscillator.
In this case, we know that the lowest energy level has an energy of 5.00 ev. Using the equation above, we can solve for the energy of the next higher level by plugging in n = 1 (since we are looking for the next level), h = 4.136 × 10^-15 eV·s (Planck's constant), and ν = ? (unknown frequency).
Solving for E, we get:
E = (1 + 1/2)hν
E = 3/2 hν
Since we don't know the frequency, we can't solve for E directly. However, we do know that the energy of the next level must be twice that of the lowest level (since the energy difference between levels is constant). Therefore, the energy of the next level is:
E = 2 × 5.00 ev
E = 10.00 ev
Learn more about harmonic oscillator here:
https://brainly.com/question/29471489
#SPJ11
different objects sitting around in a room feel warmer or cooler. if they are in thermal equilibrium, what must be true of their temperatures?
Answers
To learn the equilibrium and temperature.
What is equilibrium?
When Newton's first law is true, the equilibrium state of an object is present. When all external forces (including moments) operating on an object in a reference coordinate system are equal, the object is said to be in equilibrium. The net effect of all external forces and moments acting on this object is zero as a result.
What is temperatue?
Temperature is a unit of measurement that can be expressed on a variety of scales, including Fahrenheit and Celsius. Temperature shows the direction of the spontaneous movement of heat energy, i.e., from a hotter body (one with a higher temperature) to a colder body (one with a lower temperature).
Their temperatures must be equal if two bodies are in thermal equilibrium.
As for coldness or warmth, we generally observe that metals feel colder while non metallic objects don't (i.e. comparatively they feel warmer than metals). This is due to the fact that metals are good conductor of heat. So when we touch a metallic body, heat flows from our body and is transferred to other points of the metal object. Since our body loses heat, we feel cold. In non metals, this conduction of heat from point of contact to other locations does not happen.
Therefore, the amount of heat loss from our body is much smaller. So we don't feel that cold.
Learn more about equilibrium from the given link.
https://brainly.com/question/517289
#SPJ4
Two blocks hang from a string over a pulley. A 4 kg block on the left is pulled up by a falling second block on the right. If the acceleration is 3 m/s 2. then find the mass of block #2. Hint: after you build an equation for each mass, get all the m2 terms together and solve for m2
Answers
The mass of block #2 when a 4 kg block on the left is pulled up by a falling second block on the right, and the acceleration is 3 m/s² is 5 kg.
How to determine the mass of block #2?Mass of block #1 (m1) = 4 kg
Acceleration (a) = 3 m/s²
Let the mass of block #2 be (m2).
The equation:
Acceleration (a) = Force (F) / Mass (m)
Mass of block #1 = 4 kg
Weight of block #1 = 4 kg × 9.8 m/s²
= 39.2 N
Weight of block #2 = m2 × 9.8 m/s²
As per Newton's second law,
Total force = mass × acceleration
For block #1,
Total force = Weight of block #1
For block #2,
Total force = Weight of block #2
Net force = (Weight of block #2 - Weight of block #1)
Net force = m2g - 39.2 (where g = 9.8 m/s²)
Also, net force = Total force / Total mass
Net force = (m1 + m2) a
= m2g - 39.2
We need to find the mass of block #2 (m2), after substituting values, it becomes(4 + m2) × 3
= m2 × 9.8 - 39.23m2 - 9.8m2
= 39.2 + 12m2
= 5 kg
Therefore, the mass of block #2 is 5 kg.
Learn more about Newton's laws here: https://brainly.com/question/28171613
#SPJ11
Choose the option that best suit the question .
An inclined plane of angle Ɵ, acting as a simple machine has a velocity ratio :
(a) sinƟ
(b) 1/sinƟ
(c) cosƟ
(d) 1/cosƟ
(e) sinƟcosƟ
Answers
Answer:
(b) 1/sinƟ
Explanation:
A simple machine can be defined as a type of machine with no moving parts but can be used to perform work.
Basically, a simple machine allows for the transformation of energy into work. The six simple machines are; lever, wedge, pulley, screw, wheel and axle, and inclined plane.
Inclined plane is a simple machine set at an angle and then used to lift an object.
In Physics, the velocity ratio of a simple machine is calculated as a ratio of the distance moved by the effort to the vertical distance through which a load is raised.
Mathematically, the velocity ratio of an inclined plane of angle Ɵ, acting as a simple machine is given by the formula;
Velocity ratio (V.R) = 1/sinƟ
Basically, an increase in the angle of inclination (measured in degrees) of an inclined plane increases its velocity ratio.
Ight travels a distance of 0.926 m in 4.00 ns in a given substance. part a what is the index of refraction of this substance?
Answers
The index of refraction of this substance is 1.296.
The index of refraction of a substance is a measure of how much the speed of light is reduced when it passes through that substance compared to its speed in a vacuum. It can be calculated using the formula:
index of refraction = speed of light in a vacuum / speed of light in the substance.
In this question, the distance traveled by light in the substance is given as 0.926 m, and the time taken is given as 4.00 ns. To find the speed of light in the substance, we need to divide the distance by the time:
speed of light in the substance = distance / time.
Now we can substitute the values given in the question:
speed of light in the substance = 0.926 m / 4.00 ns.
However, the speed of light is commonly expressed in meters per second (m/s), so we need to convert the time from nanoseconds to seconds. There are 1 billion nanoseconds in a second, so:
time in seconds = 4.00 ns / 1 billion.
Now we can substitute this value into the equation:
speed of light in the substance = 0.926 m / (4.00 ns / 1 billion).
Simplifying the equation, we can multiply the numerator and denominator by 1 billion:
speed of light in the substance = (0.926 m * 1 billion) / 4.00 ns.
Calculating this value, we get:
speed of light in the substance = 231.5 * 10^6 m/s.
Now we need to find the speed of light in a vacuum. The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 3 * 10^8 m/s.
Finally, we can calculate the index of refraction using the formula mentioned earlier:
index of refraction = speed of light in a vacuum / speed of light in the substance.
Substituting the values, we get:
index of refraction = (3 * 10^8 m/s) / (231.5 * 10^6 m/s).
Simplifying the equation, we divide the numerator and denominator by 10^6:
index of refraction = 300 / 231.5.
Calculating this value, we find that the index of refraction of this substance is approximately 1.296.
So, the index of refraction of this substance is 1.296.
learn more about refraction on :
https://brainly.com/question/27932095
#SPJ11
In a physics lab, students take a long piece of string and cut it into two unequal pieces. One piece is used to suspend a large weight. The second piece is tied to the bottom of the weight as seen in the diagram below. Student 1 predicts that the upper string will always break first since it has to support the weight and the applied force, while Student 2 disagrees and predicts that the shorter piece of string will always break first if you pull slowly but with enough force to exceed the strength of the string.
(a) Which aspect(s) of Student 1’s reasoning, if any, are correct? Explain your answer.
(b) Which aspect(s) of Student 2’s reasoning, if any, are correct? Explain your answer.
(c) Which aspect(s) of both Student 1’s and 2’s reasoning, if any, are incorrect? Explain your answer.
(d) The experiment is performed and both students are surprised to learn that whether
the upper or lower string breaks first depends on whether you pull slowly or with a
sudden pull. Resolve the two lines of reasoning of Student 1 and Student 2 by
explaining the results of the experiment in a clear, concise paragraph.
Answers
Answer:
(a) The aspect of the upper string supporting the weight and the applied force
Student 1 is correct because the upper string is the source of support of the large weight and the force applied to the short string reacts at the support of the long string
(b) The aspect of Student's (2) reasoning that is correct is that the shorter piece of string will always break first, however, the statement is only true for sudden pull due to the increased force experienced by the shorter string from a more rapid change in momentum
(c) The aspect of Student 1's statement that is incorrect is the that the upper string will always break first
The aspect of Student 2's statement that is incorrect is the that the shorter piece of string will always break first
(d) A string will break when subject to a force equivalent to its breaking force. The force experienced by the string increases as the rate of pull (suddenness) increases and the suddenness increases inversely with the length of the string, as such the shorter lower string will break first from a sudden pull before the force of the pull is completely transmitted to the upper string. Whereby the lower string is slowly pulled, the force is evenly transmitted to the upper string which is then taking up the load of the weight and the applied force together and is likely to break first
Explanation:
Jamie records how much time passes from the time the fire alarm sounds until Gary gets up to exit the house. What is he measuring?
Answers
Jamie is measuring Gary's response time, which is the time it takes for Gary to react to the fire alarm and start moving towards the exit.
It is a measure of the time it takes for a person to respond to a given stimulus, such as a fire alarm, and initiate a response. Response time is often studied in various fields, including psychology, neuroscience, and human factors engineering, as it can provide insights into cognitive and behavioral processes and performance. It can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of warning signals and other safety measures in emergency situations.which is the time it takes for Gary to react to the fire alarm and start moving towards the exit.
Learn more about cognitive here:
https://brainly.com/question/28147250
#SPJ4
1 poin
What exercise could you do that works on cardiovascular endurance and
muscular strength?*
Bicep Curls
Dips
Stairs
Squats
O Other:
Answers
stairs are a great cardiovascular endurance exercise, and also help muscular strength in the legs and core.
hope this helps!
In a heat engine, 2.00 mol of a monoatomic gas are carried through the cycle ABCDA. The segment AB represents an isothermal expansion, the segment BC is an adiabatic expansion, the segment CD is an isobaric compression, and DA is a constant volume process. The pressure and temperature at A are 5.00 atm and 600 K. The volume at B is twice the volume at A. The pressure at D is 1.00 atm.
a) What is the pressure at B?
b) What is the temperature at C?
c) Find the total work done by the gas in one cycle.
Answers
(a)The pressure at B is 0.1248 atm.
(b)The temperature at C is 727.1 K.
(c)The total work done by the gas in one cycle is -1979J
General calculation:
We can use the First Law of Thermodynamics to analyze the heat engine cycle:
ΔU = Q - W
where ΔU is the change in internal energy, Q is the heat added to the system, and W is the work done by the system. For a complete cycle, ΔU = 0, so:
Q = W
We can also use the ideal gas law to relate the pressure, volume, and temperature of the gas:
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the gas constant, and T is the absolute temperature.
(a)How to find the pressure at B segment?
To find the pressure at B, we can use the fact that the segment AB is an isothermal expansion. This means that the temperature remains constant, so:
PV = nRT
PB = (nRT)/(2V) = (2.00 mol)(0.0821 L·atm/mol·K)(600 K)/(2V) = (0.0821 L·atm/mol)(600 K)/V
Since the pressure at A is 5.00 atm, we can use the fact that the temperature is constant to find the volume at A:
PV = nRT
VA = (nRT)/P = (2.00 mol)(0.0821 L·atm/mol·K)(600 K)/5.00 atm = 197.76 L
Since the volume at B is twice the volume at A, we have:
VB = 2VA = 395.52 L
Substituting into the expression for PB, we get:
PB = (0.0821 L·atm/mol)(600 K)/395.52 L = 0.1248 atm
Therefore, the pressure at B is 0.1248 atm.
(b) How to find the temperature at segment C?To find the temperature at C, we can use the fact that the segment BC is an adiabatic expansion. This means that no heat is added or removed from the system, so:
\(PV^\gamma\)= constant
where γ is the ratio of specific heats (for a monoatomic gas, γ = 5/3). We can use the fact that the volume at C is equal to the volume at A to find the pressure at C:
\(PAV^\gamma = PCV^\gamma\)
PC = \(PA(V/A)^\gamma\) = 5.00 atm\((1/2)^(^5^/^3^)\) = 1.556 atm
Since the segment BC is adiabatic, the temperature changes but no heat is added or removed from the system. Using the ideal gas law, we can relate the pressure, volume, and temperature:
PV = nRT
TC = (PCVC)/(nR) = (1.556 atm)(197.76 L)/(2.00 mol)(0.0821 L·atm/mol·K) = 727.1 K
Therefore, the temperature at C is 727.1 K.
(c) How to find the total work done by the gas in one cycle?The total work done by the gas in one cycle is the sum of the work done in each segment of the cycle:
W = WAB + WBC + WCD + WDA
For segment AB, the work done is:
WAB = -QAB = -∫PdV = -nRT∫(1/V)dV = -nRT ln(VB/VA) = -(2.00 mol)(0.0821 L·atm/mol·K)(600 K) ln(2) = -602 J
For segment BC, the work done is:
WBC = -QBC = -∫PdV = -nγRT∫(1/V)dV = -nγRT
We know that VB = 2VA and VC = 2VD, so we can express the ratio VB/VC in terms of VA/VD:
VB/VC = (2VA)/(2VD) = VA/VD
Substituting into the expression for WBC, we get:
WBC = -nγRT ln(VA/VD)
For segment CD, the work done is:
WCD = -QCD + PCDΔV = -nCpΔT + PCDΔV
where Cp is the specific heat at constant pressure, ΔT is the change in temperature, and ΔV is the change in volume. We know that the segment CD is isobaric, so ΔV = VB - VA = (2VA) - VA = VA. We can also use the ideal gas law to relate the pressure, volume, and temperature:
PV = nRTPC = (nRT)/VDSubstituting into the expression for WCD, we get:
WCD = -nCpΔT + (nRT/VD)VA = -nCp(TC - TD) + (nRT/VD)VA
For segment DA, the work done is:
WDA = -QDA + ΔU = -nCvΔT
where Cv is the specific heat at constant volume. We know that the segment DA is isovolumetric, so ΔV = 0. Using the First Law of Thermodynamics, we know that ΔU = 0 for a complete cycle, so:
QDA = -WDA = nCvΔT
Substituting into the expression for WDA, we get:
WDA = -nCvΔT
Adding up the work done in each segment, we get:
W = WAB + WBC + WCD + WDA
= -(2.00 mol)(0.0821 L·atm/mol·K)(600 K) ln(2)- (2.00 mol)(5/3)(0.0821 L·atm/mol·K)(727.1 K) ln(VA/VD)- (2.00 mol)(Cp)(TC - TD) + (2.00 mol)(0.0821 L·atm/mol·K)(600 K) ln(2)- (2.00 mol)(Cv)(TC - TA)
We know that Cp and Cv for a monoatomic gas are related by Cp = Cv + R, so we can express Cp in terms of Cv:
Cp = Cv + R = (3/2)R + R = (5/2)R
Substituting and simplifying, we get:
W = (2.00 mol)(0.0821 L·atm/mol·K)(600 K) ln(2)- (2.00 mol)(5/3)(0.0821 L·atm/mol·K)(727.1 K) ln(VA/VD)- (2.00 mol)(5/2)(0.0821 L·atm/mol·K)(727.1 K)+ (2.00 mol)(5/2)(0.0821 L·atm/mol·K)(600 K)
W = -966.2 J - 4957 J - 7476 J + 5154 J
= -1979 J
Therefore, the total work done by the gas in one cycle is -1979 J
Lean more about thermodynamics
brainly.com/question/1368306
#SPJ11
who is the current electric minister of Nepal?
Answers
i think "Barsaman Pun"
Explanation:
BARSAMAN PUN IS THE CURRENT ELECTRIC MINISTER OF NEPAL.
HOPE IT HELP.....❤❤☺A car travelling an unbanked curve of radius 200 ft notices a truckstopped on the road ahead. The driverimmediately applies brakes causing the speed of the carto decrease at the rate of 10 ft/s2. If at that instant, the stationary truckis 100 ft ahead (the distance is measured along the path) and the car is travelling at a speed of 40ft/s, whatis the magnitude of the relative velocity ofthe truck perceived by the driver of the car (i.e. from the moving frame of referenceof the car).
Answers
Answer:
u = - 40 ft / s
Explanation:
The Galilean relation for the relative velocity is
v ’= v + u
where u is the speed between the two reference frames, v is the speed of the fixed system and v 'the speed of the mobile system.
In this case the truck has a speed with respect to the ground (fixed system) 0 m / s (it is stopped), the car has a speed with respect to the ground of v = 40 ft / s,
u = v'- v
u = 0 - 40
u = - 40 ft / s
the speed perceived by the car if the system is fixed on it is -40 ft / s
why is the steering of a car wheel and axle
Answers
Answer:
have a greater mechanical advantage
Explanation:
this enables the mechanism to output a large amount of force compared to the force put into it due to ratio of the wheel and the axle therefore providing enough force to steer the rather heavy wheels while saving the driver some muscle power
27. a) Draw the magnetic field around a wire given the current is flowing to the right of the page. b) Calculate the field strength of the magnetic field in the following situation. A straight current carrying wire has a 6.8 A current in a uniform magnetic field which is at right angles to the wire. When 0.15 m of wire is in the magnetic field it experiences a force of 0.55 N. Find the strength of the magnetic field.
Answers
a) The magnetic field around a wire carrying current can be represented using concentric circles centered on the wire. The direction of the magnetic field lines can be determined using the right-hand rule: if you wrap your right hand around the wire with your thumb pointing in the direction of the current, your curled fingers will indicate the direction of the magnetic field.
b) To calculate the strength of the magnetic field, we can use the equation:
Force = Magnetic field strength × Current × Length
Plugging in the given values, we have:
0.55 N = Magnetic field strength × 6.8 A × 0.15 m
Solving for the magnetic field strength, we find:
Magnetic field strength = 0.55 N / (6.8 A × 0.15 m)
Calculating the numerical value, we can determine the strength of the magnetic field.
To learn more about magnetic field, you can visit
brainly.com/question/28814129
#SPJ11.
. Explain the concept of generational wealth. In How Jews Became White and What That
Says About America, how did the GI Bill described in the essay impact the generational
wealth for the men who served, marginalized populations, and women. Support your
response with two paragraphs.
Answers
In "How Jews Became White and What That Says About America," the author explores the impact of the GI Bill on generational wealth. The GI Bill was intended to provide educational and financial support to veterans returning from World War II. However, the bill was structured in a way that excluded many marginalized populations, including women and people of color. As a result, white men were disproportionately able to take advantage of the benefits offered by the GI Bill, including low-interest home loans and access to higher education. This allowed many white families to accumulate generational wealth that was passed down to future generations. Meanwhile, marginalized populations were left behind, unable to access the same opportunities for wealth-building. This has had a lasting impact on generational wealth in America, contributing to the racial wealth gap that exists to this day.