Answers
Muscular strength refers to the maximum force a muscle while muscular endurance refers to the ability of a muscle or group of muscles to sustain repeated contractions over an extended period without fatigue.
Some benefits of good muscular endurance include:
Enhanced physical performance Cardiovascular health What is muscular strength and endurance ?Muscular strength refers to the maximal force exerted by an individual or muscle group against resistance during a single effort. In contrast, muscular endurance denotes the ability of muscles or muscle groups to sustain repeated contractions over an extended duration without succumbing to fatigue.
Possessing commendable muscular endurance begets numerous advantages. Primarily, it bolsters overall physical performance, permitting individuals to engage in prolonged activities without succumbing to premature exhaustion. It also cultivates functional fitness, empowering individuals to execute everyday tasks with ease and efficiency.
Find out more on muscular endurance at https://brainly.com/question/16225402
#SPJ1
Related Questions
3. A renegade watermelon starts at x = 0 m and rolls at a constant velocity to x = -3.0 m at time t = 5.0 seconds. Then, it bumps into a wall and stops. Draw its position versus time graph from t = 0 s to t = 10 s.
Answers
Transform the given information into points.
If the watermelon rolled from 0 to -3.0 m in 5 seconds, then the point is (5,-3).
If the watermelon stops after 5 seconds, then draw a horizontal line there because its position is constant.

describe the motion of the ball between t = 0s and t = 1.275s.

Answers
For the beam and loading shown below (a), (b), and (c),
(a) draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams,
(b) determine the maximum absolute values of the shear and bending moment.
(a)
A graph of kinetic energy vs the mass of an object is ______________?
Answers
Answer:
The shape of the MASS vs ENERGY graph has a NON-LINEAR RELATIONSHIP.
Explanation:
Your Welcome Friend! :)
A graph of kinetic energy vs the mass of an object is non-linear.
What is the nonlinear relationship?
Changes in the output are not proportional to changes in any of the inputs in a nonlinear connection.
When a linear connection is plotted on a graph, it produces a straight line; however, when a nonlinear relationship is plotted on a graph, it produces a curve.
When graphed, motion energy is proportional to the mass of the moving item, resulting in a linear connection, and it expands with the square of its speed, resulting in a non-linear relationship.
Hence a graph of kinetic energy vs the mass of an object is non-linear.
To learn more about the nonlinear relationship refer to the link;
https://brainly.com/question/14304469
When an elastic object is changed from its original shape:
A:Energy is released
B:Work is done
C:It is ruined
D:It makes a twanging sound
Answers
Answer:
deformation : elastic deformation is reversed when the force is removed. inelastic deformation is not fully reversed when the force is removed – there is a permanent change in shape.
Explanation:
tysm
A uniform electric field is directed upward and has a magnitude of 24 N/C. A charge of -6 C is placed in this
field.
The direction of the force on the charge placed in the electric field is upward.
True or False
Answers
The statement" The direction of the force on the charge placed in the electric field is upward" is false because the direction of the force on a negative charge (-6 C) placed in an upward-directed uniform electric field of magnitude 24 N/C would be downward.
The direction of the force on a charged particle placed in an electric field is determined by the charge of the particle and the direction of the electric field. In this case, a charge of -6 C is placed in an electric field directed upward with a magnitude of 24 N/C.
The force on a charged particle in an electric field can be calculated using the formula:
F = q * E
Where F is the force, q is the charge of the particle, and E is the electric field.
Since the charge q in this case is negative (-6 C) and the electric field E is directed upward, we can substitute the values into the formula:
F = (-6 C) * (24 N/C)
F = -144 N
The negative sign in the force value indicates that the force is in the opposite direction to the electric field. Therefore, the force on the charge placed in the electric field is downward, not upward.
The force on a negative charge is always opposite to the direction of the electric field. This is because negative charges experience an attractive force towards positive charges, and electric fields are directed from positive charges to negative charges.
Therefore, the statement "The direction of the force on the charge placed in the electric field is upward." is false.
For more such information on: force
https://brainly.com/question/12785175
#SPJ8
2. An 82 kg man drops from rest on a diving board 3.0 m above the surface of the
water and comes to rest 0.55 s after reaching the water. What is the net force on the
diver as he is brought to rest?
Answers
The acceleration is 0, this means there is no net force acting on the diver as he comes to rest. The net force is equal to zero.
To determine the net force on the diver, we can use the equation of motion:
(Final velocity)² = (Initial velocity)² + 2 × acceleration × distance
The initial velocity is 0 since the diver is at rest on the diving board. The final velocity is also 0 since the diver comes to rest in the water. The distance fallen is 3.0 m.
We can solve for the acceleration using the given time:
0 = 0² + 2 × acceleration × 3.0
0 = 0 + 6.0 × acceleration
acceleration = 0 m/s²
To know more about Motion refer to this link
https://brainly.com/question/25951773
Answer:
1,143 N
Explanation:
m = 82 kg
d = 3 m
t = 0.55 s
Vf² = Vi² + 2ad
Vf² = 0 + 2(9.8 m/s²)(3 m) = 58.8 m²/s²
Vf = √58.8 m²/s² = 7.67 m/s
Use the Impulse Force equation:
FΔt = mΔv
F = (82 kg)(7.67 m/s) / (0.55 s) ≈ 1143 N
A pelican flying along a horizontal path drops a fish from a height of 5.4 m. The fish travels 8.0 m horizontally before it hits the water below. What is the pelican’s speed?
Answers
Answer:
Speed, Vfx = 7.619 m/s
Explanation:
Vertical distance, Dx = 5.4m
Horizontal distance, Dy = 8m
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8m/s²
Initial speed, Vix = 0m/s²
To find the speed, we would use the second equation of motion to find the time, t;
Dx = Vixt + ½gt²
Substituting into the equation, we have;
5.4 = 0(t) + ½(9.8)*t²
5.4 = 0 + 4.9t²
Rearranging the equation, we have;
4.9t² = 5.4
t² = 5.4/4.9
t² = 1.1020
Taking the square root of both sides;
t = 1.050 secs.
For the speed;
Dy = Vfxt
Vfx = Dy/t
Vfx = 8/1.050
Vfx = 7.619 m/s
Therefore, the speed of the pelican is 7.619 m/s

Diane is writing a summary statement of her experiment. This statement is
written.
A after data is collected and analyzed
B before writing the scientific question
C before writing the hypothesis
D at the same time data is collected.
.
Answers
a uniform rod 8m long weighing 5kg is supported horizontally by two vertical parallel strings at p and q and at distance 2m and 6m from one end.
Weight of 1kg, 1.5kg and 2kg are attached at distance of 1m 5m and 7m respectively from the same end.
find the tension in each vertical string
Answers
Answer:
Fp = 36 N
Fq = 58 N
Explanation:
Let the left end be the reference end with string p closest to it.
Let CCW moments be positive
Sum moments about p to zero
1(9.8)[2 - 1] + Fq[6 - 2] - 5(9.8)[8/2 - 2] - 1.5(9.8)[5 - 2] - 2(9.8)[7 - 2] = 0
Fq[4] = 23.5(9.8)
Fq = 57.575 ≈ 58 N
Sum moments about q to zero
1(9.8)[6 - 1] - Fp[6 - 2] + 5(9.8)[6 - 8/2] + 1.5(9.8)[6 - 5] - 2(9.8)[7 - 6] = 0
Fp = 35.525 N
or
Sum vertical forces to zero
Fp + 57.575 - (9.8)(1 + 1.5 + 2 + 5) = 0
Fp = 35.525 ≈ 36 N
What is the mass (in kg) of a Puffin flying 10 m/s with 1000 J of KE?
Answers
Answer:
20 kg
Explanation:
The kinetic energy (KE) of an object is given by:
KE = (1/2) * m * v^2
Where m is the mass of the object, and v is its velocity.
We can rearrange this formula to solve for the mass:
m = 2 * KE / v^2
Plugging in the values given:
m = 2 * 1000 J / (10 m/s)^2
m = 20 kg
Therefore, the mass of the Puffin flying at 10 m/s with 1000 J of KE is 20 kg.
estimate the work you do to mow a lawn 10m by 20m with a 50 cm wide mower. Assume you push with a force of about 15 N.
Answers
Answer:
W = 6000 Joule
Explanation:
Work is defined as force times distance
W = F * d
We know that F = 15N, we just need the distance (d)
Imagine you have a square lawn with length of 10 m and width of 20m. So, we want to know the the distance you have to travel to cover every square meter of the lawn.
The width of the mower is only 50 cm = 0.5 m.
This means that you have to go back and forth 40 times to cover 20m (lawn width), with a distance of 10 m (lawn length). So,
d = 10 (meter) * 40 (times) = 400 meter
Therefore:
W = (15) * (400) = 6000 J
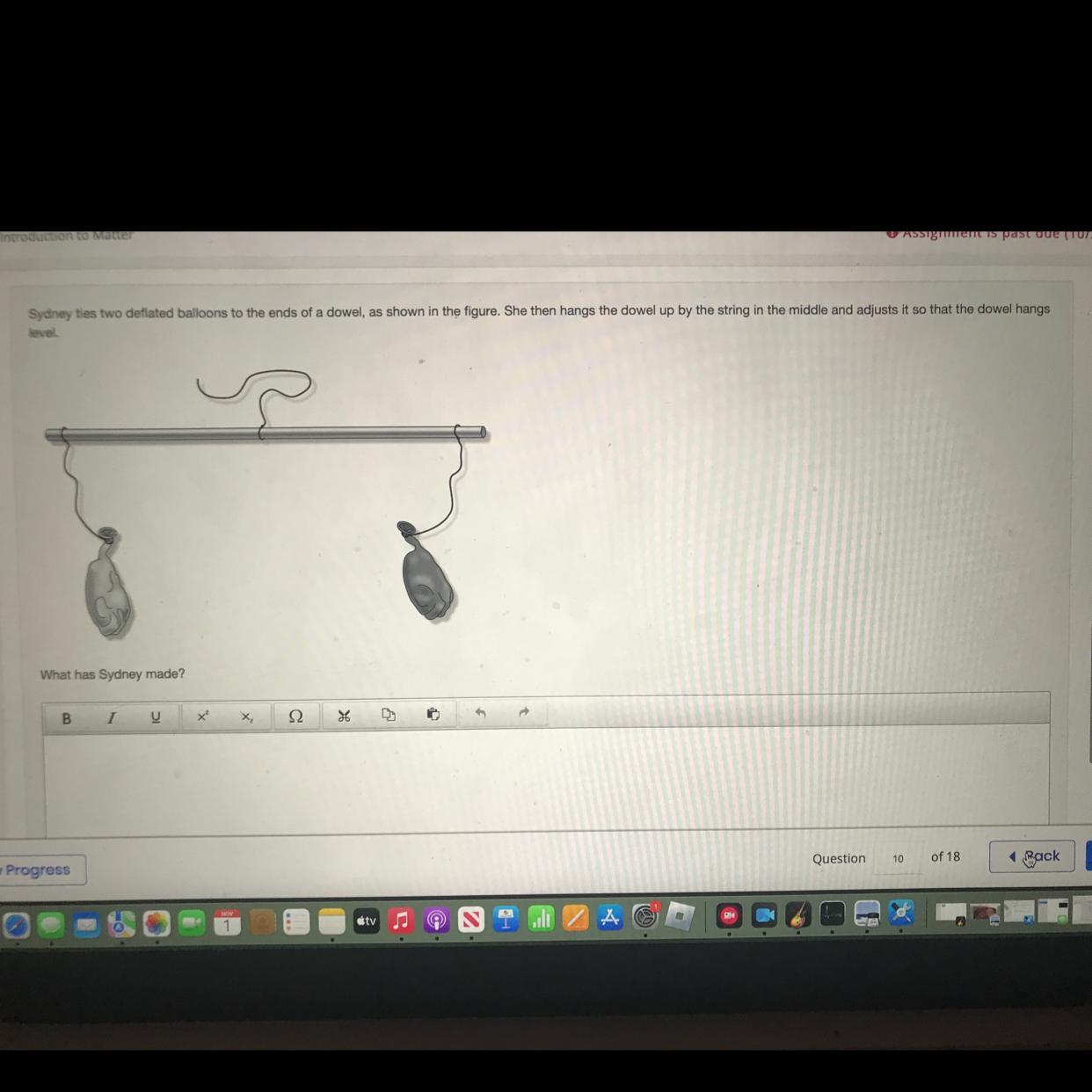
HELP!! sydney ties two deflated balloons to the end of a dowel. she then hangs up the dowel up by the string in the middle and adjust it so that the dowel hangs level. What has Sydney made?
Answers
Answer:I
Explanation:
i
Which of the following is true about conduction? Question 2 options: It is heat transfer through direct contact It can only occur in a liquid It is heat transfer in currents through a liquid It is heat transfer as a form of light
Answers
Answer:
through direct contact
Explanation:
took the test!
Light travels 186,282 miles per second.How far does it travel in an hour? IN A DAY?
Answers
A. Light travels approximately 670,616,320 miles in an hour.
B. Light travels approximately 16,094,718,080 miles in a day.
How to find out how far it travels in an hour ?Light travels at a speed of 186,282 miles per second. To find out how far it travels in an hour, we can simply multiply this speed by the number of seconds in an hour:
Distance traveled in an hour = 186,282 miles/second x 3,600 seconds/hour = 670,616,320 miles/hour
Therefore, light travels approximately 670,616,320 miles in an hour.
How to find out how far light travels in a day?To find out how far light travels in a day, we need to multiply the distance traveled in an hour by the number of hours in a day:
Distance traveled in a day = 670,616,320 miles/hour x 24 hours/day = 16,094,718,080 miles/day
Therefore, light travels approximately 16,094,718,080 miles in a day.
Learn more about multiply here : brainly.com/question/28773316
#SPJ1
2. During
particles in an ionic
solid are separated and drawn into solution.
TC
?
Answers
Answer:
dissociation
Explanation:
mark me brainliest!!
A motorcycle stoop is at a traffic light, when the light turns green, the motorcycle accelerates to a speed of 78 km/h over a distance of 50 m. What is the average acceleration of the motorcycle over this distance?
Answers
The average acceleration of the motorcycle over the given distance is approximately 9.39 m/s².
To calculate the average acceleration of the motorcycle, we can use the formula:
Average acceleration = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time
First, let's convert the final velocity from km/h to m/s since the distance is given in meters. We know that 1 km/h is equal to 0.2778 m/s.
Converting the final velocity:
Final velocity = 78 km/h * 0.2778 m/s = 21.67 m/s
Since the motorcycle starts from rest (initial velocity is zero), the formula becomes:
Average acceleration = (21.67 m/s - 0 m/s) / time
To find the time taken to reach this velocity, we need to use the formula for average speed:
Average speed = total distance/time
Rearranging the formula:
time = total distance / average speed
Plugging in the values:
time = 50 m / 21.67 m/s ≈ 2.31 seconds
Now we can calculate the average acceleration:
Average acceleration = (21.67 m/s - 0 m/s) / 2.31 s ≈ 9.39 m/s²
To learn more about acceleration
https://brainly.com/question/2303856
#SPJ8
Your friend asks you for a glass of water and you bring her 5 millilitersof water. Is this more or less than what she was probably expecting?Explain your reasoning
Answers
how is potential energy a scalar quantity even though it can be negative?
Answers
Explanation:
Potential energy is a scalar quantity because it has only magnitude and no direction. Its ability to be negative does not affect its scalar nature.
Please mark brainliest
You apply 741 J of energy to lift a box a distance of 2.83 meters, what
is the weight of the box?

Answers
Answer:
261.84 N.
Explanation:
From the question given above, the following data were obtained:
Energy (E) = work (W) = 741 J
Distance (d) = 2.83 m
Force (F) =?
Work is simply defined as the product of force and the distance moved in the direction of the the force. Mathematically, it is expressed as:
Work (W) = Force (F) × distance (d)
W = F × d
Thus, we obtained the weight of the object using the above formula.
Work (W) = 741 J
Distance (d) = 2.83 m
Force (F) =?
W = F × d
741 = F × 2.83
Divide both side by 2.83
F = 741 / 2.83
F = 261.84 N
Since force and weight has the same unit of measurement i.e Newton (N), the weight of the object is 261.84 N
Two speeding lead bullets, one of mass 15.0 g moving to the right at 295 m/s and one of mass 7.75 g moving to the left at 375 m/s, collide head-on, and all the material sticks together. Both bullets are originally at temperature 30.0°C. Assume the change in kinetic energy of the system appears entirely as increased internal energy. We would like to determine the temperature and phase of the bullets after the collision. (Lead has a specific heat of 128 J/(kg K), a melting point of 327.3°C, and a latent heat of fusion of 2.45 104 J/kg.)
Answers
Answer:
The final temperature of the bullets is 327.3 ºC.
Explanation:
Let suppose that a phase change does not occur during collision and collided bullets stop at the end. We represent the phenomenon by the First Law of Thermodynamics:
\(K_{A, o} + K_{B, o}-K_{A}-K_{B}+U_{A,o} + U_{B,o}-U_{A}-U_{B} = 0\) (1)
Where:
\(K_{A,o}\), \(K_{A}\) - Initial and final translational kinetic energies of the 15-g bullet, measured in joules.
\(K_{B,o}\), \(K_{B}\) - Initial and final translational kinetic energies of the 7.75-g bullet, measured in joules.
\(U_{A,o}\), \(U_{A}\) - Initial and final internal energies of the 15-g bullet, measured in joules.
\(U_{B,o}\), \(U_{B}\) - Initial and final internal energies of the 7.75-g bullet, measured in joules.
By definitions of translational kinetic energy and sensible heat we expand and simplify the equation above:
\(\frac{1}{2}\cdot m_{A}\cdot (v_{A,o}^{2}-v_{A}^{2})+ \frac{1}{2}\cdot m_{B}\cdot (v_{B,o}^{2}-v_{B}^{2})+(m_{A}+m_{B})\cdot c\cdot (T_{o}-T) = 0\) (2)
Where:
\(m_{A}\), \(m_{B}\) - Masses of the 15-g and 7.75-g bullets, measured in kilograms.
\(v_{A,o}\), \(v_{A}\) - Initial and final speeds of the 15-g bullet, measured in meters per second.
\(v_{B,o}\), \(v_{B}\) - Initial and final speeds of the 7.75-g bullet, measured in meters per second.
\(c\) - Specific heat of lead, measured in joules per kilogram-Celsius degree.
\(T_{o}\), \(T\) - Initial and final temperatures of the bullets, measured in Celsius degree.
Now we clear the final temperature of the bullets:
\((m_{A}+m_{B})\cdot c \cdot (T-T_{o}) = \frac{1}{2}\cdot [m_{A}\cdot (v_{A,o}^{2}-v_{A}^{2})+m_{B}\cdot (v_{B,o}^{2}-v_{B}^{2})]\)
\(T-T_{o} = \frac{m_{A}\cdot (v_{A,o}^{2}-v_{A}^{2})+m_{B}\cdot (v_{B,o}^{2}-v_{B}^{2})}{(m_{A}+m_{B})\cdot c}\)
\(T= T_{o}+\frac{m_{A}\cdot (v_{A,o}^{2}-v_{A}^{2})+m_{B}\cdot (v_{B,o}^{2}-v_{B}^{2})}{(m_{A}+m_{B})\cdot c}\) (3)
If we know that \(T_{o} = 30\,^{\circ}C\), \(m_{A} = 15\times 10^{-3}\,kg\), \(m_{B} = 7.75\times 10^{-3}\,kg\), \(v_{A,o} = 295\,\frac{m}{s}\), \(v_{B,o} = 375\,\frac{m}{s}\), \(v_{A} = 0\,\frac{m}{s}\), \(v_{B} = 0\,\frac{m}{s}\) and \(c = 128\,\frac{J}{kg\cdot ^{\circ}C}\), then the final temperature of the collided bullets is:
\(T = 30\,^{\circ}C+\frac{(15\times 10^{-3}\,kg)\cdot \left[\left(295\,\frac{m}{s} \right)^{2}-\left(0\,\frac{m}{s} \right)^{2}\right]+(7.75\times 10^{-3}\,kg)\cdot \left[\left(375\,\frac{m}{s} \right)^{2}-\left(0\,\frac{m}{s} \right)^{2}\right]}{(15\times 10^{-3}\,kg+7.75\times 10^{-3}\,kg)\cdot \left(128\,\frac{J}{kg\cdot ^{\circ}C} \right)}\)
\(T = 852.534\,^{\circ}C\)
Given that found temperature is greater than melting point, then we conclude that supposition was false. If we add the component of latent heat of fussion, then the resulting equation is:
\(\frac{1}{2}\cdot m_{A}\cdot (v_{A,o}^{2}-v_{A}^{2})+ \frac{1}{2}\cdot m_{B}\cdot (v_{B,o}^{2}-v_{B}^{2})+(m_{A}+m_{B})\cdot c\cdot (T_{o}-T)-U = 0\) (4)
\(U=\frac{1}{2}\cdot m_{A}\cdot (v_{A,o}^{2}-v_{A}^{2})+ \frac{1}{2}\cdot m_{B}\cdot (v_{B,o}^{2}-v_{B}^{2})+(m_{A}+m_{B})\cdot c\cdot (T_{o}-T)\)
If we know that \(T_{o} = 30\,^{\circ}C\), \(T = 327.3\,^{\circ}C\), \(m_{A} = 15\times 10^{-3}\,kg\), \(m_{B} = 7.75\times 10^{-3}\,kg\), \(v_{A,o} = 295\,\frac{m}{s}\), \(v_{B,o} = 375\,\frac{m}{s}\), \(v_{A} = 0\,\frac{m}{s}\), \(v_{B} = 0\,\frac{m}{s}\) and \(c = 128\,\frac{J}{kg\cdot ^{\circ}C}\), then latent heat received by the bullets during impact is:
\(U =\frac{1}{2}\cdot (15\times 10^{-3}\,kg)\cdot \left[\left(295\,\frac{m}{s} \right)^{2}-\left(0\,\frac{m}{s} \right)^{2}\right] + \frac{1}{2}\cdot (7.75\times 10^{-3}\,kg)\cdot \left[\left(375\,\frac{m}{s} \right)^{2}-\left(0\,\frac{m}{s} \right)^{2}\right]+(15\times 10^{-3}\,kg+7.75\times 10^{-3}\,kg)\cdot \left(128\,\frac{J}{kg\cdot ^{\circ}C} \right) \cdot (30\,^{\circ}C-327.3\,^{\circ}C)\)\(U = 331.872\,J\)
The maximum possible latent heat (\(U_{max}\)), measured in joules, that both bullets can receive during collision is:
\(U_{max} = (m_{A}+m_{B})\cdot L_{f}\) (5)
Where \(L_{f}\) is the latent heat of fusion of lead, measured in joules per kilogram.
If we know that \(m_{A} = 15\times 10^{-3}\,kg\), \(m_{B} = 7.75\times 10^{-3}\,kg\) and \(L_{f} = 2.45\times 10^{4}\,\frac{J}{kg}\), then the maximum possible latent heat is:
\(U_{max} = (15\times 10^{-3}\,kg+7.75\times 10^{-3}\,kg)\cdot \left(2.45\times 10^{4}\,\frac{J}{kg} \right)\)
\(U_{max} = 557.375\,J\)
Given that \(U < U_{max}\), the final temperature of the bullets is 327.3 ºC.
Which landscape feature can be caused by chemical
weathering?
OU-shaped valley
O Basalt columns
O Limestone caves
Answers
Answer: Limestone Caves
Explanation: The most common feature that can be caused purely by chemical weathering is Karst Landscape, which can lead to caverns and sinkholes.
Select the correct answer from each drop-down menu.
Rocky metallic objects found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter are(drop down). The largest known of these is(drop down).
Answers
Answer:
Blank 1 (asteroids)
Blank 2 (Ceres)
Explanation:
Rocky metallic objects found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter are asteroids The largest known of these is ceres.
What are asteroids?Asteroids are stony elements that circle the Sun. Although asteroids circle the Sun in the same way as planets, they are considerably smaller.]
A dwarf planet located between Mars and Jupiter in the asteroid belt. Ceres was the first asteroid discovered, it was originally classed as a planet,
Rocky metallic objects found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter are asteroids The largest known of these is ceres.
The correct option from the drop-down menu is asteroids and ceres.
To learn more about the asteroids refer to the link;
https://brainly.com/question/19161842
take the density of copper as 9g/cm3 find the mass of 5cm3
Answers
The mass of 5 cm³ of copper is 45 grams. This means that if we had a block of copper with a volume of 5 cm³, it would weigh 45 grams.
The density of copper is given as 9 g/cm³, which means that for every cubic centimeter (cm³) of copper, there is a mass of 9 grams (g). To find the mass of 5 cm³ of copper, we can use the following formula:
mass = density x volume
where mass is the mass of the object in grams, density is the density of the material in grams per cubic centimeter, and volume is the volume of the object in cubic centimeters.
Plugging in the values we have, we get:
mass = 9 g/cm³ x 5 cm³
mass = 45 g
Therefore, the mass of 5 cm³ of copper is 45 grams. This means that if we had a block of copper with a volume of 5 cm³, it would weigh 45 grams.
It is important to note that the density of a material is an important physical property that relates its mass to its volume, and is often used in calculations involving materials and objects of different shapes and sizes.
For more such questions on volume visit:
https://brainly.com/question/30437394
#SPJ11
Help please! View attachment below

Answers
Answer:
it is A
Explanation:
“Permafrost” is permanently frozen soil and occurs mostly in high latitudes storing a massive
amount of a particular element. As a result of climate change, permafrost is at the risk of melting and
releasing the stored element in the form of a gas. Identify the gas.
a) Ozone
b) Hydrogen
c) Nitrogen oxide
d) Carbon dioxide
Answers
How do bumper cars at an amusement pack demonstrate Newton’s third law?
Answers
Answer:
If two bumper cars collide with a certain force, then they will move away from each other in opposite directions with the same force. This demonstrates Newton's third law, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Explanation:
Consider a double-paned window consisting of two panes of glass, each with a thickness of 0.500 cm and an area of 0.760 m2 , separated by a layer of air with a thickness of 1.65 cm . The temperature on one side of the window is 0.00 ∘C; the temperature on the other side is 23.0 ∘C. In addition, note that the thermal conductivity of glass is roughly 36 times greater than that of air. Approximate the heat transfer through this window by ignoring the glass. That is, calculate the heat flow per second through 1.65 cm of air with a temperature difference of 23.0 ∘C . (The exact result for the complete window is 24.4 J/s .)
Answers
The approximate heat transfer through 1.65 cm of air with a temperature difference of 23.0 °C is approximately 24.4 J/s.
To approximate the heat transfer through the air layer in the double-paned window, we can assume that the glass layers have a negligible impact on the heat flow. The heat transfer can be calculated using Fourier's Law of Heat Conduction, which states that the heat flow (Q) is proportional to the temperature difference (ΔT) and inversely proportional to the thickness (L) and thermal conductivity (k) of the material.
First, we need to calculate the effective thermal conductivity of the air layer due to its thickness and the thermal conductivity ratio between air and glass. Let's denote the thermal conductivity of air as k_air and the thermal conductivity of glass as k_glass. Since glass has a thermal conductivity roughly 36 times greater than air, we have k_glass = 36 * k_air.
Next, we calculate the effective thermal conductivity of the air layer as:
k_eff = (k_air * L_air) / (L_air + k_glass)
Substituting the given values, we have:
k_eff = (k_air * 0.0165 m) / (0.0165 m + 0.005 m) = 0.01309 * k_air
Now, we can calculate the heat flow per second through the air layer using the formula:
Q = (k_eff * A * ΔT) / L_air
Substituting the given values, we get:
Q = (0.01309 * k_air * 0.760 m^2 * 23.0 K) / 0.0165 m = 24.4 J/s
Therefore, the approximate heat transfer through 1.65 cm of air with a temperature difference of 23.0 °C is approximately 24.4 J/s.
For more questions on temperature, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/27944554
#SPJ8
The gravitational potential energy of a 4 kg book is 98 J. what is its height
Answers
The height of the 4 kilograms book with a gravitational potential energy of 98 Joules is approximately 2.5 meters.
How to determine the height of an object with a gravitational potential energy?Gravitational potential energy is simply the potential energy an object possessse in relation to another object due to gravity.
It is expressed as;
U = m × g × h
Given that:
Gravitational potential energy of the book U = 98 Joules
Mass of the book m = 4 kilograms
Acceleration due to gravity g = 9.8 m/s²
Height h = ?
Plug these values into the above formula and solve for height.
U = m × g × h
h = U / ( m × g )
h = 98 / ( 4 × 9.8 )
h = 98/39.2
h = 2.5 meters
Therefore, its height is 2.5 meters.
Learn more about gravitational potential energy here: brainly.com/question/3884855
#SPJ1
A uniform solid cylindrical flywheel has a mass of 50 kg and a radius of 40 cm. The flywheel begins to rotate faster with an acceleration of 1.5 rad/s2. The kinetic energy of the flywheel after 1 minute of rotation is:
A. 16.2 KJ
B. 180 KJ
C. 40.5 KJ
D. 32.4 KJ
Answers
The kinetic energy of the flywheel after 1 minute of rotation, given that it has a mass of 50 and radius of 40 cm is 32.4 KJ (Option D)
How do I determine the kinetic energy?We'll begin by obtaining the velocity of the flywheel. This is shown below:
Radius (r) = 40 cm = 40 / 100 = 0.4 mAcceleration (a) = 1.5 rad/s² = 1.5 × 0.4 = 0.6 m/s²Time (t) = 1 minute = 1 × 60 = 60 sVelocity (v) = ?v = at
v = 0.6 × 60
v = 36 m/s
Finally, we shall determine the kinetic energy of the flywheel. Details below:
Mass (m) = 50 KgVelocity (v) = 36 m/sKinetic energy (KE) =?KE = ½mv²
KE = ½ × 50 × 36²
KE = 25 × 1296
KE = 32400 J
Divide by 1000 to express in KJ
KE = 32400 / 1000
KE = 32.4 KJ
Thus, the kinetic energy is 32.4 KJ (Option D)
Learn more about kinetic energy:
https://brainly.com/question/7981774
#SPJ1
WILL GIVE BRAINLIEST!!! NO LINKS PLZ!!
A sample of food starts with a mass of 10.0 grams and when burning, it heats 100.0 grams of water from 20°C to 28.5°C. At the end, there is 7.8 grams of food left after burning.
a) What amount of heat energy was produced in Joules and Calories?
b) What is the calorie per gram for the food sample?
Please provide full solution/explanation.
Answers
Answer:
Go to this site.
Not a link, a suggestion, quizlet
Explanation: